What Is Damp Proof Course | Types of Damp Proofing Course | Application of Damp Proofing Course | Advantages & Disadvantages of Damp Proofing Course
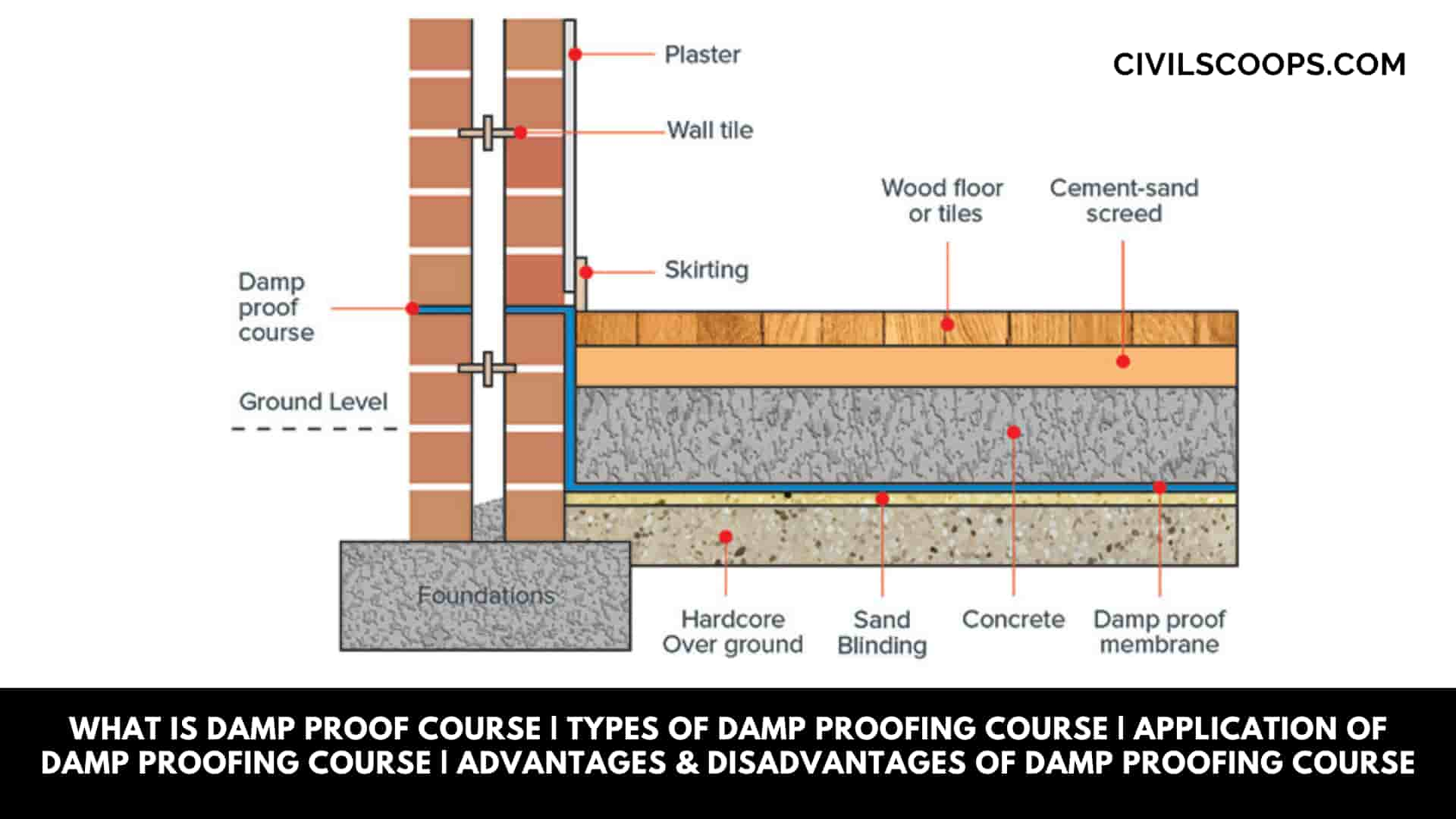
Table of Contents
What Is Damp Proof Course?
The damp proof course is an important layer for all walls of the building that is provided near the ground in the wall to prevent dampness of the walls.
In the properties of which there has no provided damp protection layer, that may be affected by excess moisture rising from the ground. This excess moisture can affect decoration, plaster, and even wet rot or effecting unprotected timbers.
