What Is Mortar | Test of Mortar | Process for Compressive Strength

Table of Contents
What Is Mortar?

Mortar is an intimate mixture of binding material, fine aggregate, and water. When water is added into the dry mixture of binding material and the inert material, binding material develops the property that binds not only the inert material but also the surrounding bricks and stones.
If the cement is the binding material, then the mortar is called cement mortar. Other mortars commonly used are lime mortar and mud mortar. The inert material used is sand.
Test on Mortar
The following tests are conducted on the prepared mortars to ensure their quality:
- Crushing Test.
- Tensile Strength Test.
- Adhesive Test.
1. Crushing Test
This test is carried out on a brick-work using the mortar. This brick-work is crushed in a compression testing machine, and the load is noted down.
Then the crushing strength is obtained as load divided by cross-sectional.
Determination of Compressive Strength of Mortar
To find the compressive strength of cement standard sand mortar cubes, the following would be the procedure and apparatus on the test.
Apparatus
Mortar Cube Size 7.06 cm x 7.06 cm x 7.06 cm

Mortar Cube Size
Apparatus for Gauging and Mixing Mortar

Apparatus for Gauging
Vibrator for Morta Cube

Vibrator
Compression Testing Machine

Compression Testing Machine
Process for Compressive Strength of Mortar.
- Take 200gm of cement and 600gm of sand in the mix ratio 1:3 by weight in a pan.
- The standard sand will be of walnut, of light, gray or whitish variety and will be free of silt.
- The sand grains will soon be angular, the shape of grains approximating into the spherical form, elongated and flattened grains being present only in very small quantities.
- Standard sand will pass through 2 mm IS sieve and will be retained on 90 microns IS sieve using the following particle size distribution.
- Mix the cement and sand in dry condition using a trowel to get one minute and then add water.
- The quantity of water will be (p/4+3)% of the combined weight of cement and sand, where p is the % of the water required to produce a paste of standard consistency determined earlier.
- Add water and mix it until the mixture is of uniform color.
- The time of mixing shall not be < 3 minutes & not > 4 minutes.
- Immediately after mixing the mortar, then place the mortar at the cube mold and prod with the help of the rod.
- The mortar will be prodded 20 times in about 8 sec to ensure the elimination of entrained air.
- If the vibrator is used, the period of vibration will be two minutes in the specified speed of 12000±400 vibrations /minutes.
- Then place the cube molds in temp. of 27±2o C and 90% relative humidity for 24 hours.
- After 24 hours, remove the cubes in the mould and immediately submerge in clean water till testing.
- Take out the cubes from the water just before testing. Testing needs to be done on their sides without any packing.
- The rate of loading needs to be 350 kg/cm2/minute and uniform.
- A test ought to be conducted for 3 cubes and report the average value as the test result for both 7day and 28-day compressive strength.
Result of Mortar Cube Test
- Compressive strength at 7 days =……….N/mm2
- Compressive strength at 28 days =……….N/mm2
2. Tensile Strength Test
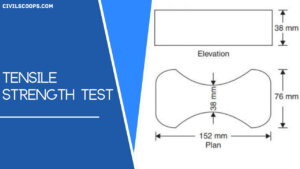
The mortar prepared is placed in a mould of bracket that has a central cross-sectional area as 38 mm × 38 mm.
After curing, the briquette (above fig) is pulled under the grips of the tensile testing machine. The ultimate load noted. Then the tensile strength of mortar is load divided from the central cross-sectional area.
3. Adhesive Test
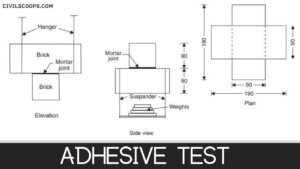
Two bricks are joined together with mortar to be tested as shown in above Fig. The upper brick is suspended from an overhead support.
A board is hung from the lower brick. Then weights are added to the board till the bricks separate. The adhesive strength is the load divided by the area of contact.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
What Is Mortar?
Mortar is a workable paste which hardens to bind building blocks such as stones, bricks, and concrete masonry units, to fill and seal the irregular gaps between them, spread the weight of them evenly, and sometimes to add decorative colors or patterns to masonry walls.
What Is Thinset?
Thinset is an adhesive mortar made of cement, fine sand and a water-retaining agent such as an alkyl derivative of cellulose. It is usually used to attach tile or stone to surfaces such as cement or concrete.
What Is Mortar Used for
Mortar is a material used in masonry construction to fill the gaps between the bricks and blocks. Mortar is a mixture of sand, a binder such as cement or lime, and water and is applied as a paste which then sets hard.
What Is Mortar Mix
Mortar, which is a mixture of water, cement, and sand, has a higher water-to cement ratio than concrete. It has a thicker consistency which makes it a great adhesive and bonding agent for bricks and tiles.
What Is Thinset Mortar?
Thinset or mortar (or thinset mortar, thinset cement, dryset mortar, or drybond mortar) is an adhesive made of cement, fine sand, and a water retaining agent such as an alkyl derivative of cellulose. Many thin-sets have latex and polymer additives in them designed to increase bonding strength.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- All About of Mezzanine Floor
- Estimate Cost of Construction Per Sq Ft
- OPC vs PPC | Difference between OPC and PPC Cement
- What is Door Frame? | 8 Main Parts of Door Frame | Types of Door Frame used in House
- Reinforced Concrete Frame | Concrete Frame Construction Details | Concrete Building Construction
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-06-30 21:05:30.
