What Is Soundness of Cement Test
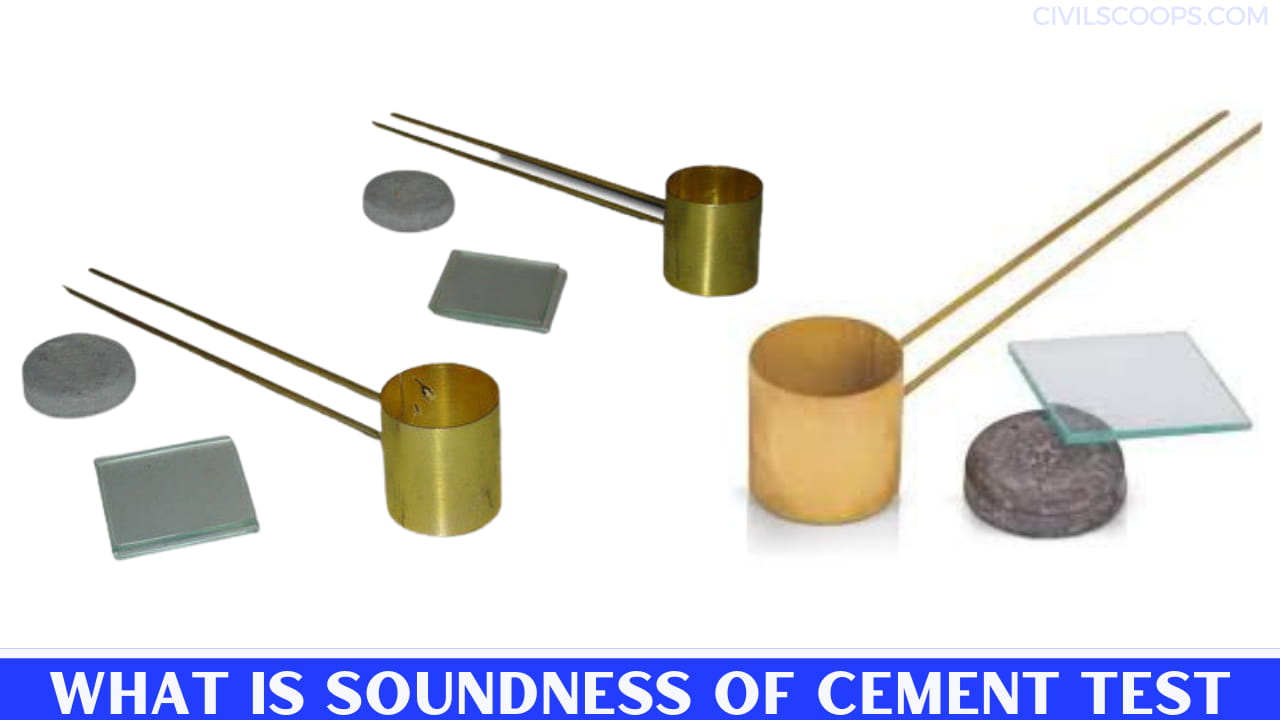
Table of Contents
What is the Soundness of Cement Test?
The soundness of the cement test Changes in volume after completion of the mold cast. After casting, the change of volume of molded cement test, this changing called the soundness of the cement test.
Relevant IS Code: IS 4031 Part 3
Two methods may determine the soundness of cement. as per below
- Le-Chatelier method
- Autoclave method
1. Le-Chatelier method
Aim:
To determine the Cement Soundness test, use the Le-Chatelier method
Apparatus:
a) Weighing Balance

b) Le-Chataleier molds/ Le chatelier apparatus

The test shall conform to IS: 5514-1969*.
c) Miscellaneous ( trowels, tray, stopwatch, etc.)

Procedure:
- Take 400gm of Cement and find its standard consistency for the Cement soundness test.
- Place the lightly oiled Le- Chatelier mold on a lightly oiled glass sheet
- Prepare a cement paste formed by gauging cement with 0.78 times the water required to give a paste of standard consistency.
- Fill the Le-Chatelier mold with this cement paste made in step (iii) of the procedure.
- Cover the mold on the top with another piece of a lightly oiled glass sheet.
- Place a small weight on this covering glass sheet and immediately submerge the whole assembly in the water at a temperature
of 27° to 32° degree Celsius and keep it there for 24 hours. - Measure the distance between the indicator points. Submerge the mold again in water. Bring to boiling point in about 25-30 minutes and keep it boiling for 3 hours.
