What Is Modulus of Rupture | What Is Flexural Modulus | What Is Flexural Stress | Flexural Strength of Concrete | Bending Modulus | What Is Flexural Strength
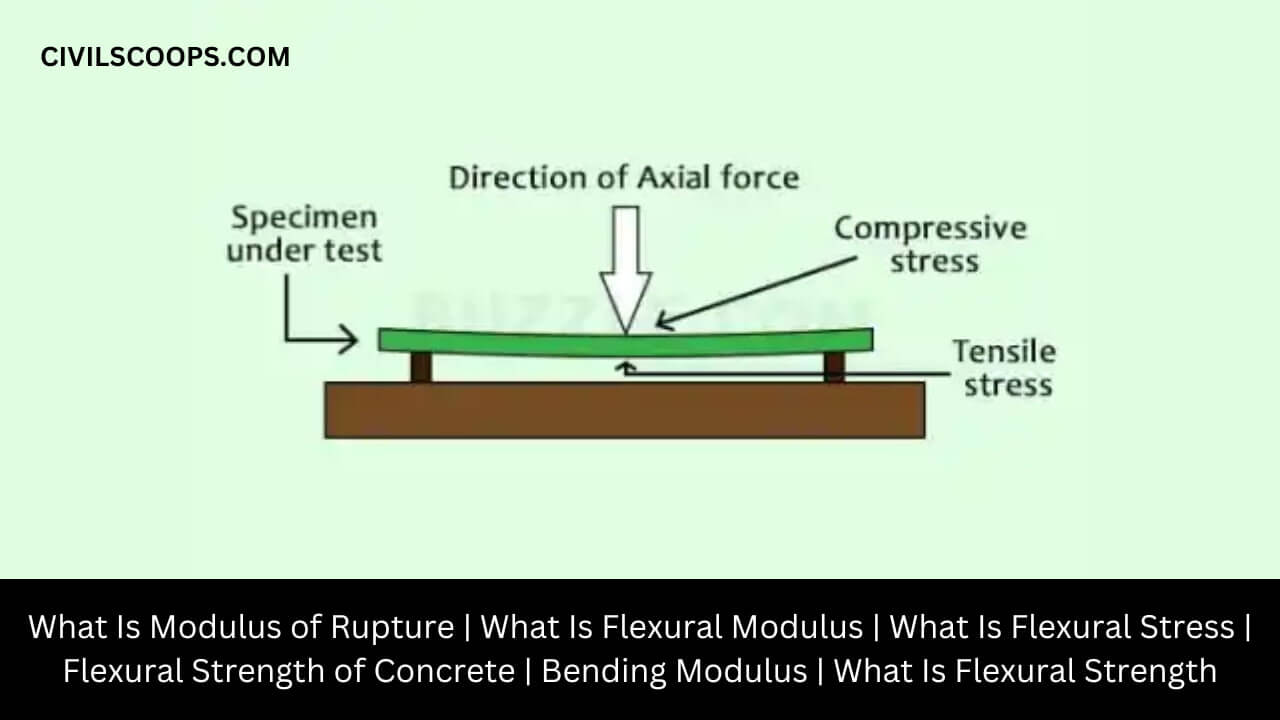
Table of Contents
Modulus of Rupture of Concrete Beam:
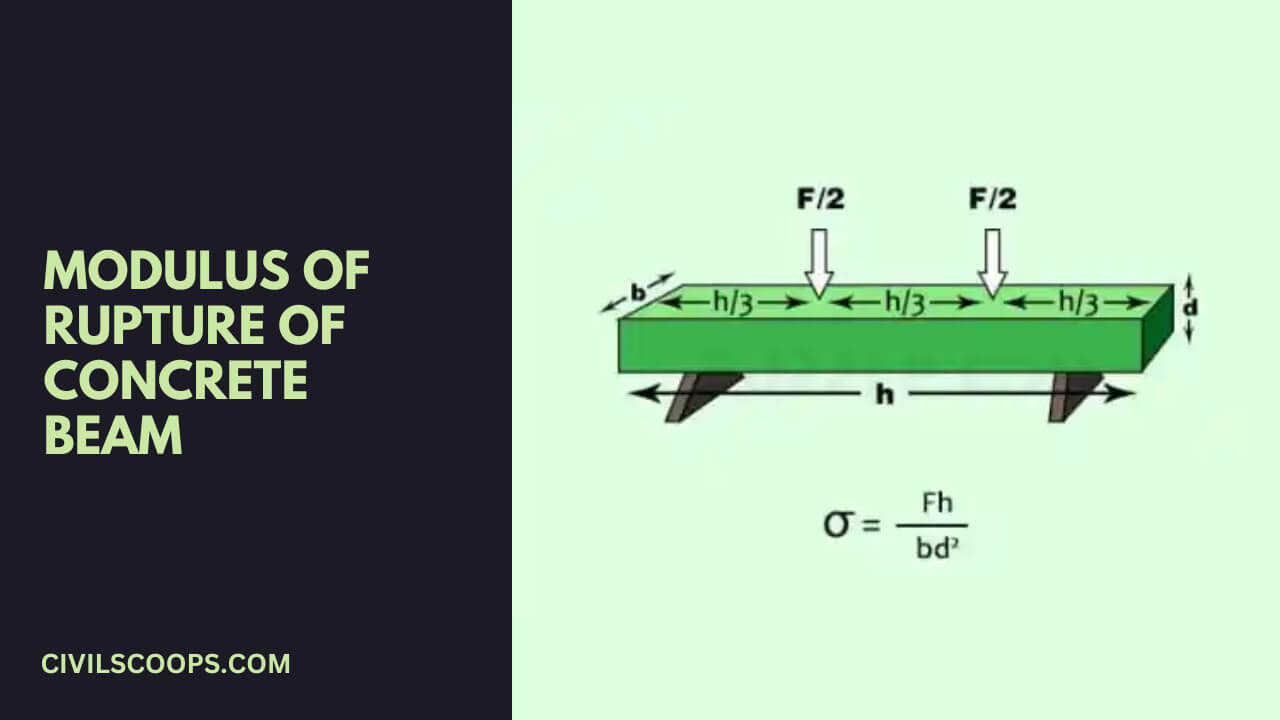
Modulus of rupture of Concrete beam indicates the amount of