Core Cutter Method | What is Compaction of Soil
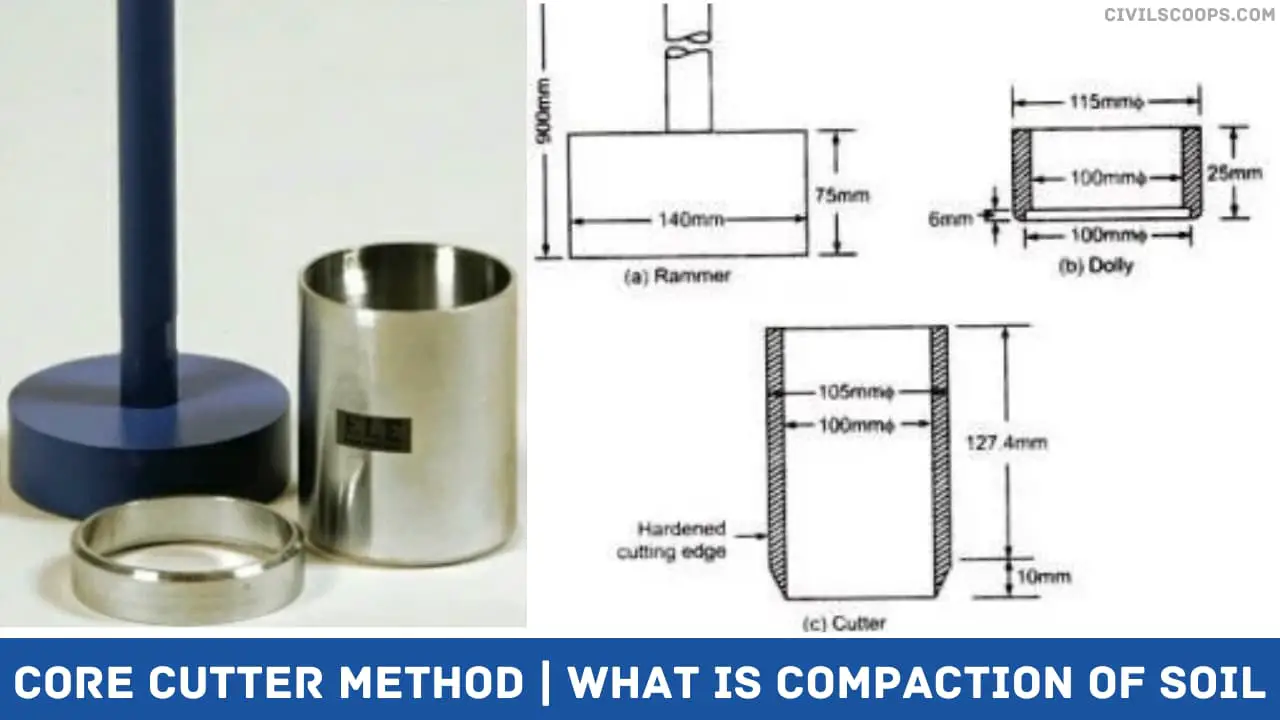
Table of Contents
What is Compaction of Soil?
Compaction of soil is area compacted by mechanical method for remove air voids in compacted soil this area of soil called compaction of soil.
Why Use Compaction of Soil?
Compaction of soil compacted soil so changes soil property. Soil well compacted and remove air voids in the soil. After done, compaction soil improved soil quality. Also, change the engineering properties of the soil. This required any construction work like. Road work, Earth dam, Different Concoction type of building, Dam, etc. Relevant is Code: IS 2720 part 29.
Soil Compaction Test Using Core Cutter Method
Let’s go into detail knowledge about core cutter test.
Aim of Core Cutter Test
To determine the Field density of Fine-grained soil by using core cutter test
Scope of Core Cutter Test
This procedure covers all relative activity for the project site.
Apparatus of Core Cutter Test
- Core cutter

Core-Cutter – of seamless steel tube, 130 mm long and 10 mm internal diameter, with a wall thickness of 3 mm, beveled at one end, of the type illustrated. The cutter shall be kept properly greased or oiled.IS Code 2720 Part 20 CI: 2.1
- Dolly / Rammer.

2.5 em high and ten10 mm internal diameter with a wall thickness of 7’5 mm with a lip to enable it to be fitted on top of the core-cutter IS Code 2720 Part 20 CI: 2.2
- Balance of 1 gm accuracy.

- Pallet knife, Straight edge, Steel rule, Pickaxe, etc.