- Removal of the mold from the water allows it to cool and measure the distance between the indicator points. The difference between
these two measurements represent the expansion of cement.
Water Bath
The water bath is capable of containing immersed Le-Chatelier molds with specimens and of raising their temperature from 27 ± 2°C to boiling in 27 ± 3 minutes. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 5.1.4
Calculation
Calculate the mean of two values to the nearest 0.5 mm to represent the expansion of cement. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 5.3
Acceptance Criteria
This must not exceed 10mm for ordinary, rigid hardening & low heat Portland cement. If in case the expansion is more than 10mm, as tested above, the cement is said to be unsound.
2. Autoclave method
Aim:
To determine the Cement Soundness test, use the Autoclave method
Apparatus:
a) Weighing Balance

b) Autoclave

C ) Graduated Glass Cylinders

Graduated glass cylinders of 150 ml capacity shall be used; the permissible variation on these cylinders shall be plus or minus one milliliter.
The main graduation lines of the cylinders shall be in circles and shall be numbered.
The east graduations shall extend at least one-seventh of the way around, and intermediate graduations shall extend at least one-fifth of the way around the cylinder. The graduation lines may be omitted for the lowest five mI. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 6.1.3
D ) Molds
Molds of 25 X 25 mm size and 282 mm internal length and other accessories conforming to IS: 10086-1982
Procedure:
- At 24 ± t h after molding, the specimens shall be removed from the moist atmosphere, measured for length, and placed in the autoclave at room temperature in a rack so that the four sides of each specimen shall be exposed to saturated steam. For the soundness of cement test From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 6.3
- The autoclave shall contain enough water to maintain an atmosphere of saturated steam vapor during the entire period of test.
From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 6.3 - Ordinarily, 7 to 10 percent of the volume of the autoclave shall be occupied by water.
- To permit air to escape from the autoclave during the early portion of the heating period, the vent valve shall be left open until steam begins to vanish. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 6.3
- The valve shall then be closed, and the temperature of the autoclave shall be raised at such a rate as will bring the gauge
pressure of the steam to 2.1 MPa in I to Ii h from the time the heat is turned on.. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 6.3 - The 2.1 ± O’lMPa pressure shall be maintained for 3 h. At the end of 3 hours period, the heat supply shall be shut off, and the
autoclave cooled at a rate such that the pressure will be less than 0.1 MPa at the end of the hour, and any pressure remaining
shall be slow-released by partially opening the vent valve until atmospheric pressure is attained.. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl
6.3 - The autoclave shall then be opened, and the test specimens immediately placed in water,
- The temperature of which is above 90°C.
- The water surrounding the bars shall·then be cooled at a uniform rate by adding cold water so that the temperature of the water
shall be lowered to 27 ± two °C in 15 min. - The water surrounding the specimens shall then be maintained at 27 ± 2°C in 15 min when the samples shall be surface-dried
and their lengths measured again. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 6.3
Calculations
The difference in lengths of the test specimen before and after autoclaving shall be calculated to the nearest 0’01 percent of the effective gauge length, which is the length between the innermost points of the metal inserts used as reference points and shall be reported as the autoclave expansion of the cement. A contraction ( negative expansion) shall be indicated by prefixing a minus sign to the percentage expansion reported. From IS Code 4031 Part 3 Cl 6.3
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
What Is Soundness of Cement Test?
In the soundness test, a specimen of hardened cement paste is boiled for a fixed time so that any tendency to expand is speeded up and can be detected. Soundness means the ability to resist volume expansion.
Soundness Test of Cement Results
Why soundness test is done on cement?
The difference between needle readings indicates the soundness of cement. The soundness limit must exceed 10 mm for ordinary, rapid hardening and low heat Portland cement. If in case the c expansion is more than 10 mm, as tested above, the cement is said to be unsound.
Importance of Soundness of Cement
The soundness of cement refers to the stability of the volume change in the process of setting and hardening. Suppose the volume change is unstable after setting and hardening. In that case, the concrete structures will crack, which can affect the quality of buildings or even cause serious accidents, known as poor dimensional stability.
Soundness Test of Cement by Autoclave Method
In the soundness test, a specimen of hardened cement paste is boiled for a fixed time so that any tendency to expand is speeded up and can be detected. Soundness means the ability to resist volume expansion.
Autoclave Expansion of Cement
The change in specimen length due to its time in the autoclave is measured and reported as a percentage. ASTM C 150, Standard Specification for Portland Cement, specifies a maximum autoclave expansion of 0.80 percent for all portland cement types.