compression and force the unstable beam can withstand under any condition and its resistance to bending.
What Is Modulus of Rupture?
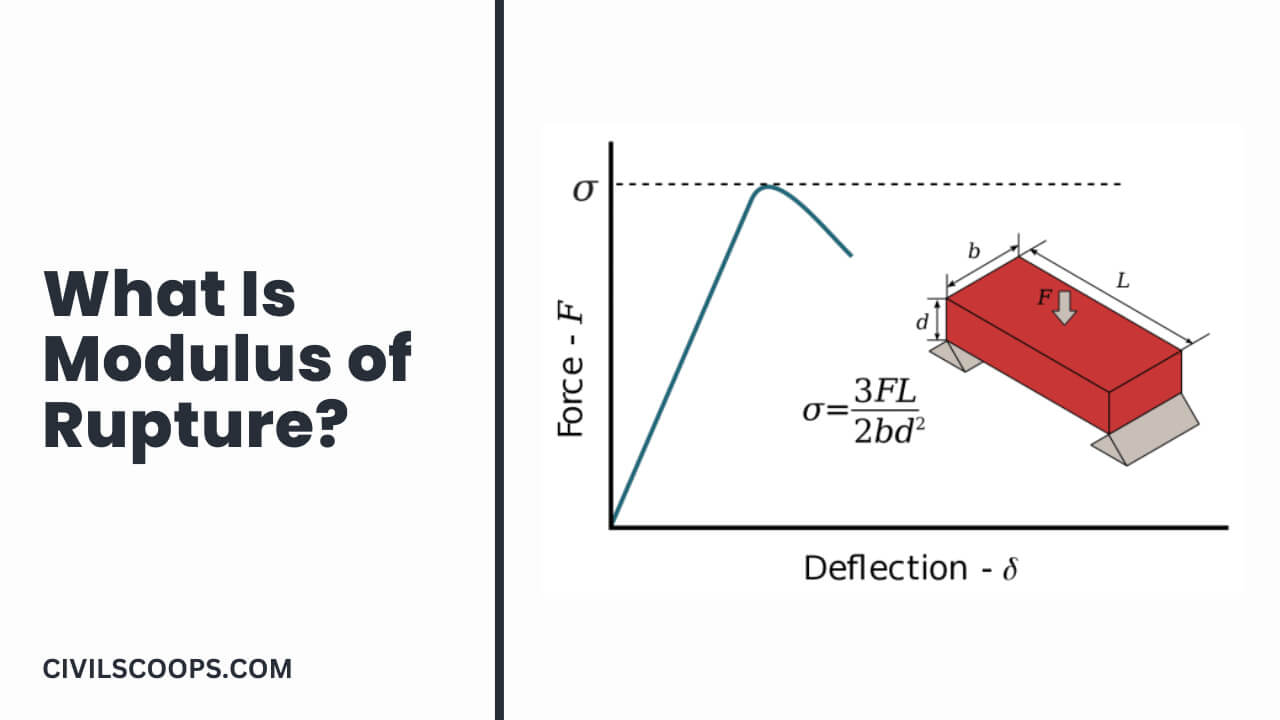
Modulus of rupture measures the strength of civil construction parts like concrete, beams, or slabs. Modulus of rupture is also known as flexural strength, bend strength, or fracture strength.
