What Is Traffic Rotaries? | Rotary Intersection | What Is Rotary Island? | Advantages & Disadvantages of Traffic Rotary
Table of Contents
What Is Traffic Rotaries?
Traffic rotaries or intersections are a special type of intersection designed by civil engineers where all the traffic is forced to move in one direction across the central island of traffic rotary. All the junction hazards, disputes, or major clash of right turn motion is turned into milder by mixing and diverging technique in traffic rotary.
In the traffic rotary system, all the vehicles are pushed to travel in a clockwise direction smoothly, and they can easily leave that place without disturbing other traffic.
The traffic rotary is mainly provided to eliminate the stopping necessity for the crossing of vehicles and to reduce the conflict area.
Rotary Intersection

Traffic rotaries or intersections are special types of intersections designed by civil engineers where all the traffic is forced to move in one direction across the central island of traffic rotary.
All the junction hazards, disputes, or major clash of right turn motion is turned into milder by mixing and diverging technique in traffic rotary.
In the traffic rotary system, all the vehicles are pushed to travel in a clockwise direction smoothly, and they can easily leave that place without disturbing other traffic.
The traffic rotary is mainly provided to eliminate the stopping necessity for the crossing vehicles and to reduce the conflict area.
What Is Rotary Island?
The rotary island is a central island. All the vehicles should rotate around the central island in one direction. All the traffic move in their different direction by rotating the central island.
Rotary Design
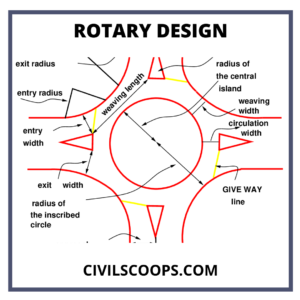
Design Element of Traffic Rotary
This design element of traffic rotary is divided into four parts those are
- Rotary Design Speed
- Entry, Exit, and Island radius of Traffic Rotary
- Width of the Traffic Rotary
- Limit of Traffic Rotary
Rotary Design Speed
- In the traffic rotary, the design speed is always lower than the flat roadway because the vehicle is in the rotational position.
- If we construct a with no speed reduction, then we must construct a costlier roundabout so that it will be more expensive construction.
- The average speed in rotary of any vehicle is 30 to 40 km per hour in rural and urban areas.
Also Read: Types of Cement Grades | Difference Between 33, 43 & 53 Grade Cement
Entry, Exit, and Island Radius of Traffic Rotary
- The input velocity of any vehicle in the rotary depends upon several variables, and those are superelevation, design speed and friction coefficient.
- The entrance of any vehicle in the rotary is slow because there is a minor curve is applied in that position. A 20 to a 25-meter radius of the curve is provided for the entry radius curve.
- The exit curve of the rotary must be smooth because vehicles can achieve higher speed due to rotational motion.
- The radius of the central island must be provided with a higher value for giving the clearance of traffic.
- The central island radius is 1.3 percent of the passageway bend.
Width of Traffic Rotary
- IRC recommends that the 7m profound two-path street can be provided in the metropolitan streets and 6.5m for rustic streets.
- In three pathways, 10.5m to 7-7.5m is the recommendation of IRC.
- The weaving width of traffic rotary is-
Weaving length= [(e1+e2)/2]+3.5 m
Where,
e1= width of the carriageway of the section
e2= width of the carriageway at the exit of traffic rotational
- Weaving length decides how the traffic blend and wander.
Limit of Traffic Rotary
- The traffic rotational limit is controlled by the limit of each weaving zone. The observational equation of weaving zone time limit is-
Qw= [280w[1+e/w][1-p/w]] / [1+w/l]
Where,
- e= normal section and leave width
- w= weaving width
- i= length of weaving
- p= degree of weaving traffic to the non-weaving traffic
p= (b+c)/(a+b+c+d)
- 6 to 18 meters is the weaving width at the rotational part.
- The carriageway for the area and extend to the weaving width is 0.4 to 1.
- The extent of the weaving width of the rotary is 0.12 to 0.4.
- The weaving length at the combination is 18 and 90 m.
Advantages of Traffic Rotary
- One of the main advantages of traffic rotary is to regulate the vehicles in one direction only that’s why it reduces traffic accidents between crossing movements.
- In a traffic rotary system, all the vehicles are entered at a low pace and go through it at the same speed.
- The other most important advantage of traffic rotary is no vehicles are to be stopped due to traffic signals in that, so it approves a smooth regulation of traffic.
- In the traffic rotary system, all the vehicles are pushed to a slower pace; that’s why it reduces the chances of major accidents, injuries, etc.
- In the traffic rotary, we do not need any type of signal or traffic police.
- Traffic rotaries are best for moderate traffic systems with irregular geometry for the approaches of three or four intersections.
Disadvantages of Traffic Rotary
- All the cars need to slow down at the junction point. This is the reason for an average delay in the traffic rotary.
- In the traffic rotary system in the time of moderately light traffic, cars must reduce their speed.
- Traffic rotary construction needs some large area and requires flat land, that’s why it’s a little bit expensive, and it can not be constructed in the hilly region.
- In the traffic rotary, all the traffic has a moderate speed, but in case of higher pedestrians movement, it would be challenging to drive.
[note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- What Is Tie Beam? | Tie Beam Details | Ties in Column | Tie Beam Design | Concrete Tie Beam | Tie Beam Reinforcement Details
- Types of Curing | Concrete Curing Time | How to Cure a New Concrete Slab | What Is Curing of Concrete | How Long Does Concrete Take to Dry | How Long Does It Take for Cement to Dry
- What Is Sheepsfoot Roller? | Characteristics of Sheepsfoot Rollers | Difference Between Padfoot and Sheepsfoot Rollers
- Monolithic Slab I Monolithic Definition I Monolithicfooting I Monolithic Slab Foundationl Monolithic Slab Foundation Design L What Is a Monolithic Slab L How to Form a Monolithic Slab
- What Is a Spillway | Types of Spillway | Definition Spillway | Spillway Design
[/note]
Originally posted 2021-09-28 09:17:30.