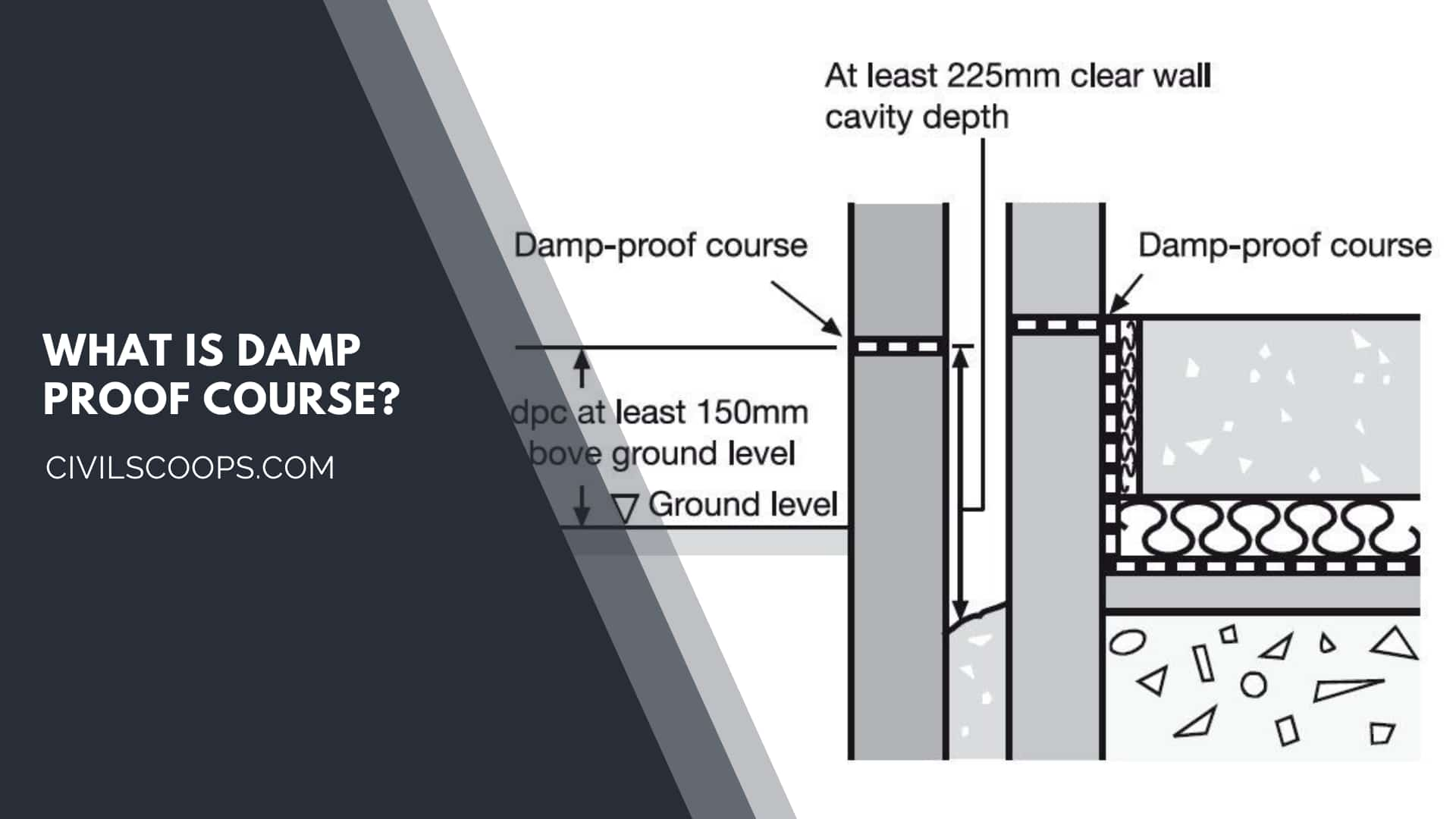
A damp proof course minimum of 150 mm should be provided above the walls in most properties. As a mortar course with plastic DPC sheet or bitumen may appear by poking through.
To prevent rising damp from occurring in all new properties the damp proof course is required. To avoid the dampness in the properties at first we have to inspect the properties by a specialist damp surveyor.