The modulus of rupture determined by the loading of the third point is less than the modulus of rupture determined by the loading of the center point, sometimes up to 15%.
Modulus of Rupture is defined as the final strength related to the failure of the beams by the flexibility equal to the moment of bending in the fracture divided by part of the beam section.
The calculation of the modulus of rupture is considered important for construction equipment for the following reasons. The calculation from Modulus of Rupture helps us to build structural elements such as beams, cantilevers, shafts, etc.
It provides a parameter for the development of dynamic building materials. It is a predictive tool for both resistance and durability of the construction project.
What Is Flexural Modulus?
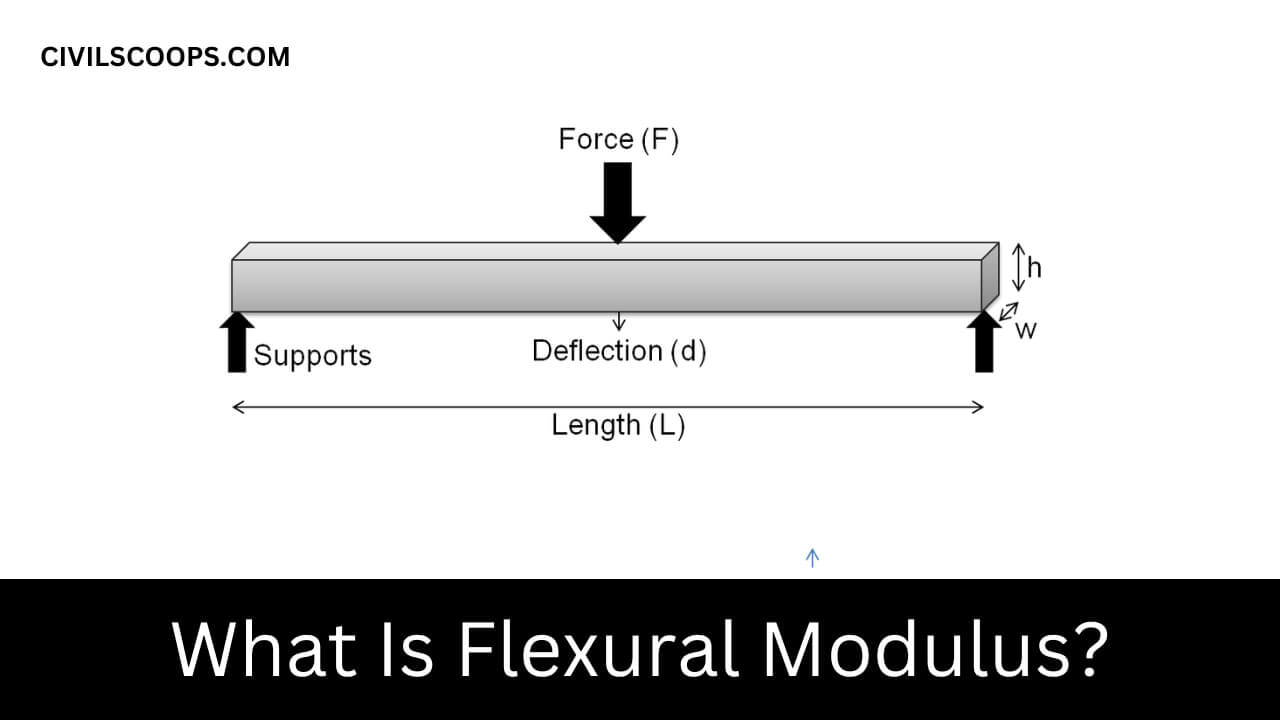
- In mechanics, the flexural modulus or bending modulus is a powerful material that is calculated as a measure of stress pressure on the flexural flexion or inclination of an object that resists bending.
- Flexural Modulus is determined from the slope of the pressure curve formed by the flexural test (such as ASTM D790) and uses power units in each position.
- The flexural modulus described using a three-point curve test takes the stress line response.
- Ideally, the flexibility or bending of the stiffness mode is similar to the tensile modulus (Young’s modulus) or the compression modulus of elasticity. In fact, these values may vary, especially in polymers which are usually viscoelastic (time-dependent) materials.
