Different Between Clamp Burning and Kiln Burning | What Is Clamp Burning | What IS Kiln Burning
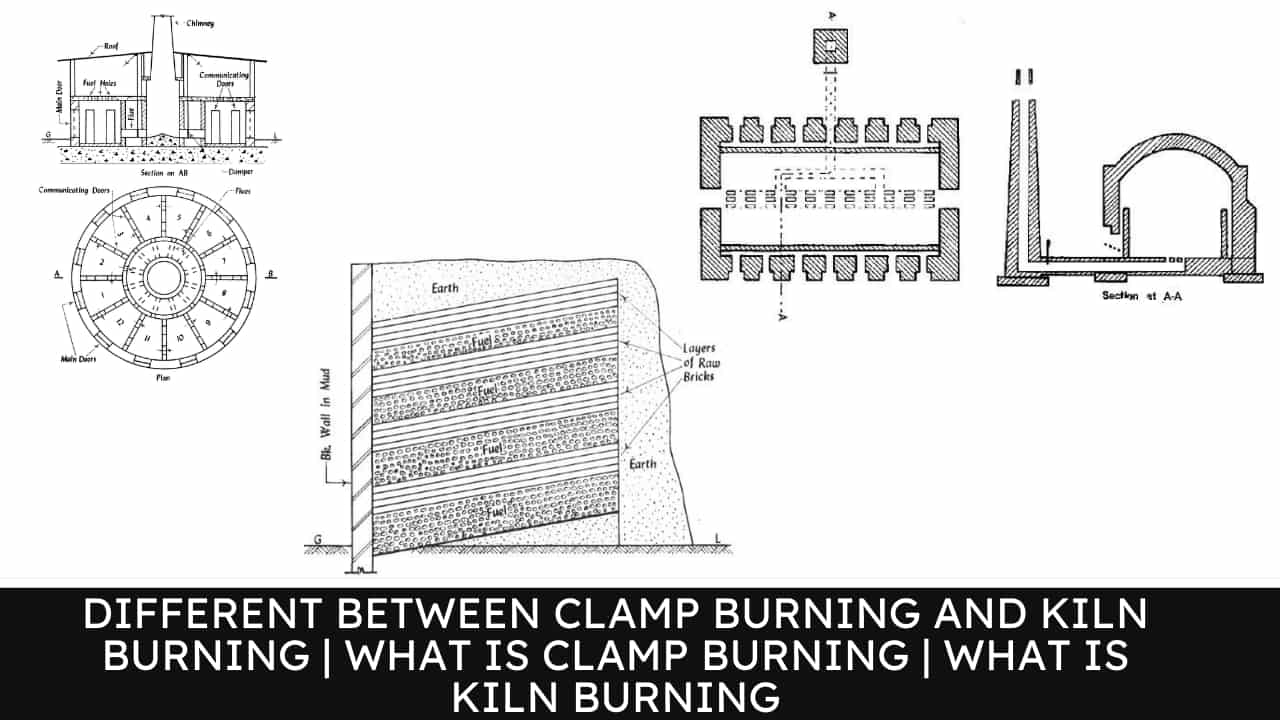
Table of Contents
What Is Clamp Burning?

A typical clamp is shown below figure The bricks and fuel are placed in alternate layers. The amount of fuel is reduced successively in the top layers.
Each brick tier consists of 4–5 layers of bricks. Some space is left between bricks for the free circulation of hot gasses. After 30 percent loading of the clamp, the fuel in the lowest layer is fired and the remaining loading of bricks and fuel is carried out hurriedly.
The top and sides of the clamp are plastered with mud. Then a coat of cow dung is given, which prevents the escape of heat.
The production of bricks is 2–3 lacs and the process is completed in six months. This process yields about 60 percent of first-class bricks.
Advantages of Clamp Burning
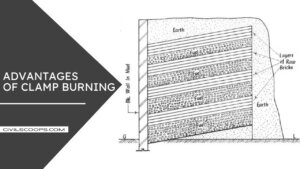
Here, the pros of clamp burning are as follows.
- Bricks produced are tough and hard due to gradual burning and cooling processes.
- It is Cheap and economical
- No skilled labour or supervision is required for the construction of clamps.
