Difference Between Whole Circle Bearing and Quadrantal Bearing | What Is WCB | What Is QB
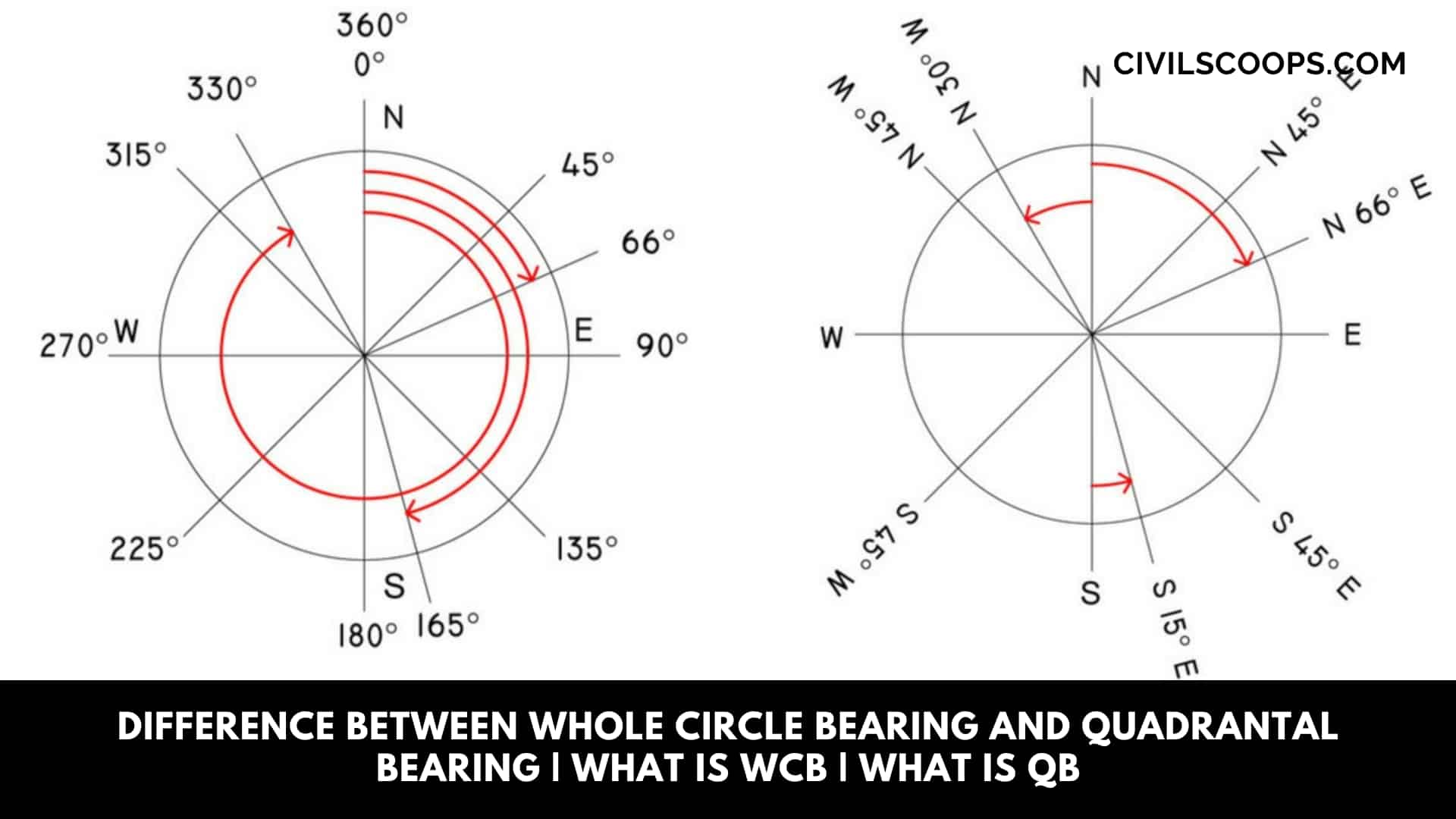
Table of Contents
Introduction of WCB Vs. QB
Whole circle bearing(WCB) and Quadrantal bearing(QB) are the two types of bearing which is used in the field of surveying for the purpose of measurement of the bearings.
In this article, you will get to know about the whole circle bearing and Quadrantal bearing and their differences.