DPC Full Form
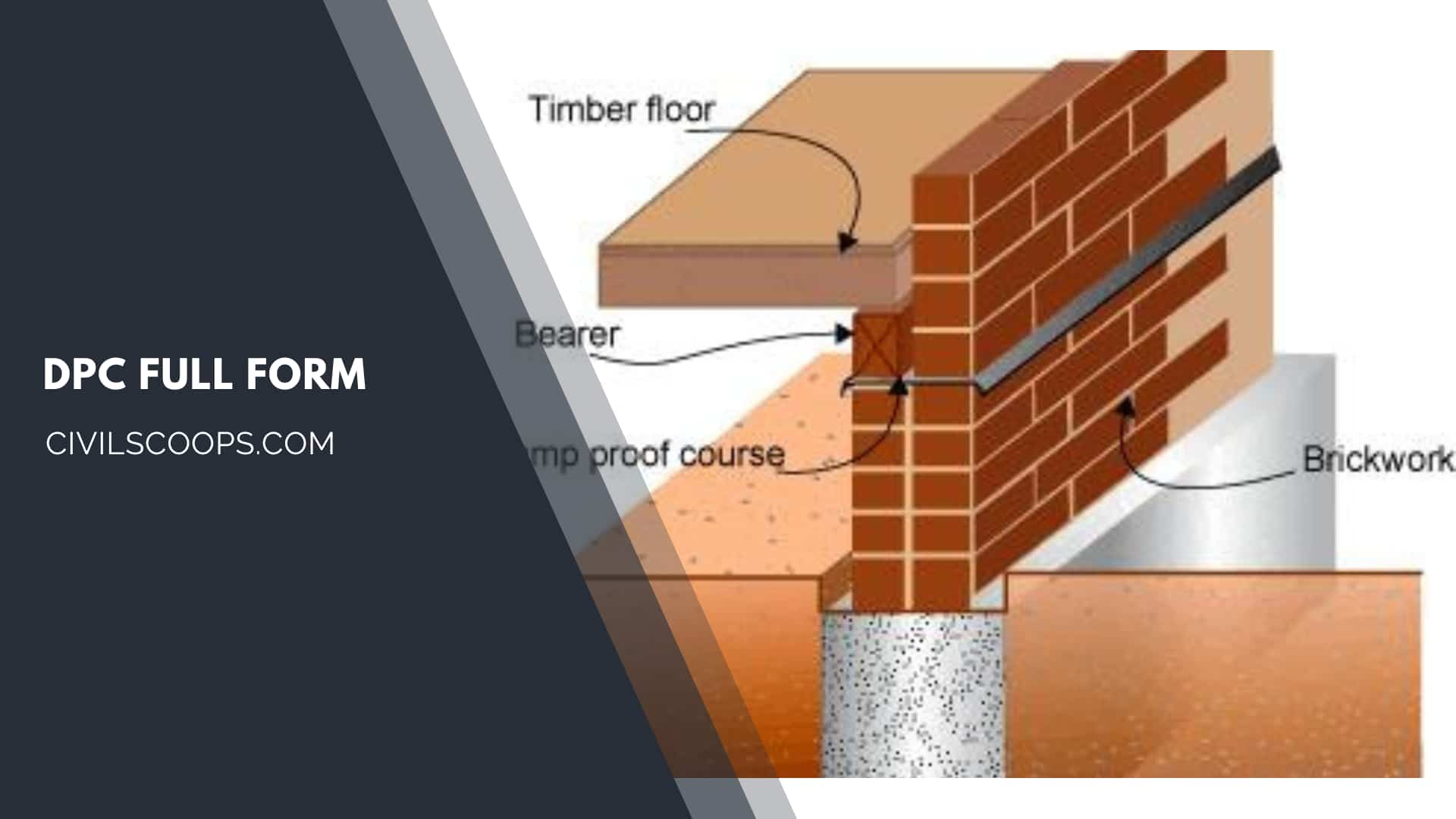
The full form of DPC, in civil engineering, is Damp Proof Course. It normally provides near the ground in the wall to prevent dampness in the.
Also Read: Requirements of Good DPC | Prevention of Dampness | Methods of Damp proofing
DPC History

In London in the year 1975, the DPC or damp proof course became mandatory. A solid layer of DPC is built and provided in the walls of the constructions and placed above the ground level so through the capillary action the moisture rising over the wall should be prevented.
The dampness problem makes your interior or exterior walls fade and it is looking so unnatural. The material used in 1975 as DPC is –jute, bitumen, hessian, and slate. Above them, the slate layer is the most useable material at that time.
