Joints of Stone Masonry | Type of Joints of Stone Masonry | General Principles Which Are Used in the Construction of Stone Masonry

Table of Contents
Joints of Stone Masonry

The construction which is done with the help of stones and bonded together with mortar is known as Stone Masonry. Stone Masonry is widely used where the stones are available in abundance. The stone masonry is the type of masonry construction which is done with stones and cement mortar.
Stone Masonry is used for the construction of foundations, walls, plinth, sand columns. In this article, you will get to know about the joints of stone masonry and types of joints in stone masonry.
Stone masonry is stronger and durable as compared to brick masonry. Stone masonry is used in the olden days for the construction of various Structures.
Stone Masonry is the art of building structures from stones. Stones are abundantly available in nature. Stones are cut and dressed into different shapes and prove to be economical material for Construction. In the stone masonry, some through stones are provided at the right angle.
General Principles Which Are Used in the Construction of Stone Masonry:
- The stones which are used in the construction of stone masonry should be hard, tough, and durable.
- The pressure which is acting on the stones should be in the vertical plane.
- The heads and the stones should not be of dumb bell shape.
- The stone should be dressed properly as per the requirements.
- A large flat stone should be used under the ends of girders and trusses two uniformly distributed loads.
- The water which is used in the construction of the stone masonry is of good quality.
- It is very necessary for to you give your stone masonry e in a proper manner for a period of 2 to 3 weeks after the construction.
- The plumb bob should be used to check the accurate verticality of the stone masonry walls.
- Stonemasonry should be design to take the compressive stresses and not tensile stresses.
Type of Joints of Stone Masonry
There are different types of joints in the stone masonry which helps to bond with each other.
- Butt or Square Joint.
- Rebated or Lapped Joint.
- Tongued and Grooved Joint.
- Cramped Joint.
- Tabled or Bed Joint.
- Plugged Joint.
- Dowelled Joint.
- Saddle Joint.
- Slate Joint.
1. Butt or Square Joint
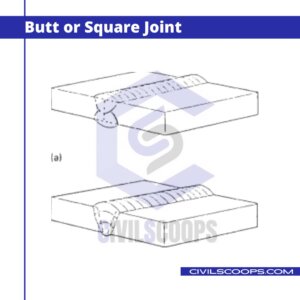
The butt joint is very simple and commonly used to join in the construction of stone masonry work. In the case of butt or square joint, the dressed edge of the two adjacent stones is placed side by side. The two adjacent stones which are placed in this type of joint are abutted with each other.
2. Rebated or Lapped Joint

The lapped joints are provided in the stone masonry where the movements of the stone units have to be prevented. This type of joint is also known as rebated joints.
The rebates are also provided to prevent the movements of the stones. The length of rebates should not be less than 70 mm. These types of joints are widely used in the construction of earthwork and coping on gables.
3. Tongued and Grooved Joint

In this type of joint, the stone is made by providing a tongue and a corresponding groove on the adjacent stones. This type of joint is provided to prevent sliding.
Also Read: How a Building Is Constructed | Components of Building
4. Cramped Joint
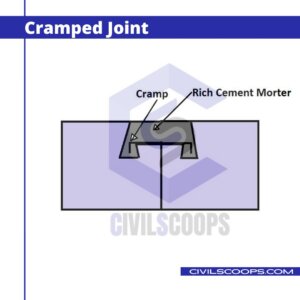
In the case of the cramped joint, the holes are provided on the adjacent stones. The cramps are used in this type of joint to connect the stones.
The cramped are the pieces of non-corrosive material whose ends are turned down up to a depth of 4 to 5 cm. The length of the cramp varies from 200 mm to 300 mm. The hole must be cramped with the help of cement water after placing the cramp into its proper location.
5. Tabled or Bed Joint
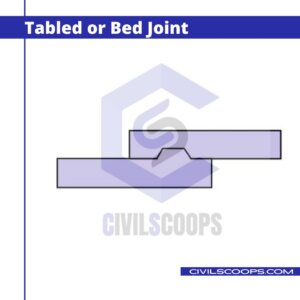
Tabled joints are used where the lateral pressure is very high and it is necessary to prevent it. In this type of joint, to prevent the lateral pressure at joggle is formed on the upper surface of the bed stone.
Recess is formed on the bottom surface of the stones which laying above the bed stone. The tabled joint is widely used where the lateral pressure is to be prevented such as in the case of sea walls.
6. Plugged Joint
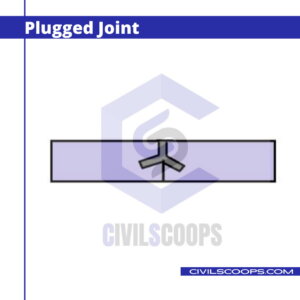
The plugged joint is the same as the cramped joint. In this type of joint, the cuts are made in the sites of adjacent stones after arranging the stones in the proper position. This type of joint is widely used for coping and cornices works.
7. Dowelled Joint
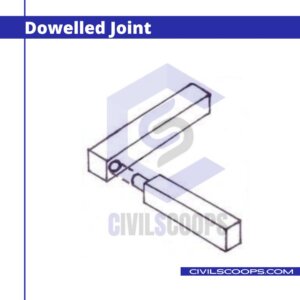
In this type of joint a hole is made into each stone and the dowels of small pieces of hard stone or brass are used to connect the stones with the help of cement mortar.
The dowelled joint is used to prevent the adjacent stones against displacement or sliding. The thickness of the dowels is used of 5 cm and 10 to 15 cm long. This types of joints prevent unwanted displacement of these stones.
8. Saddle Joint