- Rapid moisture meter

- Note 1: These designs have been found satisfactory, but alternative designs may be employed provided that the essential requirements are fulfilled. IS Code 2720 Part 20
- Note 2: Essential dimensions are underlined. (Tolerance on all essential dimensions shall be ±O’25 mm ).IS Code 2720 Part 20
Procedure of Core Cutter Test
Here, Soil Compaction Test (Core Cutter Test) Steps are as follows.
- The internal Volume of core cutter shall be calculated by taking dimensions nearest to 0.25 mm (By vernier).
- Cutter shall be weighed to the nearest gm.
- A small area, approximately 30 cms square of the soil layer to be tested shall be exposed and leveled.
- Cutter shall be placed vertically on soil with dolly on top.
- Cutter shall be rammed down vertically into the soil layer until only about 15 mm of dolly protrudes above the surface.
- The cutter shall be dug out of surrounding soil by a pickaxe.
- Soil from both the ends shall be trimmed flat to the ends of the cutter.
- The cutter containing soil mass shall be weighed to the nearest gm.
- The soil mass shall be removed from cutter, and representative sample shall be tested for water contents with the help of rapid moisture meter.
When soil mass is dry, and the cutter is not properly filled up or looses soil while handling. In such a case test is to be done by sprinkling water and testing after a suitable lapse of time.
Calculations of Core Cutter Test
Bulk Density Yb of Wet Soil is as below
Yb = (Ws – Wc ) / Vc , gms /cm3
Dry Density Yd is as below:
Yd = 100 Yb / (100 + w ) , gms /cm3
Where w = Water Content %
Core cutter method Lab report: Dry Density to be recorded to 2nd place of a decimal in gms/cm3. Water Content % to two significant figures ( e.g.- 23, 2.3, 0.23 )
Sample of Excel Sheet FDD by core cutter
[su_table responsive=”yes”]
| Field Dry Density by Core Cutter | |||||
| Location | Level | ||||
| MDD | OMC | ||||
| MDD Report no. | Tested as per | ||||
| Description | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | ||
| 1. Weight of wet soil + Core cutter (W1) ( gms) | |||||
| 2. Weight of Empty Core cutter (W2) (gms) | |||||
| 3. The volume of Core Vc (cc) | |||||
| 4. Weight of wet soil Ww = W1-W2 (gms) | |||||
| 5. Bulk Density γ = Ww / Vc (gm/cc) | |||||
| 6. Moisture Meter Reading (R) | |||||
| 7. Moisture Content Wc = R / (100-R) x100 | |||||
| 8. Dry density γd = γ / (1+ Wc) (gm/cc) | |||||
| 9. % Compaction (γd / MDD ) x 100 | |||||
| Remarks ( If Any) – | |||||
[/su_table]
More Information about Core Cutter Method
- This was about the best method for earth compaction. Overall the method for earth compaction is excellent
- This method easy to perform on-site at the time.
- This method requires using soil O.M.C (optimum moisture content )& M.D.D (Maximum Dry Density )
- Also, check our core soil moisture content value nearby +5% of compere soil.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Core Cutter Method
Core cutter method is used for finding field density of cohesive/clayey soils placed as fill. It is rapid method conducted on field. It cannot be applied to coarse-grained soil as the penetration of core cutter becomes difficult due to increased resistance at the tip of core cutter leading to damage to core cutter.
Compaction Test Calculation
The percent compaction for the field density test is calculated by dividing the dry density of the soil by the maximum dry density from the proctor test.
Compaction Test of Soil
A lab technician will start by sifting and moisture conditioning of the soil. Once the soil is prepped the soil will go into a cylindrical mold to be compacted at various moisture contents and weighted. The test is to see how much of the material can be compacted into the same volume at various amounts of moisture.
IS Code for Core Cutter Method?
This part [IS:2720 (Part XXIX)-1975] deals with the determination of dry density of soil in place by using a core-cutter. The in-place density of soil is needed for stability analysis, for the determination of the degree of compaction of compacted soil, etc.
What Are Dimensions of Core Cutter?
Specifications :It consists one each of : Cylindrical core cutter made of steel, 127.3 mm long and 100mm internal diameter. Steel Dolley, 25 mm high with a lip to enable it to be located on top of the core cutter. Rammer with detachable steel rod.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- History of Remote Sensing | Application of Remote Sensing
- What Is Quick Setting Cement | Uses of Quick Setting Cement
- What Is Slump Cone Test | Principle of Slump Test | Types of Concrete Slump
- Difference Between Veneer and Laminate | What Is Veneer | What Is Laminate
- What Is Foundation | What Is Purpose of Providing Foundation | Types of Foundation
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-07-11 07:31:55.