- The alignment of the flexural modulus with Young’s modulus also takes the corresponding model of pressure and stiffness as the bend models have strong and compressive pressures. Polymers in particular, have different types of compression and stiffness of the same material.
- Flexural modulus of rupture is about 10% to 20% of the compressive strength, depending on the type, size, and volume of the awesome aggregate used in the concrete block.
What Is Flexural Stress?
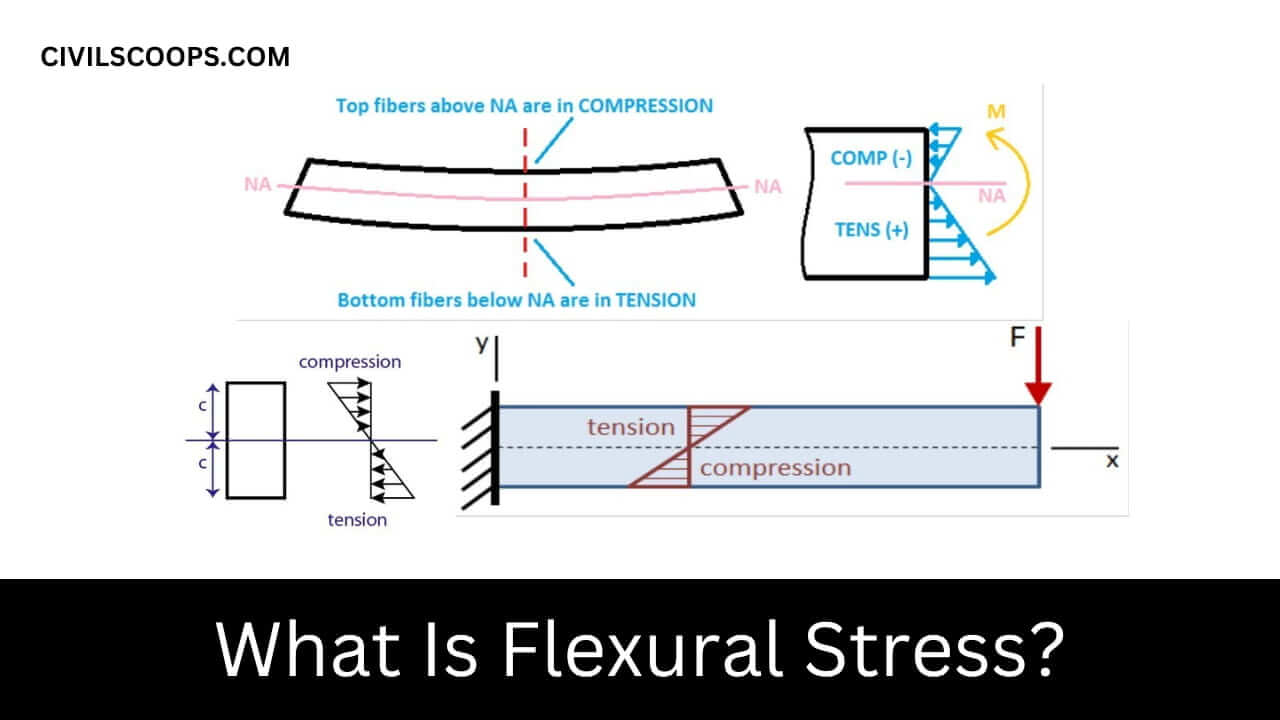
The stress caused by the bending moment in a structural member is known as Flexural Stress or Bending Stress. Flexural Stress or Bending Stress usually occurs in two cases.
One case is called bending of simply support beams and the other case is called bending of cantilever beams. Flexural Stress for simply supported structural beams acts on the two surfaces differently.
The upper surface of the bending beam is in compression stress and the bottom surface of the beam is in tension stress. The neutral axis or the center axis of the beam is a region of zero stress.
The flexural stress (σ) is defined by the formula σ = MC / I. In the above formula, M = Bending moment, which is calculated by multiplying the force by the distance between that point of interest and force. C = Distance from Neutral Axis and I = moment of inertia.
Flexural Stress of cantilevered beam also has a similar formula. The M, C, and I formulas can be complex, depending on the exact configuration and structure of the beam.
Flexural Strength of Concrete:

- Flexural Strength of Concrete is the ability of a beam or a slab of concrete to withstand failure.
- Flexural strength of concrete is a measure of the strength of concrete strength and resistance to failure is a measure of unstable concrete slab or slab.
