What Is Shear Wall | Classification of Shear Walls |Advantages of Shear Wall | Functions of Shear Wall | Important Point Shera Wall

Table of Contents
What is a Shear Wall?
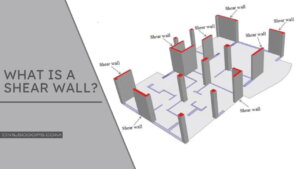
Shear wall is a structural member used to resist lateral forces, i.e., parallel to the plane of the wall. In other words, Shear walls are vertical elements of the horizontal force resisting system.
Shear wall is a structural member in a reinforced concrete framed structure to resist lateral forces such as wind forces.
This is rarely practical since it also utilizes the space a lot, so they are positioned at the ends. It is better to use walls with no openings in them. So, usually, the walls around lift shafts and stairwells are used.
Classification of Shear Walls
- Column Supported Shear walls.
- Core Type Shear Walls.
- Rigid Frame Shear Walls.
- Framed Walls with Infilled Frames.
- Simple Rectangular Types and Flanged Walls.
- Coupled Shear Walls.
- Cantilever Shear Wall
Types of Shear Wall
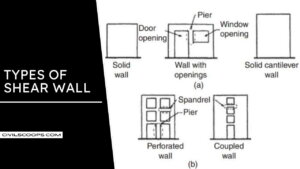
Here, the different types of shear wall are as follows.
- Concrete Shear Wall
- Steel Plate Shear Wall
- Plywood Shear Wall
- RHCBM (RC Hollow Concrete Wall Masonry.)
Functions of Shear Wall
The main functions of a Shear Wall can be described as follows
- Strength to a building
- Stiffness to a building
1. Strength to a building
Shear Wall must provide lateral shear strength to the building to resist the horizontal earthquake forces, wind forces, and transfer these forces to the foundation.
2. Stiffness to a building
Shear Walls provide large stiffness to building in the direction of their orientation, which reduces the lateral sway of the building and thus reduces damage to the structure.
Purpose of Shear Wall
- Here, the purpose of shear wall are as follows.
- The verticle or gravity loads on the structure.
- The counter shear and uplift forces.
- The lateral loads of earthquakes and wind.
- To make the structure more stable.
Advantages of Shear Wall
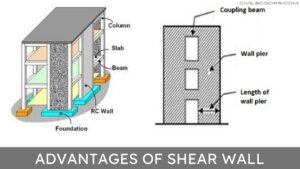
Here, the pr0s of shear wall are as follows.
- These walls provide more strength, stability, and stiffness to a building.
- Reduce lateral sway of a building.
- Easy to construct and easily implemented at the site.
- Thinner walls, hence lightweight.
- Effective in minimizing earthquake damage in structural and non-structural elements.
Disadvantages of Shear Wall
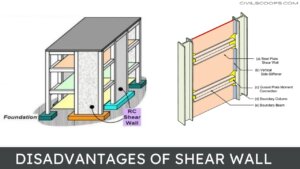
Here, the cons of shear wall are as follows.
- Shear walls are difficult to construct.
- They have a flimsy appearance.
- Also, loud banging sounds associated with the buckling of web plates.
- It has low stiffness and energy dissipation capacity.
- Also, requires large moment connections.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Shear Wall
In structural engineering, a shear wall is a vertical element of a system that is designed to resist in-plane lateral forces, typically wind and seismic loads. In many jurisdictions, the International Building Code and International Residential Code govern the design of shear walls.
What Is Shear Wall?
While columns and load-bearing walls keep buildings standing up, carrying the compression load of the structure down to its foundation, the shear wall is what keeps structures from blowing over, resisting the lateral forces of wind and seismic activity.
How Do Shear Walls Work?
A shear wall is a general term for a wall that is designed and constructed to resist racking from forces such as wind using masonry, concrete, cold-formed steel, or wood framing. Shear walls significantly reduce the sway of a structure to reduce damage to the structure and its contents.
What Structures Need Shear Walls?
Most homes and buildings in high-wind and earthquake-prone regions require exterior shear walls. However, larger houses and high-rise structures also need interior shear walls to protect against lateral wind and seismic forces.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
- Mortar Vs Cement | Types of Cement | Types of Mortar
- All About Formwork Failure | What Is Formwork Failure | Causes of Formwork Failure
- All About Rate Analysis | What is Rate Analysis | Rate Analysis of Earth Work, Brick, Concrete and Plaster
- How to Calculate Staircase Qty | Concrete & Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) | Staircase Reinforcement Details
- All About Flagstone | Introduction of Flagstone | What Is Flagstone | What Is a Flagstone Patio | Types of Flagstone
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-06-23 13:23:39.
