All About of Window | What Is Window | Selection Criteria for a Window | Types of Windows

Table of Contents
What Is Window?
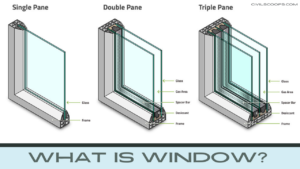
The word ‘window’ is considered to be derived from an old Norse word ‘Vindauga’. ‘Vinduga’ is made with two separate words ‘vind’ which means air and ‘agua’ which means eyes. Combined it symbolizes airflow and vision.
It is an opening that is engraved in a wall or roof that stands for a window. The basic purpose to have a window is to work as a natural ventilation system for air, an opening for incoming light, and give a spectrum view of the outside.
Like the doors, windows are a crucial part of the house. It is considered one of the most important elements of house making as well as the aesthetics of the house. Special windows make the house look special and eye-catching. So the profuse relevance of windows in the exterior and the interior design can not be disregarded.
For sunlight, windows are the only way you can have them. Also, they make an indispensable connection with nature. The homeowner will want to let some sunshine in and also he may aspire to see the sunset from inside the house.
Having windows can also be lifesaving sometimes. In case of an emergency like breaking out of fire or in other situations, windows can be used as an escape root. Sometimes some windows are situated in particular places which can be accessed easily. These windows are made while keeping in mind that emergencies can happen anytime. So using these windows escaping is easier.
Before selecting a window one must take a look at the selection criteria of a window.
Selection Criteria for a Window

Before making a window one must be careful as the uses of windows differ. Various types of windows are there and each type of window has its different use. Some such criteria are given below which must not be overlooked.
- Purpose- It is crucial to select the purpose of a window as the purposes differ so do the type of windows. For different purposes, different types of windows are made. And the places of the windows differ too. If the purpose of the window is to let in sunlight for the day then the window must be situated on the southeastern side of the house. If the purpose is to get a look at the rising sun then it should be placed at the ease of the house from where the sun can be seen in the morning. If the purpose is to get a cold or warm breeze then it should be placed on the side from which direction the air usually blows. And some would prefer their window in the southwest of their house as it will enable the homeowner to take a view of the setting sun.
- Climate– Climate plays a vital role in all over making the house. From the design to choosing the used material, climate conditions must be considered. So as with windows. The place, dimensions, and material of the window should be used according to the climate. If you live in a house that is situated in a hot prone area then you must not consider your window to be in the southeast or on the southwest side as it is going to let in a lot of sunshine throughout the day and thus making the environment inside your house impossible to live in. On the other hand, if you live in a colder region then you always should go for a window placed in the southeast and the southwest. For the materials, climate also needs to be looked at. If the climate is humid or moist like the places that are situated near the sea, materials that are not theatrical to corrosion should be used.
- Location- similar todoors, windows are also needed to be placed in the places which are best for the desired purpose for which the window is made. The windows make the appearance of the house look good and also unknowingly catch the visitor’s eyes. If placed wrongly, the exterior looks and the desired aesthetics of the house could be ruined. So it is necessary to place the windows in the right places. Also, the location of the windows must not be inaccessible as cleaning the windows is a mess and takes a lot of care. So windows must be made in places that are easily accessible.
- Noise Isolation- noise isolation is a crucial matter of fact as disturbing noises can ruin your mood as well as health. Also, noises from outside can spoil your concentration while performing important tasks such as reading. So windows must not be placed at a side in which there is a continuous source of the noise. If any religious place is noisy like a temple, church, mosque, or other sources like a railway line, railway track, or even a high road, a market is near your house then you should not consider making windows on that side of your house. Noisy places need thick glassed windows as glass is a good insulator of sound.
- Air Infiltration – a window is the best way to get air ventilation to your room so it is important to consider a window on the side of the airflow.
- Water Penetration – windows must resist the unwanted airflow and water intrusions during the time of a cyclone or thunderstorm or even rain. Water can damage the floor and unwanted airflow can harm the inside of the room as during cyclones winds usually bring a lot of dust with them.
So a window must be largely sturdy to resist the water penetration and provide perfect insulation from the outside calamity. Also, precautions need to be taken in case the window glass does not bump into the wall and break( if the window is openable)
Modulating the Façade of the House- windows can alter the perception of a house or building depending upon its type, placement, material, glass color, number, and articulation. It plays a heavy role in modulating the façade of the house.
Also, Read: ll About of Shoring | What is Shoring | Types of Shoring | Types of Shoring in Construction
Types of Windows
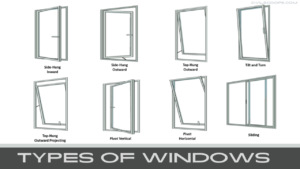
In the world of architecture, there are numerous types of windows available. Each one of the window types has different names and multiple uses. Below some types of windows are given for architectural purposes.
- Casement windows
- Fixed windows
- Sliding windows
- Corner windows
- Bay windows
- Bow windows
- Sash/ Glazed windows
- Metal windows
- Pivoted windows
- Double hang windows
- Louvered windows
- Clerestory windows
- Gable windows
- Dormer windows
- Lanterns
- Skylights
- Ventilators
- Lunette
1. Casement Windows