- The relative flexural strength and contrast or requirements should be based on the same aggregate size and loading adjustment. Modulus of Rupture measured on a third-point load (ASTM C78) is lower than that determined by the average point load (ASTM C293), sometimes 15 percent
- Flexural strength of concrete is approximately 10 to 15 percent of the compressive force depending on the size of the compound and the type, size and volume of the compound used.
- For structural members of a concrete structure, the Modulus of Rupture rating is obtained by the equation Fr = 7.5 (fc’)
- Here, Fr is the Modulus of Rupture.
- Fc’ is the specified compressive strength.
- Here Modulus of Rupture is critical in the construction design; the best measurement is established from laboratory tests of specific compounds and materials used.
- Flexural strength is one measure of the strength of concrete strength. It is the standard of a fixed beam or slab to withstand bending.
Bending Modulus:
Rigidity (or stiffness) is the property of a polymer defined by the Flexural modulus or bending modulus of stiffness. Bending Modulus is therefore one of the most important of properties of solids material.
Bending Modulus refers to the ability of an object or material to bends. It is a measure of rigidity or resistance to bending when force is applied differently at the long edges of a sample also known as a three-point bending test.
The Bending modulus is represented by the slope of the first part of the straight line of the stress curve and is calculated by dividing the change in stress by a change corresponding to the strain.
Therefore, Bending Modulus is also known as the ratio of measurement of stress to strain.
Also Read: All About Sand | What Is Sand | 29 Types of Sand | Composition of Sand
What Is Flexural Strength?
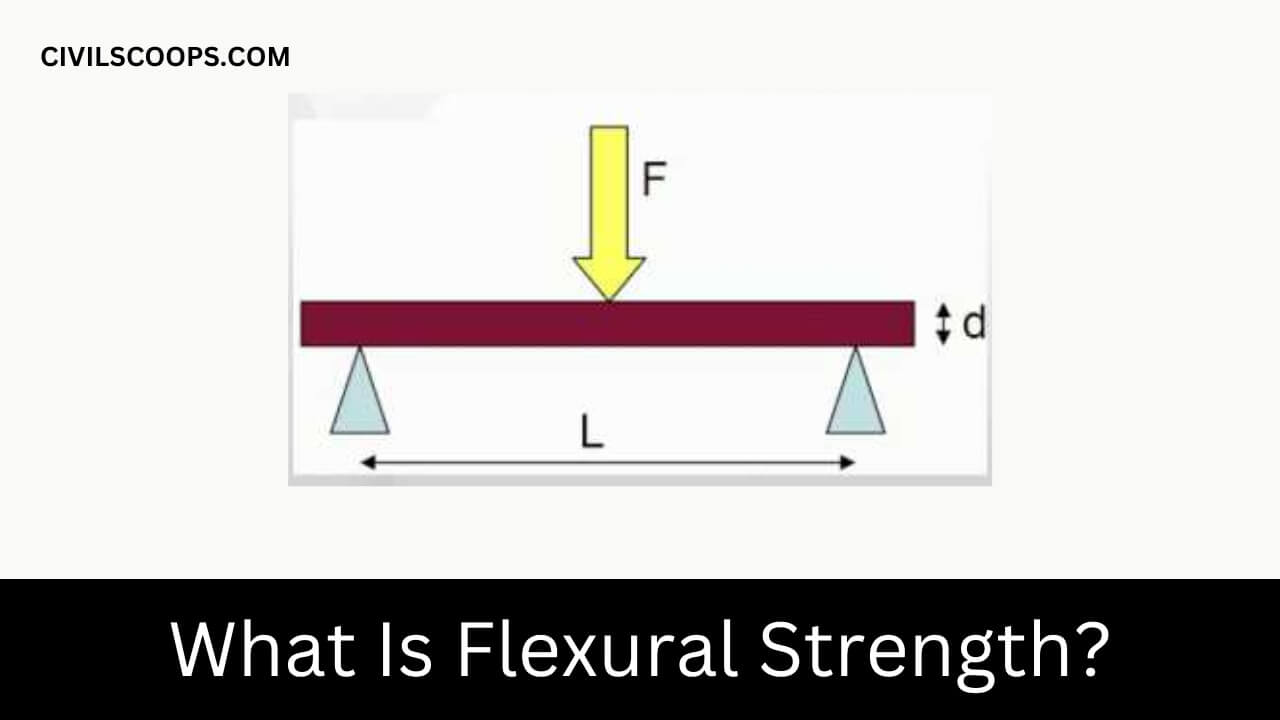
Flexural strength is an indirect measure of the strength of concrete strength. It is a measure of the high pressure on the surface of the thickness of the reinforced concrete beam or slab where it fails to bend. It is measured by loading 150 x 150-mm (or (100 x 100-mm) concrete beams with a span length of at least three times.