Types of Damp Proofing Course
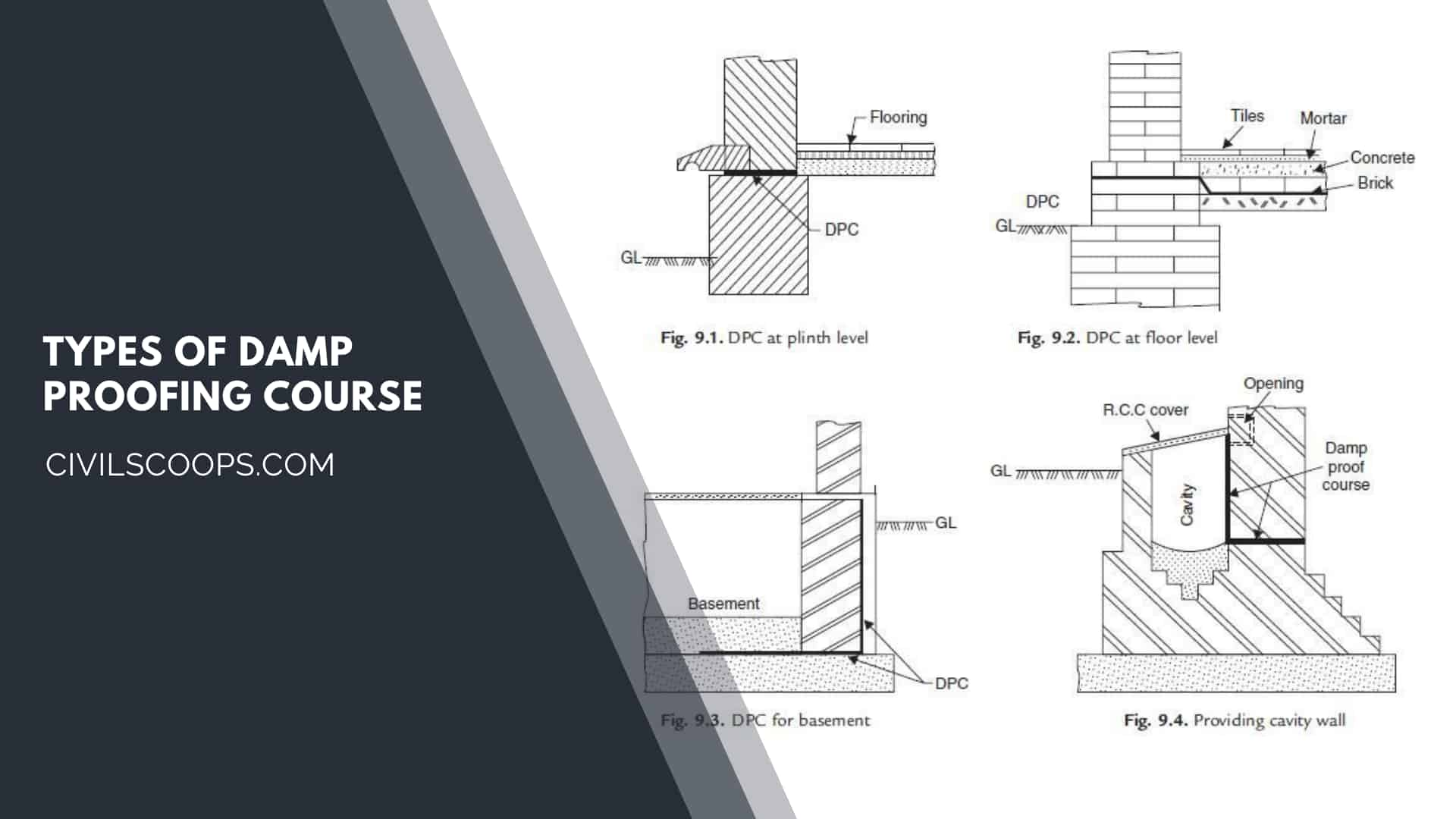
Many types of damp proof course’s are below
1. Hot Bitumen

The hot bitumen type of damp proofing course is a flexible material that is placed on the mortar or the concrete bed. The hot bitumen course at least with a minimum thickness of 3mm should be applied.
2. Bituminous Felts

The bituminous felt also flexible material. It is easy to available in the rolls of normal wall width and easily lay. On a cement mortar, it can easily be laid.
