Requirements of Good DPC | Prevention of Dampness | Methods of Damp proofing
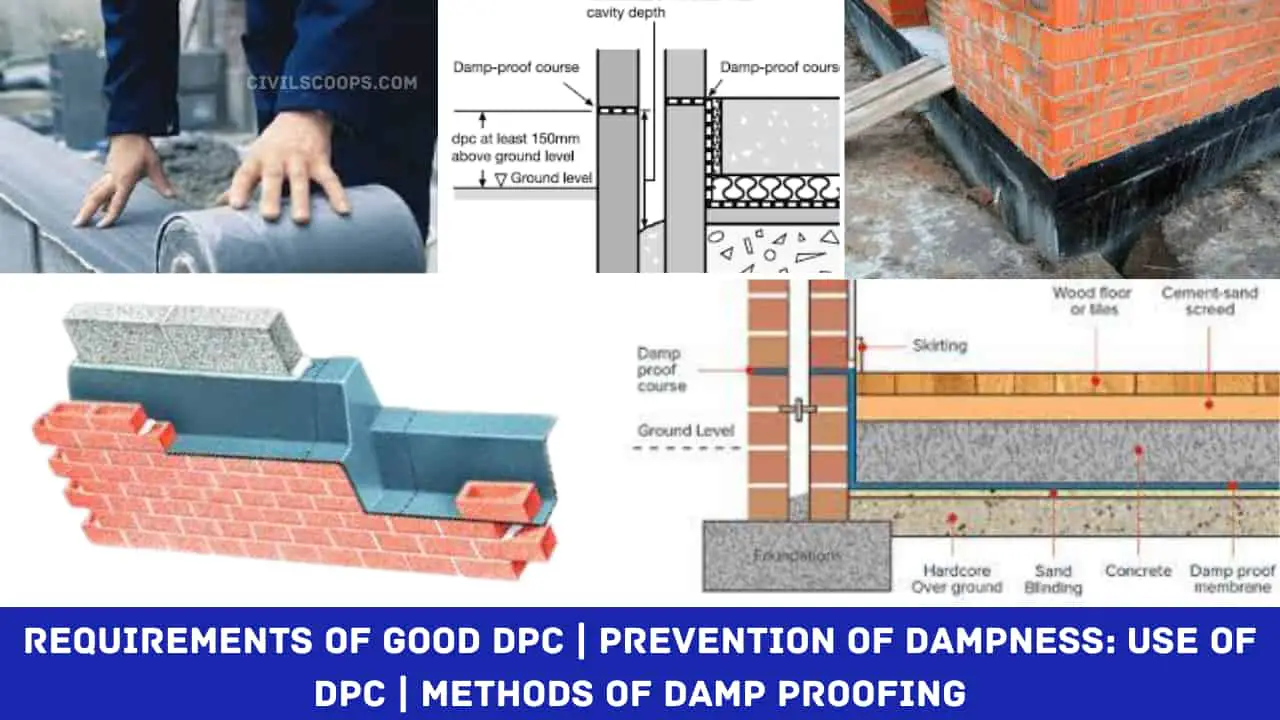
Table of Contents
Requirements of Good DPC
Here, the list of requirements of a good DPC are as follows.
- Totally impervious and should not allow travel of dampness.
- Durable and keep the building damp-proof permanently.
- Economical and easy in laying.
- Able to resist load to which it is subject.
- Accommodate some structural movement without fracture.
Prevention of Dampness
List of privation of dampness concrete ara as follows.
- Prevention of dampness in a building is done by various methods. The most common method is the use of a damp proof course (DPC).
- The other methods are damp-proof surface treatment, integral damp-proofing treatments, cavity or hollow walls, shot concrete, and pressure grouting or cementation. A sectional view of building wall and floor is shown above figure. In this figure. A layer of damp proof course (DPC) of 2.5 cm applied to the wall and floor is shown.
- This layer of DPC consists of water repellent materials such as cement concrete, or mortar mixed waterproofing compound in powder form, bituminous felts, mastic asphalt, plastic sheets, metal sheets of copper and lead, PVC sheets, slates, stones, bricks, etc.
- The rigid materials like stones, bricks, slates are painted with bitumen. This layer or membrane is interposed in the building structures, as shown above, figure. Basically, this DPC is provided to prevent the water from rising from sub-soil or ground and getting into the different parts of the building.
- This damp proof course may be provided horizontally or vertically in floor and wall. The choice of effective DPC materials for a building requires a judicious selection. It depends on the climatic and atmospheric conditions of the area and site, nature of the structure.
General Principles of Damp-Proofing
The following points are general principles of damp proofing.
- The general principles observed in the case of all the damp-proofing methods are as follows:
- The damp-proof course may be horizontal or vertical.
- The horizontal damp-proofing course should cover the full thickness of the wall.
- At junctions and corners of a wall, the horizontal damp-proofing course should be laid continuous.
- The damp-proof course should be laid continuous, so as to make proper protection from dampness.
Methods of Damp-proofing
The following methods are generally adopted to prevent dampness in a structure.
- Membrane Damp-proofing
- Integral Damp-proofing
- Surface Treatment
- Guniting
- Cavity Wall Construction.