Flexural strength is about twelve to twenty percent of compressive strength, depending on the type, size, and volume of coarse aggregate used.
Flexural strength is expressed as the “Modulus of Rupture” (MR) in MPa and is determined by standard test methods ASTM C78 (third point loading) or ASTM C293 (intermediate loading). Flexural strength helps us to judge the quality of the materials used in construction.
Flexural Strength Formula:
Flexural strength of a beam can be calculated using the equation
F = (PL)/ (2bd).
Here,
- F = Flexural strength of concrete (in MPa).
- P = Failure Load (in N)
- L = Effective span of the beam (in mm).
- b = Breadth of the beam (in mm).
- d = Depth of the beam (in mm).
Modulus of Rupture Formula:
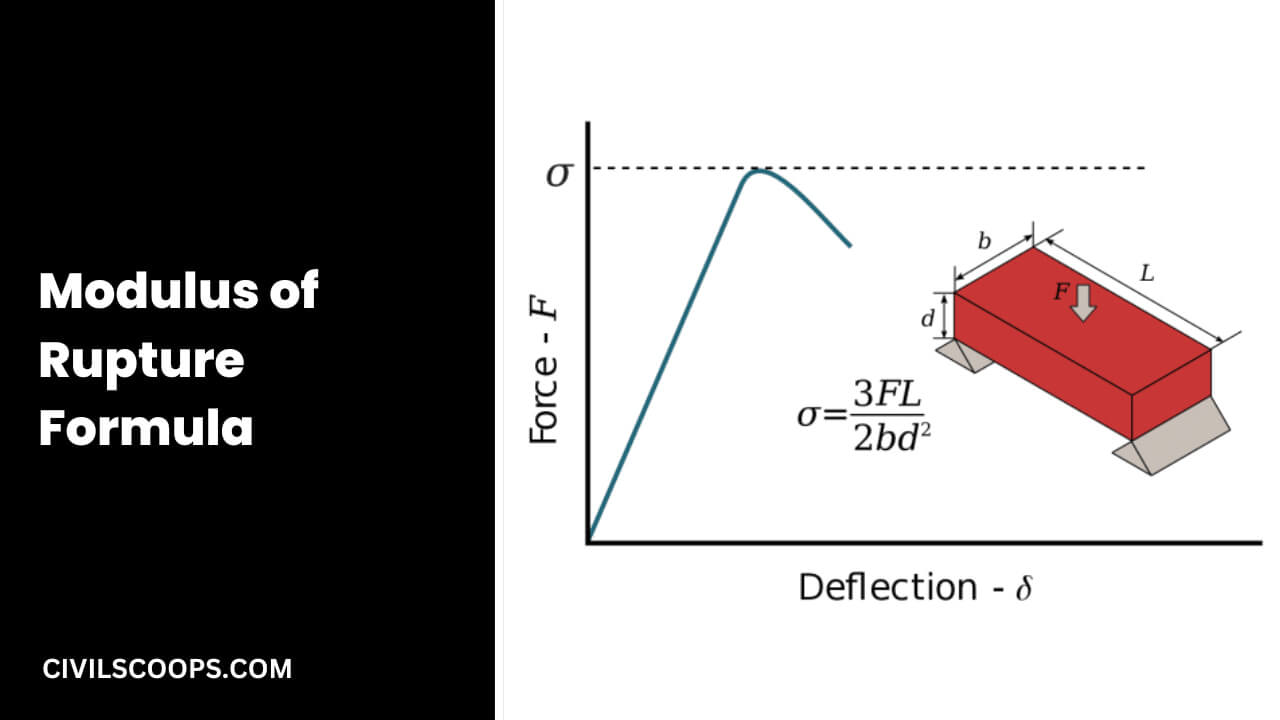
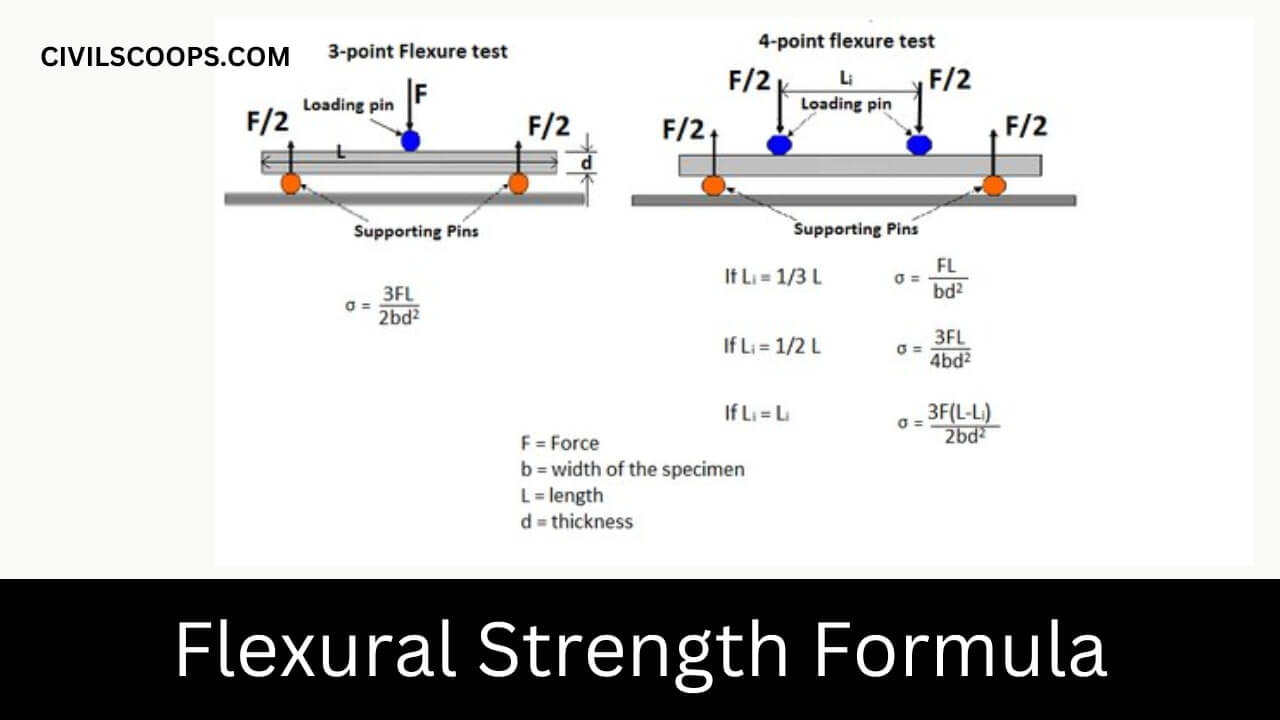
The breakdown Modulus of Rupture Formula varies with a different types of system loading.
#1. For first system, a rectangular sample under a load on a three-point bend setup.
Modulus of Rupture = (3FL)/(2bd2)
Here,
- F = load (force) at the cracked point (N).
- L = Total length of the support span.
- b = Total width of the support span.
- d = Total thickness of the support span.
#2. For the second system, a rectangle sample under a load on a four-point bend setup, where the loading span is one third the length of the support span.
Modulus of Rupture = (FL)/(bd2)
Here,
- F = load (force) at the cracked point (N).
- L = Total length of the support (outer) span.
- b = Total width of the support (outer) span.
- d = Total thickness of the support (outer) span.
#3. For the third system, a rectangle sample under a load on a four point bend setup, where the loading span is half the length of the support span.