At the all corner full overlap is provided and at the joints of the overlap 100 mm is provided. If necessary the laps are sealed with bituminous. The bituminous felts materials are available in rolls, so especially in cold weather, they should be unrolled carefully.
3. Metal Sheets

The metal sheets are also flexible material. The damp proof course provides copper and aluminum. The weight of the metal should not be less than 200 N/m2 and the thickness depend on this.
4. Mastic Asphalt

The mastic asphalt is a semi-rigid material and creates a good impervious layer as a damp proofing course. Mastic asphalt is a most durable and impervious material.
5. Stone

Slates, granites the two-course of a dense and sound stone laid in cement mortar with vertical breaking joint is work a great damp proof course. As in the case of roof surface sometimes the stone can be fixed.
6. Mortar

The mortar is used as a level course on the bed level and it is a ratio of the mixture of 1 part of cement and 3 part of sand. To increase the workability of the mortar some quantity lime is to be added. The waterproofing mortar should be prepared for the plastering works.
7. Cement Concrete

As a damp proof course, a cement concrete paste is provided in a ratio of 1:2:4 at the plinth area at the structure. The thickness of the cement concrete layer is varied between 40 to 150 mm. The cement concrete damp proof layer is a very effective material.
Damp Proof Course Material

There are four types of materials that are commonly used in
- Flexible material.
- Semi-rigid material.
- Rigid material.
- Grout materials.
1. Flexible Material
Flexible materials are those materials that never deformed their shape and when a certain amount of load is applied they tend to crack, which is known as a flexible material.
2. Semi-Rigid Material
The combination materials or mastic asphalts are used as semi-rigid material.
3. Rigid Material
The rigid materials are stone, first-class bricks, cement concrete, slates, etc.
4. Grout Materials
The grout materials are consists polymers, cement slurry or acrylic-based chemical.
Application of Damp Proofing Course
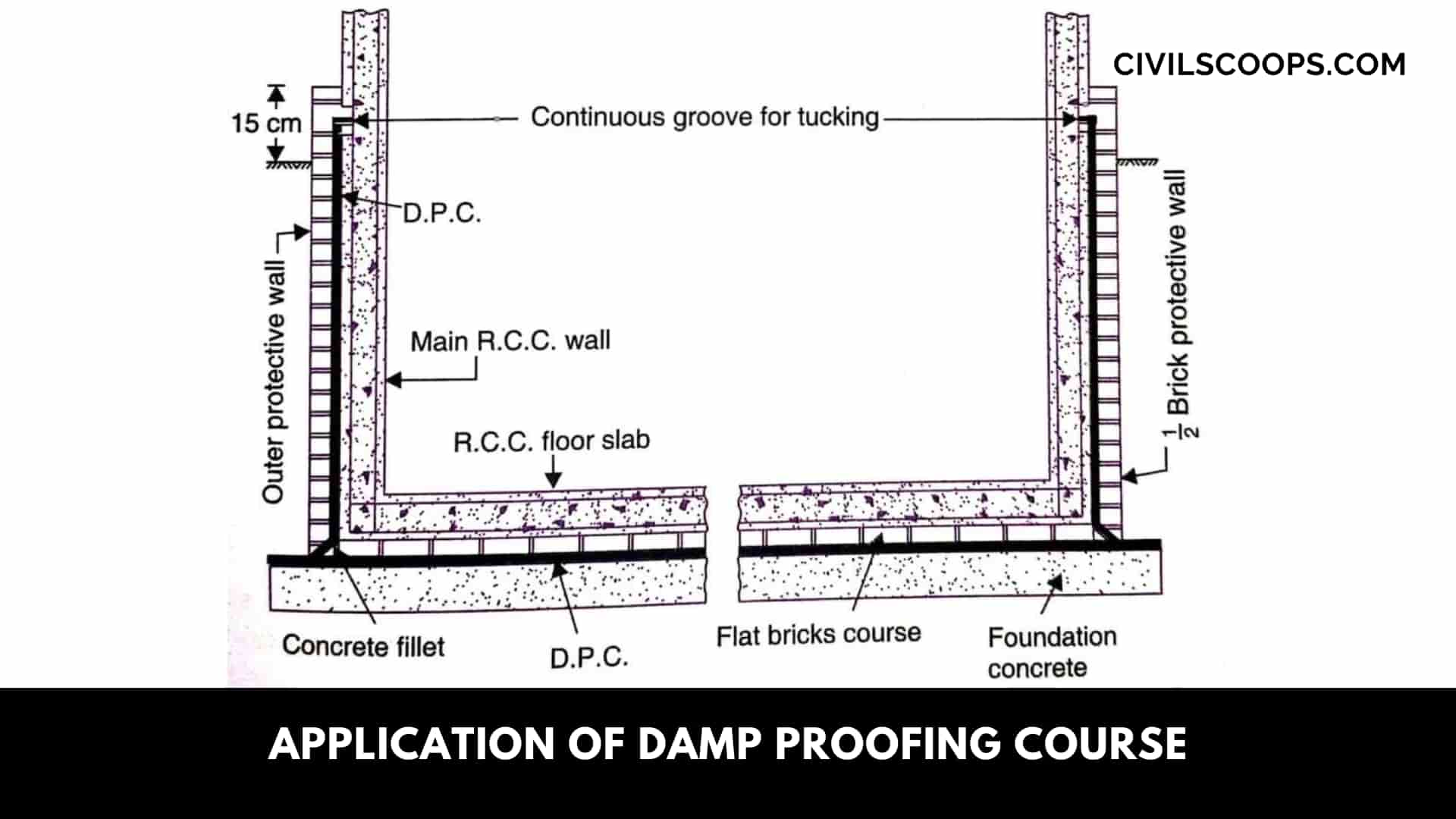
- The application of damp proof course is by this we can prevent all health issues that can see in the future on the structure.