A window when attached to the frame with a hinge or more is called a casement window. A casement window is a type of window which can be pushed and thus opened or closed. Usually, two sashes open outwards thus creating a wide opening that ranges about 90 degrees or more.
They are usually used in pairs or singly. If used in pairs then they are likely to have a common frame. In the areas where there is more ventilation needed, casement windows are best suited. Places like bathrooms and kitchens are such places.
A standard casement window will have the height vary from 2.5 feet to 6.5 feet. The width stands from 1.2 feet to 2.11 feet. A casement window can open the way you want them to. But more usual windows open outwards. This ability of opening widely enables the windows to let more sunshine in and catches the breeze. For additional characteristics, screens can be used with casement windows for undesirable dust particles and insects.
Casement windows add a classic and add some charm that reflects upon the likings of the homeowner. Casement windows can match other window designs like sliding windows, picture windows, etc.
About the security objectives, casement windows work here too. They can not be opened from the outside by any means so the house is safer with these types of windows. Be careful about having the casement window in the bedroom as they do not go well with air conditioning as they open outwards.
The size of a casement window is adjusted to the size of the wall. Casement windows are maybe a little bit expensive.
2. Fixed Windows

Fixed windows are generally fixed as appeared by the name. These types of windows are different than casement windows. They are not able to be opened or closed and are fixed at a place in the wall of a room of your house.
Glazed shutters are fixed with the frame fully and light can pass through the window. Waterproof shutters are recommended for fixed windows. Fixed windows are mostly seen in houses that are situated in beautiful vast landscape areas, in mountain areas where nature has to offer so much to see. Fixed windows are for a broad outside view of the house.
These types of windows are also referred to as ‘picture windows’ because when you see an outside view that mesmerizes you the windows usually appear as a picture hanging on the wall. These types of windows are very useful also for light passing.
The size of fixed windows can vary as the purpose along with the climate, area, and geographical landscape varies. If you want a very large view of the external side then you can go for a humongous fixed window and if you just want a normal view then you can go with a medium-sized window. Simply put, picture windows are of a custom size. Large windows size up to 8 feet high and 9 feet wide.
Glass is commonly used with fixed windows as glass is transparent and allows lighting to come in. These types of windows are not recommended for cyclone/thunderstorm prone areas as glass can easily break in a thunderstorm or a cyclone.
While going for glass the owner has the choice to choose a particular type of glass as many kinds of glass for fixed windows are available. If sunshine is desired then windows that let in sunlight must be opted for by the owner. If only the purpose is to get only the view of the outside but avoid incoming sunlight then glass that blocks sunlight could be used. Every type of glass is suitable for fixed windows.
Air conditioning is supported in these types of windows as the glass panes are directly mounted on the window. Also, unbelievable isolation could be given by these fixed windows.Fixed windows are also cheaper than other windows so it is affordable and pocket friendly.
3. Sliding Windows

As appeared by the name these types of windows are the windows that slide. Sliding windows can slide both upwards downward and sideways. The movement is caused by rollers that are attached to the frame. Generally in shops, these types of windows are used.
Slide windows are usually with two or more panes. Each pane slides over one another. Slide windows are larger than casement windows. Generally, glass is used with the sliding panes of the window as glass blocks air but lets in the sunshine. These types of windows are good insulators so they support air conditioning.
4. Corner Windows

A window situated at the corner where both sides meet is known as a corner window. These types of windows are comprised of two or more Sashes. Simply put two windows adjacent to each other at the corner and that is a corner window.
For a house with pleasant surroundings, corner windows are best suited as they open the interior offering a large panoramic view of the outside.
Corner windows also give the house a unique look that makes the house appear different from other houses. Corner windows also make a large opening for sunlight to come in. Unlike fixed windows corner windows can be opened if the owner wants them to be built similarly.
5. Bay Windows