Let’s look in detail knowledge about the method of waterproofing.
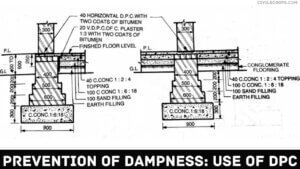
1. Membrane Damp-proofing
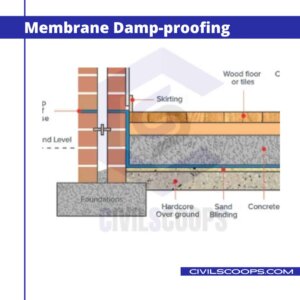
This consists of providing layer or membrane of water-repellent material between the source of dampness and the part of the structure adjacent to it.
This type of layer is commonly known as a damp proof course (or D.P.C.), and it may comprise of materials like bituminous felt, mastic asphalt, silicone, epoxy, polymers, plastics, cement concrete, etc. Depending upon the source of dampness, D.P.C. may be provided horizontally or vertically in floors, walls, etc.
2. Integral Damp-proofing
This consists of adding certain water-proofing compounds with a concrete mix to increase its impermeability. Such compounds are available in powdered as well as in liquid form. The compounds made from clay, sand, or lime help to fill the voids in concrete and make it waterproof.
Another form of compound like alkaline silicates, aluminum sulfates, calcium chlorides, etc. Reacts chemically when mixed in concrete to produce waterproof concrete.
Pudlo, promo, Imperio, etc. are some of the commercially made preparations of waterproofing compounds commonly used. In general, one kg of waterproofing compound is added with one beg of cement to make the mortar or concrete waterproof.
3. Surface Treatment

It has been observed that the moisture finds its way through the pores of materials used in finishing. These pores must be filled up in order to check the entry of moisture.
Surface treatment consists in filling up the pores of the surface subjected to dampness. The bituminous solution, cement coating, paints, and varnishes, etc. are used for surface treatment. The walls plastered with lime cement plaster of proportion 1 : 1: 6 is found effective to prevent dampness in the wall due to rain.
4. Guniting

This consists of depositing an impervious layer of rich cement mortar over the surface to be waterproofed. The operation is carried out by a machine known as a cement gun.
The surface to be treated is first thoroughly cleaned and wetted properly. Cement and sand have usually taken in the proportion of 1 : 3 to 1: 4 are then fed into the machine. The mixture is finally shot on the prepared surface under a pressure of 2 to 3 kg/cm2 by holding the nozzle of 75 to 90 cm from the working face.
The quantity of water in the mix can be controlled by means of regulating the valve. Since the material is applied under pressure, it ensures dense compaction and better adhesion of the rich cement mortar, and hence the treated surface becomes waterproof.
5. Cavity Wall Construction
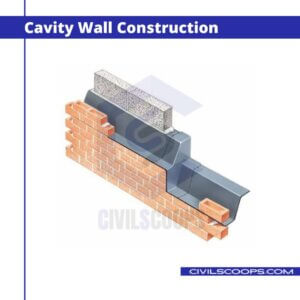
This consists of shielding the main wall of the building by an outer wall leaving a cavity in between the two. The cavity prevents the movement of moisture from the outer to the inner wall. The outer skin wall is termed as a cavity wall.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
DPC Full Form
The full form of “DPC” is “Damp Proof Course“, where “D” stands for “Damp“, “P” stands for “Proof” and “C” stands for “Course”.
DPC Level in Construction
The damp proof course (DPC) is generally applied at basement levels, which restricts the movement of moisture through walls and floors. The selection of materials for the damp proof course and its various methods of application in buildings is discussed.
Damp Proof Course Material
A DPC is a durable, impermeable material such as slate, felt paper, metal, plastic or special engineered bricks bedded into the mortar between two courses of bricks or blocks. It can often be seen as a thin line in the mortar near ground level.
Types of DPC
Here, the different types of damp proof courses are as follows.
- Electro-osmotic damp proof course.
- Chemical damp proof course.
- Pressure grouting.
- Membrane damp proof course.
- Integral damp proof course.
- Cavity wall damp proof course.
Methods of Damp Proofing
- Membrane damp proofing.
- Integral damp proofing.
- Surface treatment.
- Cavity wall construction.
- Guniting.
- Pressure grouting.
Damp Proof Course Specification.
Damp proof course shall consist of cement, coarse sand and stone aggregate of 1:1 ½:3 proportion with 2% of impermo or cem-seal, or Acco proof by weight of cement or other standard water proofing compound (1 kg per bag of cement).
Thickness of DPC
The DPC should be of 40mm thickness and should be of uniform thickness. It should not be provided at the locations of the door openings. The top level of DPC should match with the planned finished floor level.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- All About of Mezzanine Floor
- What Is a Spillway | Types of Spillway | Definition Spillway | Spillway Design
- What is Door Frame? | 8 Main Parts of Door Frame | Types of Door Frame used in House
- What Is Seasoning of Timber? | Methods of Seasoning of Timber | Purpose of Seasoning of Timber
- What Is Geodetic Surveying | What Is Plane Surveying | Geodetic Surveying Vs Plane Surveying | Difference Between Plane Surveying and Geodetic Surveying
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-07-09 11:11:36.