- It is applied to prevent the exterior wall moisture and protect from dampness.
- The application of damp proof course is it helps to prevent dank and musty smell around the property that coming from the untreated mold.
- The damp proof course is applied as an important layer for all walls of the building that is provided near the ground in the wall to prevent dampness of the walls.
- To increase the paint life on the walls to remove the dampness by damp proof course. It is the most important application of damp proof course.
- By the damp proofing course, we know the value and condition of the property.
- To prevent the structural problems by the wet rot and dry rot the damp proof course is applied.
- The concrete damp proof course generally applies to the water storage structure such as a damp, reservoir, etc.
Properties of Material for DPC
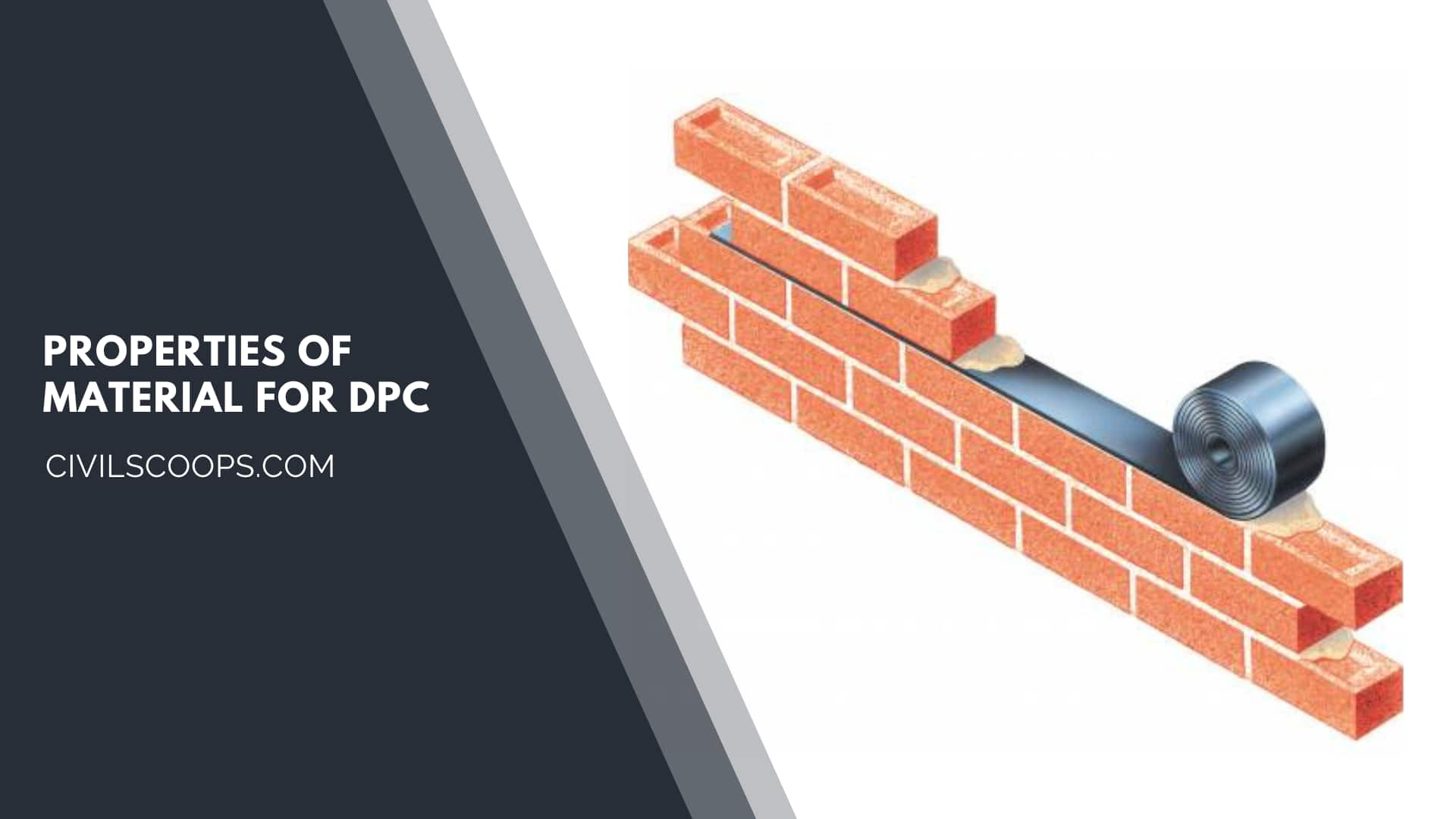
The properties of materials for DPC is
- The most important property of DPC material is it should be impervious.
- The second property of these materials is they should be enough durable and strong, or capable to withstand both live load as well as dead load without damage.
- The properties of DPC material are its always be dimensionally stable.
- To make the structure economical the material used for DPC should be cheap.
- Another important property of the materials should be free from deliquescent salts like nitrates and sulfates chlorides.
- The material should be able to carry out leakproof joining work.
Advantages of Damp Proofing Course

There have many advantages of damp proof course that’s are below
- The first important advantage of a damp proof course is by this we can prevent all health issues that can see in the future on the structure.
- The advantage of a damp proof course is it helps to prevent dank and musty smell around the property that coming from the untreated mold.
- To increase the paint life on the walls to remove the dampness by damp proof course.
- The concrete damp proof course is generally used at the water storage structure such as a damp, reservoir, etc. which is another advantage of a damp proof course.
- By the damp proofing course, we know the value and condition of the property.
- To prevent the structural problems by the wet rot and dry rot.
Disadvantages of Damp Proofing Course

