How to Calculate Staircase Qty | Concrete & Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) | Staircase Reinforcement Details

Table of Contents
Parts of Stairs Parts Names & Details

A various part of Stair:
Step:
A flat surface, especially one in a series, on which to place one’s foot when moving from one level to another. all step is composed of tread and riser.
Tread:
Tread is a scrap of the stairway that’s stepped in. It’s the top or flat surface to press beneath the feet. It’s trodden on while climbing or descending the staircase.
It’s constructed to the same thickness as another floor. There’s always one fewer tread than risers at stairs. The general horizontal distance of the stairs is going to be the number of threads added together.
The horizontal projection of a step in a staircase is called tread. It is also known as goingIn residential buildings, the tread length provided is 250 mm while in public buildings maximum length 270 mm to 300 mm.
Riser:
This riser is the vertical portion between each tread on the stair. Not all stairs have risers. The rise-less steps are called the open thread.
Open riser stairs have grown in popularity Recently years. Closed tread stair has risers included. This vertical board forms the face of the step, also forms the space between one step and the next.
Rise provided could be uniform. It is normally hight at 150 mm to 175 mm in residential buildings while it is kept between hight 120 mm to 150 mm in public buildings. However, in commercial buildings, more rise is provided from the consideration of the economic floor area.
Nosing:
Nosing is the flat protruding edge of a stair at which most foot traffic occurs. Mostly, it’s the half curved molding fixed into the ends of those threads exposed at a half that covers where the balusters fit into the treads.
Nosing is the border of the tread projecting beyond the face of the riser and the face of a cut string. This is the place where the thread above a riser overhangs it. Sometimes, the tread may not have a nosing.
Base Rail or Shoe Rail
For systems in which the baluster doesn’t start at the treads, they go to a base rail. This allows for identical balusters, avoiding this second baluster problem.
Landing:
This is a platform provided between two flights.
How to Calculate Staircase Qty?
Here we are going to calculate the Qty of Staircase. We will divide the amount of stairs into two parts. In the first part we will calculate the concrete, then we will calculate all the steel.
- Concrete Calculation for Staircase
- Bar Bending Schedule for Staircase
Let’s go detail knowledge of Calculate Staircase Qty
1. Concrete Calculation for Staircase
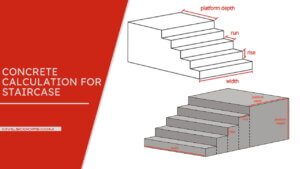
Staircase Reinforcement Details
Concrete calculation
Section 1
- Landing area concrete = L x B x H
- Landing area concrete = 1.7 M. x 3.25 M. x 0.150 M.
- Landing area concrete = 0.830 Cu.m.——–(1)
Section 2
- Wasit slab area concrete = L x B x H x N
- Wasit slab area concrete = 3.85 M. x 1.5 m. x 0.150 M. x 2 Nos.
- Wasit slab area concrete = 1.732 Cu.m. ——–(2)
Section 3
- Steps area concrete = L x Vloume of trianglar area x N x Q
- Steps area concrete = 1.5 M. x( 0.300 M. x 0.150 M x (1/2)) x 2 Nos. X 11 Qty
- Steps area concrete = 0. 75 Cu.m. ——–(3)
Section 4
- Beam area concrete = L x B x H X N
- Beam area concrete = 1.5 M. x 0.44 M. x 0.300 M. x 2 Nos.
- Landing area concrete =0.400 Cu.m.——–(4)
- Total Concrete of Staircase = (1) + (2) + (3) + (4)
- Total Concrete of Staircase = 0.830 Cu.m. + 1.732 Cu.m. + 0. 75 Cu.m. + 0.400 Cu.m.
- Total Concrete of Staircase = 3.712 Cu.m.