Modulus of Rupture = (3FL)/(4bd2)
Here,
- F = load (force) at the cracked point (N)
- L = Total length of the support span.
- b = Total width of the support span.
- d = Total thickness of the support span.
#4. For the last system, a rectangle sample under a load on a four point bend setup, where the loading span is neither one third nor half the support span.
Modulus of Rupture = (3F[L-Li])/(2bd2)
Here,
- F = load (force) at the cracked point (N).
- L = Total length of the support (outer) span.
- Li = Total length of the loading (inner) span.
- b = Total width of the support (outer) span.
- d = Total thickness of the support (outer) span.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Modulus of Rupture of Concrete
fcr=0.7√fck N/mm2.
Modulus of Rupture Formula
You can calculate the modulus of rupture, “sigma,” using the equation σr = 3Fx/yz2 for the load force F and size dimensions in three directions, x, y and z, of the material. In this case, the load is the external force put on the material of interest.
Modulus of Rupture Units
The modulus of rupture is a measurement of pressure, or force per unit area. Scientists and engineers use an array of magnitudes for pressure in determining the modulus of rupture. You can find it expressed in units of pascals or megapascals as well as pounds per square inch, or psi.
Modulus of Rupture Wood
Modulus of Rupture, frequently abbreviated as MOR, (sometimes referred to as bending strength), is a measure of a specimen’s strength before rupture. It can be used to determine a wood species’ overall strength; unlike the modulus of elasticity, which measures the wood’s deflection, but not its ultimate strength.