Cement Autoclave Test
The typical expansion test places a small sample of cement paste into an autoclave (a high-pressure steam vessel). The autoclave is slowly brought to 2.03 MPa (295 psi) and then kept at that pressure for 3 hours. The change in specimen length due to its time in the autoclave is measured and reported as a percentage.
Soundness Test of Aggregate
Soundness is the percentage loss of material from an aggregate blend during the sodium or magnesium sulfate soundness test. This test, which is specified in ASTM C88 and AASHTO T104, estimates the resistance of an aggregate to in-service weathering. It can be performed on both coarse and fine aggregate.
Durability Test of Aggregate
Durability Index is an abrasion loss test that looks specifically at the production of clay-like fines as an aggregate sample degrades. These fines are known to be detrimental to asphalt mixtures. The test is also used to determine the suitability of aggregates for use in bases, backfill, and riprap.
Sodium Sulfate Soundness Test
Description. The most common soundness test involves repeatedly submerging an aggregate sample in a saturated solution of sodium or magnesium sulfate. This process causes salt crystals to form in the aggregate pores, which simulate ice crystal formation (Figures 1 and 2).
Soundness Test on Aggregate
Overview. The soundness test determines an aggregate’s resistance to disintegration by weathering and, in particular, freeze-thaw cycles. Aggregates that are durable (resistant to weathering) are less likely to degrade in the field and cause premature HMA pavement distress and, potentially, failure.
Sodium Sulphate Soundness Test
sodium-sulfate soundness test A method of testing the weathering resistance, particularly to frost action, of building materials. A sample is soaked in the saturated sodium-sulfate solution, drained, and dried. This is repeated, and the sample is examined for cracks. The method simulates the stresses due to frost action.
Soundness Test of Cement Determines
The soundness test determines whether hardened cement paste is prone to excessive expansion by boiling the test specimens for a fixed period of time.
Soundness Test of Cement by Le Chatelier Method
The soundness of cement may be determined by two methods, namely the Le-Chatelier method and the autoclave method. In the soundness test, a specimen of hardened cement paste is boiled for a fixed time so that any tendency to expand is speeded up and can be detected. Soundness means the ability to resist volume expansion.
Soundness Test of Cement Is Code
IS code for soundness of cement. The soundness test of cement shall be conducted as per IS 4031 Part 6, and the Le chatelier apparatus is confirmed as per IS code 5514.
Soundness Test of Cement by Le-Chatelier’s Apparatus Gives Unsoundness Due to
The unsoundness in cement is due to the presence of an excess of free lime that could be combined with acidic oxide at the kiln.
Soundness Test of Aggregate Apparatus
The soundness test determines an aggregate’s resistance to disintegration by weathering and, in particular, freeze-thaw cycles. Aggregates that are durable (resistant to weathering) are less likely to degrade in the field and cause premature HMA pavement distress and, potentially, failure.
Soundness Test of Aggregate Results
Overview. The soundness test determines an aggregate’s resistance to disintegration by weathering and, in particular, freeze-thaw cycles. Aggregates that are durable (resistant to weathering) are less likely to degrade in the field and cause premature HMA pavement distress and, potentially, failure.
What Is the Workability of Concrete?
What is the Workability of Concrete? Workability of Concrete is a broad and subjective term describing how easily freshly mixed concrete can be mixed, placed, consolidated, and finished with minimal loss of homogeneity.
What Is the Density of Concrete?
2.4 g/cm³
What Is the Chemical Composition of Cement?
The cement contains 35 to 40 percent lime, 40 to 50 percent alumina, up to 15 percent iron oxides, and preferably not more than about 6 percent silica. The principal cementing compound is calcium aluminate (CaO · Al2O3).
What Is Concrete Workability?
What is the Workability of Concrete? Workability of Concrete is a broad and subjective term describing how easily freshly mixed concrete can be mixed, placed, consolidated, and finished with minimal loss of homogeneity.
What Are the Chemical Properties of Cement?
Chemical Properties of Cement
- Tricalcium aluminate (C3A) Low content of C3A makes the cement sulfate-resistant.
- Tricalcium silicate (C3S)
- Dicalcium silicate (C2S)
- Ferrite (C4AF)
- Magnesia (MgO)
- Sulfur trioxide.
- Iron oxide/ Ferric oxide.
- Alkalis
What Is the Specific Gravity of Cement?
3.1 to 3.16 g/cc
Basically, specific gravity defines that the substance is how much heavier than water or a reference substance of the same volume. The specific gravity of cement ranges from 3.1 to 3.16 g/cc. By this statement, we can ensure that cement is 3.1-3.16 times heavier than the water of the same volume. And it sinks in water.