2. Bar Bending Schedule for Staircase
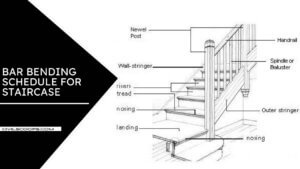
Staircase Reinforcement Details
Section 1
- Landing Area Bar Bending Schedule
- Distribution bar 8 mm C/C 120 mm Length 3.25 in Y-axis Distribution area 1.5m
- So No, of 8 mm Steel bar = 1.5 M. / 0.120 M. = 12.5 Nos
- Consider 13 Nos. steel bar use Top Side +13 Nos Steel use Bottom Side
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = L x Nos of steel x Weight of Steel
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = 3.25 x 13 x 2 x 0.395 (0.395 kg/m is 8mm dia steel bar weight)
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = 33.34 kg ——– (1)
- Section 1 Total = 33.34 kg
Section 2
- Wasit slab Bar Bending Schedule
- Distribution bar 8 mm C/C 140 mm Length 1.5 in Y-axis Distribution area 3.89m
- So No, of 8 mm Steel bar = 3.89 M. / 0.140 M. = 27.75 Nos
- Consider 28 Nos. steel bar use Top Side +28 Nos Steel use Bottom Side
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = L x Nos of steel x Weight of Steel
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = 1.5 x 28 x 2 x 0.395 (0.395 kg/m is 8mm dia steel bar weight)
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = 33.1 kg ——– (2-1-1)
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia C/c 80 mm distance
- Length of main bar bottom area = 1.5 M. – 0.180 M. + 0.150 M. + 3.89 M. + 0.450 M.
- Length of main bar bottom area = 5.81 m
- Nos of bar 10 mm dia C/c 80 mm distance = 1.5 M. / 0.080 M. = 18.75 Nos.
- Consider 19 Nos. steel bar use Bottom bar Side
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia steel bar = 5.81 M. X 19 Nos. X 0.617 kg/m (0.617 kg/m is 10mm dia steel bar weight)
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia steel bar = 68.11 kg ——– (2-1-2)
- Main bar Top Area 10mm dia C/c 80 mm distance
- Length of main bar top area = 1.7 M. – 0.180 M. + 3.89 M. + 0.450 M. +0.250 M.
- Length of main bar top area = 6.11 m
- Nos of bar 10 mm dia C/c 80 mm distance = 1.5 M. / 0.080 M. = 18.75 Nos.
- Consider 19 Nos. steel bar use Bottom bar Side
- Main bar Top Area 10mm dia steel bar = 6.11 M. X 19 Nos. X 0.617 kg/m (0.617 kg/m is 10mm dia steel bar weight)
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia steel bar = 71.63 kg ——– (2-1-3)
- Section 2-1 total = 33.1 kg + 68.11 kg + 71.63 kg = 172.84 kg
Section 2-1
- Wasit slab Bar Bending Schedule
- Distribution bar 8 mm C/C 140 mm Length 1.5 in Y-axis Distribution area 3.83m
- So No, of 8 mm Steel bar = 3.83 M. / 0.140 M. = 27.75 Nos
- Consider 28 Nos. steel bar use Top Side +28 Nos Steel use Bottom Side
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = L x Nos of steel x Weight of Steel
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = 1.5 x 28 x 2 x 0.395 (0.395 kg/m is 8mm dia steel bar weight)
- Weight of distribution of 8 mm dia steel bar = 33.1 kg ——– (2-2-1)
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia C/c 80 mm distance
- Length of main bar bottom area = 1.5 M. – 0.180 M. + 0.150 M. + 3.83 M. + 0.450 M.
- Length of main bar bottom area = 5.78 m
- Nos of bar 10 mm dia C/c 80 mm distance = 1.5 M. / 0.080 M. = 18.75 Nos.
- Consider 19 Nos. steel bar use Bottom bar Side
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia steel bar = 5.78 M. X 19 Nos. X 0.617 kg/m (0.617 kg/m is 10mm dia steel bar weight)
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia steel bar = 67.75 kg ——– (2-2-2)
- Main bar Top Area 10mm dia C/c 80 mm distance
- Length of main bar top area = 1.7 M. – 0.180 M. + 3.83 M. + 0.450 M. +0.250 M.