- The disadvantage of the damp proof course, in the damp proof course sometimes develops all cracks.
- Another disadvantage of the damp proof course is it has level problems.
- Up to the roof sometimes the damp proof course creates patches this is the disadvantage of the damp proof course.
- The most common disadvantage of damp proof course is it increases the self-weight of the whole structure.
Uses of Damp Proofing Course

There have been many uses of damp proof course that are below
- The important uses of a damp proof course are by this we can prevent all health issues that can see in the future on the structure.
- The uses of damp proof course are it helps to prevent dank and musty smell around the property that comes from the untreated mold.
- The damp proof course is an important layer for all walls of the building that is provided near the ground in the wall to prevent dampness of the walls.
- The concrete damp proof course is generally used at the water storage structure clasp, reservoir, etc.
- To increase the paint life on the walls to remove the dampness by damp proof course. It is the most important use of damp proof course.
- By the damp proofing course, we know the value and condition of the property.
- It is used to prevent the exterior wall moisture and protect from dampness.
- To prevent the structural problems by the wet rot and dry rot the damp proof course is used.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Dpc Full Form
Damp proofing is accomplished several ways including all : A damp-proof course (DPC) is a barrier through the structure designed to prevent moisture rising by capillary action such as through a phenomenon known as rising damp. Rising damp is the effect of water rising from the ground into property.
Difference Between Dpc and Dpm
Firstly it’s important to make the distinction between and DPC and DPM: DPC stands for damp proof course whilst DPM stands for damp proof membrane. A DPC is a material placed between courses of brickwork to stop the rise of water up the walls.
What Is Dpc in Construction?
A damp proof course (DPC) is a form of damp proofing installed in a property to prevent rising damp and associated problems. There are various methods to install a DPC so our guide will help you to understand the different types of damp proof course available,why a DPC might fail, and how to fix a broken DPC.