What Is the Average Particle Size of Cement?
What is the average particle size of cement? Explanation: Approximately 95% of cement particles are smaller than 45 microns, and the average particle size is 15 microns. 4.
What Are the Components of Concrete?
Concrete is made up of two components, aggregates and paste. Aggregates are generally classified into two groups, fine and coarse, and occupy about 60 to 80 percent of the volume of concrete. The paste is composed of cement, water, and entrained air and ordinarily constitutes 20 to 40 percent of the total volume.
What Are the Components of Cement?
Cement is manufactured through a closely controlled chemical combination of calcium, silicon, aluminum, iron, and other ingredients. Common materials used to manufacture cement include limestone, shells, and chalk or marl combined with shale, clay, slate, blast furnace slag, silica sand, and iron ore.
What Are the 4 Components of Concrete?
Concrete is a mixture of cement, air, water, sand, and gravel–it’s as simple as that! Not exactly. The typical concrete mix is made up of roughly 10% cement, 20% air and water, 30% sand, and 40% gravel. This is called the 10-20-30-40 Rule–though proportions may vary depending on the type of cement and other factors.
What Are the Main Components of Concrete?
Concrete is made up of two components, aggregates and paste. Aggregates are generally classified into two groups, fine and coarse, and occupy about 60 to 80 percent of the volume of concrete. The paste is composed of cement, water, and entrained air and ordinarily constitutes 20 to 40 percent of the total volume.
Why Is Cement Called Portland?
The inventor Joseph Aspdin of England patented the basic process in 1824, naming it for the resemblance of the cement when set to portland stone, a limestone from the Isle of Portland.
What Is Consistency of Cement?
The standard consistency of cement varies between 25-and 35%. To prepare a mix of cement paste, 25-35% water by weight of cement is added to achieve good consistency of cement.
What Consistency Should Concrete Be?
peanut butter-like consistency
The concrete should have a peanut butter-like consistency. It should not be soupy. If so, add a small amount of dry concrete to stiffen the mix.
What Consistency Should Cement Be?
Work the mix with a hoe, gradually adding water until the mix reaches a uniform, workable consistency. Properly mixed concrete should look like thick oatmeal and should hold its shape when it is squeezed in a gloved hand.
What Is the Initial Setting Time of Cement?
30 minutes
The initial setting time of cement is the time when the paste (cement + water) starts losing its plasticity. This means that if the initial setting time of cement is 30 minutes, the cement mortar or concrete must be placed in position within 30 minutes of adding water. If delayed, mortar or concrete will lose strength.
What Is the Final Setting Time of Cement?
Final setting time of Cement
The time at which cement completely loses its plasticity and becomes hard is the final setting time of cement. The time taken by cement to gain its entire strength is the Final setting time of cement. For Ordinary Portland Cement, The Final Setting Time is 600 minutes (10hrs).
Why Gypsum Is Added to Cement?
Gypsum is called the retarding agent of cement, which is mainly used for regulating the setting time of cement and is an indispensable component. Without gypsum, cement clinker can condense immediately by mixing with water and releasing heat.
What Is the Setting Time of Cement?
The time at which cement completely loses its plasticity and becomes hard is the final setting time of cement. The time taken by cement to gain its entire strength is the Final setting time of cement. For Ordinary Portland Cement, The Final Setting Time is 600 minutes (10hrs).
What Is the Meaning of Soundness of Cement?
The soundness of cement refers to the stability of the volume change in the process of setting and hardening. Suppose the volume change is unstable after setting and hardening. In that case, the concrete structures will crack, which can affect the quality of buildings or even cause serious accidents, known as poor dimensional stability.
Who Invented Cement?
Joseph Aspdin
Cement as we know it was first developed by Joseph Aspdin, an enterprising 19th-century British stonemason, who heated a mix of ground limestone and clay in his kitchen stove, then pulverized the concoction into a fine powder. The result was the world’s first hydraulic cement: one that hardens when water is added.
Who Invented Portland Cement?
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19th century by Joseph Aspdin and is usually made from limestone.
What Are the Properties of Cement?
Properties of Good Cement
- Provides strength to masonry.
- Stiffens or hardens early.
- Possesses good plasticity.
- An excellent building material.
- Easily workable.
- Good moisture-resistant.
What Is All Purpose Cement Used for?
All-Purpose Solvent Cement is a medium-bodied, multi-purpose product that creates a strong bond between ABS, PVC, and CPVC pipe and fittings.