- Length of main bar top area = 6.05m
- Nos of bar 10 mm dia C/c 80 mm distance = 1.5 M. / 0.080 M. = 18.75 Nos.
- Consider 19 Nos. steel bar use Bottom bar Side
- Main bar Top Area 10mm dia steel bar = 6.05 M. X 19 Nos. X 0.617 kg/m (0.617 kg/m is 10mm dia steel bar weight)
- Main bar Bottom Area 10mm dia steel bar = 70.92 kg ——– (2-2-3)
- Stection 2-2 Total = 31.1 kg + 68.09 kg +70.92 kg = 170.11 kg
- Total Secction 2 weight = 172.84 kg + 170.11 kg = 342.95 kg
Section 3
- Beam area bar bending schedule
- 8mm dia Ring Size for lenth of column ring = Column Size – Cover
- Ring Size for lenth of column ring = ( L of Column – cover – cover + B of Coumn – cover – cover + Hook ) x 2
- Ring Size for lenth of column ring = (600 -25 -25 + 300 – 25 -25 +8 ) x 2
- 8mm dia Ring Size for lenth of column ring = 1.616 M.
- No ring requirement = Length / Spacing
- No ring requirement = 1.5 /0.140 = 11 Nos
- Weight of ring = 1.616 x 11 x 0.395 = 7.02 kg ——–(3-1)
- Length of Bar = Length of bar +( wall bering + wall bering ) + ( End side L Bend x No of Qty )
- 12 mm dia Length of Bar = 1.5 + (0.200 + 0. 200 ) + (0. 300 X 4)
- Length of Bar = 3.1 M.
- Weight of ring Main bar = 3.1 x 6 x 0.89 = 16.554 kg ——–(3-2) (0.89 kg/m is 12mm dia steel bar weight)
- Section 3 total = 7.02 kg + 16.554 kg = 23.57 kg x 2 ( Beacuse of same two beam ) = 47.51 kg
- Total Weight of Staircase Bar Bending secdule
- Section = Section 1 + Section 2 + Section 3
- Section = 33.34 kg + 342.95 kg + 47.51 kg
- Total Weight of Staircase Bar Bending secdule = 423.79 kg.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
How Do You Calculate Reinforcement in Stairs?
Steps to calculate the reinforcement required for Doglegged Staircase:
- Find the length of X Bar & Y bar.
- Find the No. of X Bars & Y bars.
- Evaluate the total length of X Bars & Y Bars.
- Find out the total weight of steel required.
What Concrete Is Best for Stairs?
The mix design for exterior concrete stairs should be at least a 4000 psi mix with a low water/cement ratio. In colder climates specify air-entrainment in the concrete to help resist freezing, thawing, and deicing chemicals.
What Is the Space Under the Stairs Called?
If there is not another flight of stairs immediately underneath, the triangular space underneath the stairs is called a “spandrel”. It is frequently used as a closet.
What Steel Is Used for Stairs?
Stainless steel is another metal that is widely used in staircases and railings, especially for indoor applications. Stainless steel is named for the fact that it does not stain, corrode or rust as easily as ordinary (structural) steel.
How Do You Calculate Steel for Stairs?
Steps to calculate the reinforcement required for Doglegged Staircase:
- Find the length of X Bar & Y bar.
- Find the No. of X Bars & Y bars.
- Evaluate the total length of X Bars & Y Bars.
- Find out the total weight of steel required.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- All Abot Parts of Stairs Parts Names & Details | Parts of Stairs Parts Names & Details
- All About M-Sand And River Sand | What is M-Sand | M-Sand Bonding Strength | What is River Sand |
- All About Roof Vent | What Is a Roof Vent | Different Types of Roof Vents | Advantages of Roof Ventilation
- All About Flagstone | Introduction of Flagstone | What Is Flagstone | What Is a Flagstone Patio | Types of Flagstone
- All About Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry | Introduction of Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry | Important Point in Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry | Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-06-17 17:51:37.