- There is lot of saving in fuel.
Disadvantage of Clamp Burning
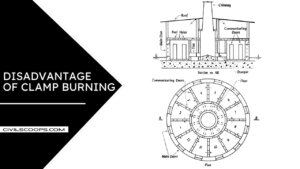
Here, the cons of clamp burning are as follows.
- Bricks produced are of irregular shape due to the settlement of bricks on turning of fuel to ashes.
- It is a slow process and flame regulation is not possible
- Quality of bricks is not uniform. Bricks at bottom, are found overburnt, while at top and sides are found to be under burnt.
What Is Kiln Burning?

The kiln used for burning bricks may be underground, e.g. Bull’s trench kiln or overground, e.g. Hoffman’s kiln. These may be rectangular, circular, or oval in shape.
When the process of burning bricks is continuous, the kiln is known as a continuous kiln, e.g. Bull’s trench and Hoffman’s kilns.
On the other hand, if the process of burning bricks is discontinuous, the kiln is known as an intermittent kiln.
Type of Kiln Burning
Here, the two different types of kiln burning are as follows.
- Intermittent Kiln
- Continuous Kiln
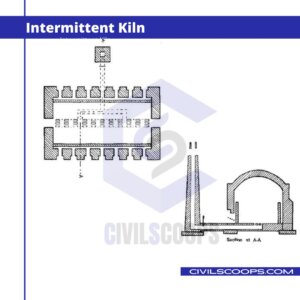
Intermittent Kiln
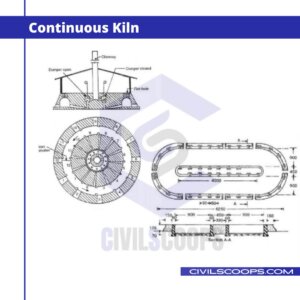
Continuous Kiln
Clamp Burning Vs Kiln Burning
[su_table responsive=”yes” alternate=”no”]
| Sr.No. | Particulars of Comparison | Clamp Burning | Kiln Burning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initial cost | Initial cost is low | Initial cost is high |
| 2 | Type of structure | Clamps are tempray | Kilns are permanent structure |
| 3 | Daily output | 25,000 to 1,00,000 bricks be burnt depending upon size of clamp. | 25,00 bricks can be burnt continuosly daily. |
| 4 | Quality of bricks | Average 60% quality bricks obtained. | Average 90% quality bricks can be obtained. |
| 5 | Fire regulation | Controlled firing can not be maintained throughout the process. | Controlled firing can be be maintained through the processes. |
| 6 | Cost of fuel consumption | Less, because local fuel materials like stores etc can be used. | Cost of fuel consumption is high, because only coal is used as the fuel. |
| 7 | Brining period | 2 to 6 months are necessary for burning and cooling. | Only about one day is necessary for burning and about 10 to 12 days for cooling of one chamber. |
| 8 | Preferability | Preferable for a small quantity and ordinary bricks. | Preferable for large, and continuous quality and pf quality production desired. |
| 9 | Wastage of heat | More wastage of heat because fire controlling and proper regulation is not possible. | Minimum wastage of heat because of proper heat regulation system. |
| 10 | Supervision | Supervision is not necessary | Skilled and continuous supervision is necessary. |
| 11 | Operations | Only burning of bricks is done. | Dry, heating and cooling operations are done sequentially. |
[/su_table]
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Different Between Clamp Burning and Kiln Burning
Clamp burning is suitable when bricks are to be manufactured on a small scale and when the demand for bricks is not continuous. Kiln burning is suitable when bricks are to be manufactured on a large scale and when there is a continuous demand for bricks
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Types of Cement Grades | Difference Between 33, 43 & 53 Grade Cement
- What Is a Spillway | Types of Spillway | Definition Spillway | Spillway Design
- What Is Fresh Concrete? | Properties of Fresh Concrete | Factors Affecting Workability
- What Is Seasoning of Timber? | Methods of Seasoning of Timber | Purpose of Seasoning of Timber
- What Is Sheepsfoot Roller? | Characteristics of Sheepsfoot Rollers | Difference Between Padfoot and Sheepsfoot Rollers
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-06-29 18:22:10.