What Colour Is Cement?
Cement essentially consists of four mineral phases: two calcium silicates, a calcium aluminate, and a mixed crystal known as calcium aluminate ferrite (C4AF). While the first three appear as pure white minerals, pureC4AF has a brown color because of its iron content. So theoretically, pure cement would be brown.
What Is the Role of Cement in Concrete?
Cement plays a major role within a concrete mixture and affects the most important aspects of the mix, such as: workability, compressive strength, drying shrinkage, and durability. Through the process of hydration, cement particles react with water, binding the aggregate, and the strength matrix develops (Weiss, 1999).
What Type of Material Is Cement?
Cement is manufactured through a closely controlled chemical combination of calcium, silicon, aluminum, iron and other ingredients. Common materials used to manufacture cement include limestone, shells, and chalk or marl combined with shale, clay, slate, blast furnace slag, silica sand, and iron ore.
What Are the Different Types of Cement?
Different Types Of Cement
- Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC)
- Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC)
- Rapid Hardening Cement
- Extra Rapid Hardening Cement.
- Low Heat Cement.
- Sulfates Resisting Cement.
- Quick Setting Cement.
- Blast Furnace Slag Cement.
What Is the Soundness of Cement?
The soundness of cement refers to the stability of the volume change in the process of setting and hardening. Suppose the volume change is unstable after setting and hardening. In that case, the concrete structures will crack, which can affect the quality of buildings or even cause serious accidents, known as poor dimensional stability.
Soundness Test of Cement
The soundness of cement may be determined by two methods, namely the Le-Chatelier method and the autoclave method. In the soundness test, a specimen of hardened cement paste is boiled for a fixed time so that any tendency to expand is speeded up and can be detected. Soundness means the ability to resist volume expansion.
Which Type of Cement Is Best?
Grade 33 and Grade 43 OPC cement are the old grades of cement used for residential construction, and nowadays, it is replaced by OPC 53 grade of cement. OPC 53 grade cement is the best cement for concrete.
Which Type of Cement Is Best for House Construction?
The cement types that are good for construction are Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) and Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC). OPC has three types: 33 Grade for non-RCC, 43 Grade for plastering, and 53 Grade for fast-paced projects. PPC makes the structure denser, making it perfect for mass concreting works.
What Is Water Cement Ratio?
The water-cement ratio is the ratio of the weight of water to the weight of cement used in a concrete mix. A lower ratio leads to higher strength and durability but may make the mix difficult to work with and form. Workability can be resolved with the use of plasticizers or super-plasticizers.
Which Is the First Cement Factory in India?
to start manufacturing Cement in Porbandar in Gujarat. However, even before that, a small cement factory was established in Madras in 1904 by a company named South India Industrial Ltd.
What Cement to Use for Fence Posts?
Fast-setting concrete is ideal for installing fence posts since it doesn’t need to be mixed in a bucket or a wheelbarrow. Once you’ve finished digging your post holes, add about three to four inches of gravel into the bottom and compact it using a post or a 2×4.
What Is the Difference Between Concrete and Cement?
What is the difference between cement and concrete? Although the terms cement and concrete often are used interchangeably, cement is actually an ingredient of concrete. Concrete is a mixture of aggregates and paste. The aggregates are sand and gravel or crushed stone; the paste is water and portland cement.
What Is the Difference Between Mortar and Concrete?
Basically, concrete is stronger and more durable, so it can be used for structural projects such as setting posts, whereas mortar is used as a bonding agent for bricks, stones, etc. Concrete is a mixture of water, cement, and sand, just like mortar.
What Is the Difference Between Portland Cement and Regular Cement?
White portland cement is made from the same raw materials as regular portland cement but contains little or no iron or manganese, the substances that give conventional cement its gray color. Some portland cement meets requirements for multiple cement types.
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Difference Between Short Column and Long Column
- What Is Estimate? | Types of Estimate | Advantage of Estimate | Disadvantage of Estimate
- What Is Tie Beam? | Tie Beam Details | Ties in Column | Tie Beam Design | Concrete Tie Beam | Tie Beam Reinforcement Details
- What Is Development Length | Why We Provide Development Length | How to Calculate Development Length | Development Length for Single Bars
- What Is Epoxy? | What Is Epoxy Flooring? | Types of Epoxy Flooring | Advantages of Epoxy Flooring | Disadvantages of Epoxy Flooring | Uses of Epoxy Flooring | Application Process of Epoxy Flooring
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2022-09-07 11:06:30.