Types of Dpc
Different Types of Damp Proof Courses
- Damp Proof Course (DPC) Injection. Installing this damp-proof course involves injecting a liquid or cream into the wall.
- Electro Osmotic Damp Proofing Course.
- Damp proof membrane.
- Pressure grouting.
- Cavity wall damp proof course.
- Chemical damp proof course.
What Is Dpc Level in Building?
The damp proof course (DPC) is generally applied at basement levels, which restricts the movement of moisture through walls and floors. 2. What is the abbreviation of DPC in Construction? The abbreviation of DPC is the Damp Proof Course.
What Is Dpc Material?
A DPC is a durable, impermeable material such as slate, felt paper, metal, plastic or special engineered bricks bedded into the mortar between two courses of bricks or blocks. It can often be seen as a thin line in the mortar near ground level.
What Is the Purpose of Dpc?
A damp-proof course protect rising building walls from moisture which may rise in a capillary way from the ground through the foundations or the floor slab. The barrier is laid horizontally and is an indispensable component of the building structure.
How to Use Dpc?
Damp Proof Course Injection – This system involves a cream or liquid being injected into the wall in order to act as a water repelling layer to stop the damp from the ground rising above the damp proof course. This is commonly known as a chemical damp proof course injection.
Dpc Specification
Damp Proof Course or DPC is the protective layer applied to prevent the rising of moisture to the walls from the ground due to capillary action. It is usually 2.5 cm thick with a ratio of rich cement concrete 1:1.5:3 or 2 cm thick with cement mortar 1:2 mixed with standard waterproofing material.
Dpc Installation
Lay the DPC on a full even bed of fresh mortar in one continuous length, for the full width of the leaf. Provide at least a 100mm overlap at any joint or corners. The DPC must not obstruct the cavity. Ensure the external edge of the DPC is visible and not bridged by mortar when completing pointing of the mortar joint.
Thickness of Dpc
The DPC should be of 40mm thickness and should be of uniform thickness. It should not be provided at the locations of the door openings. The top level of DPC should match with the planned finished floor level.
What Is Dpc in Building?
A damp proof course (DPC) is a form of damp proofing installed in a property to prevent rising damp and associated problems. There are various methods to install a DPC so our guide will help you to understand the different types of damp proof course available,why a DPC might fail, and how to fix a broken DPC.
What Does Dpc Stand for in Construction?
A damp proof course is one of the most important elements of a property. The DPC protects the property against moisture rising from the ground.
Building Regulations Dpc Level
The Building Regulations require at least 150mm between the dpc and the ground or any paving. This is what is known as ‘Best Practice’. However, there are situations where it is just not possible, or practical, to maintain this regulation.
Dpc Ratio
DPC is made up of cement concrete of mix 1:2:4 (1-cement: 2-coarse sand: 4-12.5mm stone aggregate) mixed with a good quality waterproofing compound.
Is Dpc Necessary?
A damp proof course is essential to install, particularly at the basement level or at the building’s foundation upon construction. It prevents rising of moisture through the floors and walls. Excessive moisture can lead to severe damage to your property.
Disadvantages of Dpc
A major disadvantage of DPC is that it can only protect walls – not floors or other parts of the building – and only against rising damp. You will still need DPM to prevent damage from condensation and water ingress. DPC is also available in an injectable/chemical form.
Dpc Level
The DPC in the inner wall is usually below floor level, (under a suspended timber floor structure), or, with a solid concrete floor, it is usually found immediately above the floor slab so that it can be linked to the DPM under the floor slab.
Dpc Below Ground Level
Damp proof courses (DPCs)
The outside ground level should be at least 150mm below the damp proof course and ideally avoid hard surfaces next to the stone as water will splashback in heavy rain causing damage to the stone. This may be unavoidable in tenements built tight to the pavement.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Difference Between Footing and Foundation | What is Footing and Foundation
- What Is GIS In Surveying | Definitions of GIS | Parts & Work Flow of GIS | Advantages of GIS
- How Are Bridges Built | How Are Bridges Constructed | Factors Associated with Building Bridges
- Waterproof a Concrete Roof | Old Concrete Roof Waterproofing | Concrete Roof Sealant Flat Concrete Roof Waterproofing
- Plinth Area Meaning | Plinth Area Definition | What Is Plinth Area | Plinth Area Rate | Plinth Area Estimate | How to Calculate Plinth Area of a Flat
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-06-10 08:48:23.