A saddle joint is provided to protect the joints in the cornices. This type of joint is also known as a water joint. Saddle joints are used in the cornices and other weather surfaces to divert the water away from the joint.
9. Slate Joint
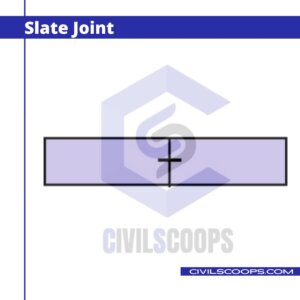
In this type of joint grooves are made on the sides of the surface of the adjacent stones. A piece of Slate is placed between the gross of the adjacent stones.
Important Points Which Should Be Considered While Construction of the Stone Masonry
- Here are some points which should be observed in the construction of the stone masonry
- In the construction of the stone masonry, all these stones should be laid upon the natural beds.
- Stones that are used in masonry should be well seasoned hard tough and has a uniform texture.
- The stone should be free from defects like cracks and cavities.
- The vertical joints in stone masonry should be staggered.
- Proper bonding should be maintained throughout the construction of the stone masonry.
- Stones that are used for the construction of the stone masonry should be wetted before its use.
- Stone Masonry should be cured properly for at least two weeks.
- In the case of the Stratified rocks, the stone should be placed on its quarry bed surface in such a way that the line of pressure should be Normal.
FAQ
Stone Masonry
Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculptures using stone as the primary material. It is one of the oldest activities and professions in human history.
Joints of Stone Masonry
- Butt or Square Joint.
- Rebated or Lapped Joint.
- Tongued and Grooved Joint.
- Cramped Joint.
- Tabled or Bed Joint.
- Plugged Joint.
- Dowelled Joint.
- Saddle Joint.
- Slate Joint.
Basic Principles of Stone Masonry
- No stone should be laid taller than it is long, except at corners.
- Avoid blocking or running joints with only one stone on at least one side of a vertical joint.
- Avoid setting more than three stones against a riser.
- Risers should be evenly distributed throughout the wall.
Important Points Which Should Be Considered While Construction of the Stone Masonry
The stones which will be used in stone masonry must be enough strong, hard, durable, and well seasoned. It should ensure that the stones are well watered before using them. Otherwise, they will absorb water from the mortar, which leads to reduces the strength of the mortar joint.
Stone Masonry
What is stone masonry? Stonemasonry is essentially a type of construction technique that uses stones as the main material. Stones are cut, shaped, and placed to form structures and designs. Masons use them together with mortar to build foundations, walls, floors, and columns.
Stone Masonry Wall
What is stone masonry? Stonemasonry is essentially a type of construction technique that uses stones as the main material. Stones are cut, shaped, and placed to form structures and designs. Masons use them together with mortar to build foundations, walls, floors, and columns.
Cast Stone Masonry
Cast stone masonry is a refined architectural concrete building unit, manufactured to mimic natural cut stone and used in unit masonry applications. Cast stone can be made from white and/or grey cement, manufactured or natural sands, carefully selected crushed stone, or well-graded natural gravels.
Ashlar Stone Masonry
Ashlar is a finely dressed stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruvius as opus isodomum, or less frequently trapezoidal.
Laterite Stone Masonry
Laterite stone blocks are being used as masonry material for housing construction in the Malabar region of western India for ages, because of being abundant, relatively easy to cut and shape and show good performance in many applications.
Stone Masonry and Brick Masonry
Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculptures using stone as the primary material. It is one of the oldest activities and professions in human history.
Stone Masonry Building
What is stone masonry? Stonemasonry is essentially a type of construction technique that uses stones as the main material. Stones are cut, shaped, and placed to form structures and designs. Masons use them together with mortar to build foundations, walls, floors, and columns.
Medieval Stone Mason
There were three main classes of stonemasons. They were the apprentice, journeymen, and the master mason. At a cathedral construction site, the master mason is usually the head and he oversees the work of all skilled and unskilled laborers.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Building Layout | How to Building Layout | Construction Layout Techniques
- How a Building Is Constructed | Components of Building
- What Is Bituminous Road? | Bituminous Road Construction | Bituminous Road Layers | Bituminous Macadam | Bituminous Road Construction Process | Advantages of Bitumen Road | Disadvantages of Bitumen Road | Application Road
- What Is Super Elevation? | Superelevation Definition | Purpose of Providing Superelevation in Roads | Calculation of Superelevation in Roads | Minimum and Maximum Superelevation in Roads | Method of Providing Superelevation to the Roads
- What Is Lintel? | Function of Lintel | Types of Lintel
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-09-09 13:09:32.