Bay windows are the windows that extend outward from the wall creating more space inside the room. Bay windows are usually the combination of three or more windows that are joined together.
Bay windows can be of many shapes besides the square. Bay windows can be hexagonal or octagonal also.Bay windows do not touch the ground. They extend outward from the wall but stay above the ground.Bay windows are so decorative and expensive also bay windows make that house look classy.
The Bay window which has three sides is usually six feet high and generally 2 to three feet wide.
6. Bow Windows

Bow windows are another type of window that extends outward the wall like a bay window.Bow windows are usually considered to have a fixed window in the middle paired with two angled windows on both sides.Now windows are highly fashionable, giving an outstanding look to the house.
Bow windows are largely seen in old European mansions which symbolize luxury. Bow windows give the illusion of a larger space inside the room in which the window is constructed. Bow windows also give a large view of the outside and sunshine can come into the room through the large opening of the window. Different colored glasses can be used in bow windows making them appear more vibrant and luring people.
7. Sash/glazed Windows

The word ‘glaze’ means a window has inserted a glass. Glazed windows are the windows that have been inserted glass into them.
Glazed windows can have one, two, or three panes of glass in them. Depending upon the number of panes, the glazed windows are divided into categories as single glazed windows, double glazed windows, and triple glazed windows.
A single sheet of glass into the pane is referred to as a single glazed window. This kind of window is mostly found in older times but in today’s time having a single glass pane is not a good idea as it does not provide sturdiness to the window as well as makes the windows vulnerable to hard weather conditions.
Double glazed windows are windows that consist of two sheets of glass. Double glazed windows are a perfect example of brilliant engineering. In double-glazed windows, the two glasses do not touch each other rather they consist of argon gas in the space between them. This not only provides better heat isolation but also gives noise-free inside.
Triple glazed windows are just like double glazed windows having another layer of glass at the side of them. Each gap between every two glasses contains argon gas. These types of windows are so much expensive. In winter-prone areas where there is so much cold outside and the best quality of isolation is needed, triple glazed windows must be used.
8. Metal Windows

Mainly made of steel or any other metal, metal windows are the kind of windows that gives the house a contemporary historic classy look. Metal windows are made with steel frames or aluminum frames that give your house security, and sturdiness, and are impossible to break in. Metal windows also offer a good view of the outside.
Metal windows are easily replaceable. In case of renovation of an old house that had plastic or some other kind of window in it, metal windows can easily be used. These windows are pocket friendly and they are advantageous too. Metal windows, if used with glazing, give proper isolation to heat thus saving energy for a good extinction. They can keep the room hotter on cold days and colder on hot days.
Metal windows are energy efficient and also provide very good lighting conditions to the house. Metal windows can not offer an uninterested view like other windows but this uninterrupted view has its different beauty.
9. Pivoted Windows

A window when fixed on a pivot is called a pivoted window. Pivoted windows are one kind of movable window that can move either horizontally or vertically. These types of windows are similar to casement windows.
The shitter can oscillate vertically or horizontally. Wooden frames, as well as metal frames, can be used in pivoted windows. These windows are lightweight and pivoted windows are very easy to handle and also good for cleaning.
One, two, three, or more pivoted frames can be placed side by side making a large pivoted window. This will offer light and proper ventilation. The main purpose of this kind of window is ventilation.
10. Double-Hung Windows

Double-hung windows are windows that have two sashes that are operable and movable. Both the sashes slide downwards and upward.
This kind of window is used for ventilation purposes. Generally, two or three sets of double-hung windows are placed side by side on the wall. A single window with two sashes is common today.
Being efficient for energy saving, hung windows are preferred all over the world. The top and the bottom sash give proper ventilation to the room. Double-hung windows are a bit costly and take regular maintenance.
11. Louvered Windows

These types of windows offer ventilation but do not let you see the outside scenario as they are made of wooden or glass and sometimes metal-framed louvers.
The shutter of these kinds of windows is made with louvers that are fixed with two rails, a bottom rail, and a top rail. The louvers are inclines inside the house on a slope of about 45 degrees. That allows to air come in and very little light comes in.
The shutter blocks the complete outside view. But the purpose of this blocking is not for the outside scenery. The main purpose to block the view is proper privacy inside the house. Even if the window is opened, one can not see what is going on inside the house. These kinds of windows are used in places like the bathroom and toilet and some other private places.
12. Clerestory Windows