Modulus of Rupture Test
Modulus of rupture (MOR) is like a three-point bend test. MOR measures the bond strength of the test specimen. For castables, it measures the bonding strength of the cement matrix.
Flexural Modulus Vs Elastic Modulus
The flexural modulus is the three-point bending analog to the elastic modulus for tensile loading, and both elastic moduli should theoretically have the same value, although this is not always observed.
Flexural Modulus
The flexural modulus (also known as the bending modulus) is defined as the tendency of a material to bend or is described in terms of flexural deformation, the ratio of stress to strain.
Flexural Strength Vs Yield Strength
The flexural strength of a material is defined as its ability to resist deformation under load. For materials that deform significantly but do not break, the load at yield, typically measured at 5% deformation/strain of the outer surface, is reported as the flexural strength or flexural yield strength.
Flexural Strength Vs Compressive Strength
Compressive strength is measured when force is applied uniformly on one surface while the opposite face is fully supported. Flexural strength is measured by what is essentially a bend test. The material is supported on two points placed at the edges of the material while force is applied to its center.
Flexural Strength of Steel
The bending strength for mild steel both at peak and at break increased as the thickness increases. Bending strength at peak are 364.50, 378.33 and 381.87 N/mm2 for 1, 1.5 and 2 mm respectively with 2 mm expectedly showing the greatest bending strength.
Flexural Strength of Concrete
The flexural strength of concrete is one measure of the tensile strength of unreinforced concrete. It refers to the ability of the concrete beam or slab that is being tested to resist bending. It is measured in Modulus of Rupture (MR), a measurement that is used to inform the design of concrete products.
Flexural Strength of Concrete at 7 Days
At 7 days the flexural strength of concrete in water curing increases by 15.33%. At 28 days, the flexural strength of concrete in water curing increases by 5.59%. At 56 days, the flexural strength of concrete in water curing increases by 5.56% as shown in table II.
Flexural Strength of Concrete Vs Compressive
Flexural MR is about 10 to 20 percent of compressive strength depending on the type, size and volume of coarse aggregate used. However, the best correlation for specific materials is obtained by laboratory tests for given materials and mix design.
Flexural Strength of Concrete Beam
Flexural strength is one measure of the tensile strength of concrete. It is a measure of an unreinforced con- crete beam or slab to resist failure in bending. It is measured by loading 6 x 6-inch (150 x 150-mm) con- crete beams with a span length at least three times the depth.
Minimum Flexural Strength of Concrete
A flexural strength of 4.1 MPa (600 psi) is required to open pavement to traffic prior to 14 days after placement. These specifications raise several issues with regard to the quality of concrete specified and the methods used to ensure compliance with the specifications.
Bending Modulus Vs Young’s Modulus
But how can they be different? Young’s/elastic modulus is measured in the tensile test, by pulling a sample of the material and measuring the stress/strain response. In the bending test we bend the sample instead, but the fibers at the bottom (as seen in the picture) are in tension.
Flexural Modulus Vs Flexural Strength
Flexural strength is defined as the maximum stress at the outermost fiber on either the compression or tension side of the specimen. Flexural modulus is calculated from the slope of the stress vs. strain deflection curve.
Flexural Stress Formula
So to calculate the flexural strength (σ), multiply the force by the length of the sample, and then multiply this by three. Then multiply the depth of the sample by itself (i.e., square it), multiply the result by the width of the sample and then multiply this by two.
Flexural Strength Vs Tensile Strength
The flexural strength is higher than the tensile one. Indeed, for two samples of the same size, only one half of the sample is stressed in bending while the whole is in tension, then fewer defects are involved in bending. Nevertheless, the Weibull law often underestimates the flexural strength.
Flexural Strength Formula
So simply multiply the force applied by the length, and then divide this by the width of the material multiplied by the depth of it squared.
Modulus of Rupture Concrete
Modulus of rupture is a measure of the tensile strength of concrete beams or slabs. Flexural strength identifies the amount of stress and force an unreinforced concrete slab, beam or other structure can withstand such that it resists any bending failures.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Properties of Stones | Requirements of Good Building Stones
- Standard Height of Window from Floor Level | Window Sill Height from Floor
- Definition of Design Period | Why Design Period is Provided | Factors Affecting Design Period | Design Period Values
- What Is Azimuths Surveying | What Is Bearings Surveying | Difference Between Azimuths and Bearings in Surveying
- How Much Does It Cost to Pump a Septic Tank | Why Septic Tanks Required Pumping | Typical Problems Leading to Septic Tank Pumping
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-03-04 12:30:36.