Clerestory windows are the windows that are situated in a room in which the height of the room is different from that of the other rooms. Thus allowing air circulation and lights which were blocked.
This kind of window adds additional heat to the room making the house warmer. Being situated above the side the incoming light can light the house entirely.
Sometimes more heat can damage the house so clerestory windows are not recommended for hotter regions. Clerestory windows are usually situated at the end of the southside making the light come in throughout the day and the year.
13. Gable Windows

A gable roof is a roof that creates flat areas at the back, front, and side. A window made on the gable is called a gable roof. A gable window gives proper lighting conditions and allows ventilation. Also, it gives a stunning look to the house.
14. Dormer Windows

The word ‘dormer’ came from the Latin term ‘dormitories‘ which means sleeping room. So dormer windows are windows that are situated in a bedroom. But the main theme of these kinds of windows is that they elevate from a sloping roof.
Dormer windows are like gable windows Dormer windows provide an extraordinary look to the house.
15. Lanterns

Lanterns are windows that are placed on the roof. In places where light is blocked from all the sides so the window on a side can not let the sunshine in, lanterns are made.
Lanterns are fixed with glass panels that give high transparency and good isolation. High-quality glasses should be used in lanterns. Lanterns do not give ventilation to the room so another alternative for ventilation must be used.
16. Skylights
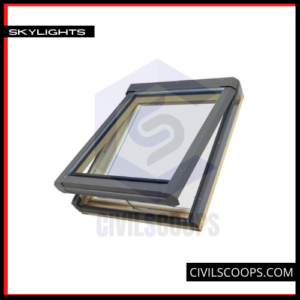
The synonym of skylight is rooflights which symbolizes windows made on the roof. Skylights are sometimes movable but can also be not movable. That means skylights can/ can not be opened. The sole purpose of skylights is to draw lights in.
Skylights also give a stunning view of the sky. So people who love to see the sky and the stars can go for skylights. Skylights are placed high above the roof allowing no air to come in.
17. Ventilators

As the name suggests the windows are made solely for ventilation purposes and are called ventilators. Ventilators are situated on the uppermost side of the wall. Generally, the air inside the house gets hotter and then travels towards the upper side. So having a ventilator makes it easier to let the air out.
There are many types of ventilators. Some _ventilators are attached to a fan for easily passing out the hot air. Ventilators can be round in shape mostly.
18. Lunette

‘Lune’ in lunette means ‘Moon’. lunette windows are windows that are shaped like semicircular or crescent. A window that is attached to a lunette is a lunette window. Lunette windows are very classic and ornamental. They are so decorative and lunette windows add magnificent beauty to the house it is built.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Difference Between Plane Surveying and Geodetic Surveying
- What Is Sheepsfoot Roller? | Characteristics of Sheepsfoot Rollers | Difference Between Padfoot and Sheepsfoot Rollers
- What Is Traffic Rotaries? | Rotary Intersection | What Is Rotary Island? | Advantages & Disadvantages of Traffic Rotary
- What Is Tie Beam? | Tie Beam Details | Ties in Column | Tie Beam Design | Concrete Tie Beam | Tie Beam Reinforcement Details
- Types of Curing | Concrete Curing Time | How to Cure a New Concrete Slab | What Is Curing of Concrete | How Long Does Concrete Take to Dry | How Long Does It Take for Cement to Dry
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Type of Windows Do I Have in My House?
Many different window types make up the construction of your house. Consider your needs in each space — such as ventilation, light or privacy — when choosing windows for your home.
Some window styles can be opened to let in fresh air, while others are inoperable but designed to allow maximum natural light to flood your rooms. Your windows also help define the style of your house whether it is traditional or modern. You can customize nearly any window to suit your changing tastes and needs.
What Are the Best Windows to Put in Your House?
These classic windows provide good ventilation, offer access for cleaning, and are easier to replace than more unique window styles. Because they work against gravity, double- or single-hung windows may not stay open as desired if not properly maintained.
What Are the Best Windows for a House?
These classic windows provide good ventilation, offer access for cleaning, and are easier to replace than more unique window styles. Because they work against gravity, double- or single-hung windows may not stay open as desired if not properly maintained.
What Are the Different Types of Windows for Houses?
- Double-Hung.
- Single-Hung Windows.
- Slider Windows.
- Casement Windows.
- Awning Windows.
- Hopper Windows.
- Bay Windows.
What Are the Best Home Windows
The best window brands ahead have established and proven their reputations for making well-constructed and dependable windows.
- Andersen Windows.
- Pella.
- Milgard Windows & Doors.
- Simonton Windows & Doors.
- Alside.
- JELD-WEN.
- Marvin.
- Loewen.
Originally posted 2022-05-30 09:36:29.