What Is Whole Circle Bearing (WCB)
Whole Circle Bearing
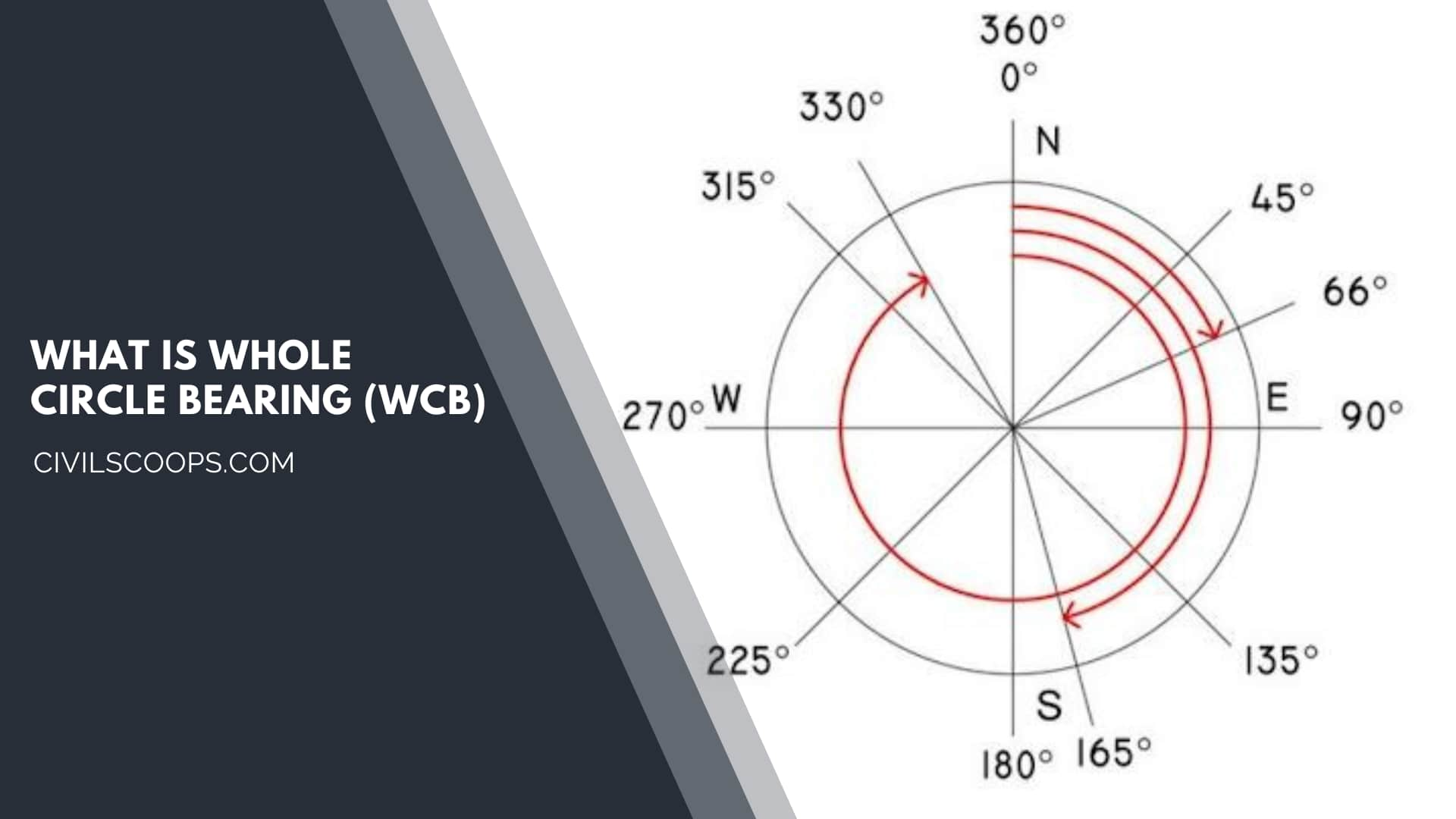
- The whole circle bearing (WCB) is defined as the bearing of the line at any point which is measured with respect to the Meridian is known as Whole circle bearing.
- The Whole Circle bearings values range from 0° to 360°.
- The Whole circle bearing is generally used in the Prismatic compass.
- The whole circle bearing is used to measure the angle in the clockwise direction from the magnetic North.
- The Prismatic compass is graduated by Whole circle bearing.
Example of Whole Circle Bearing (WCB)
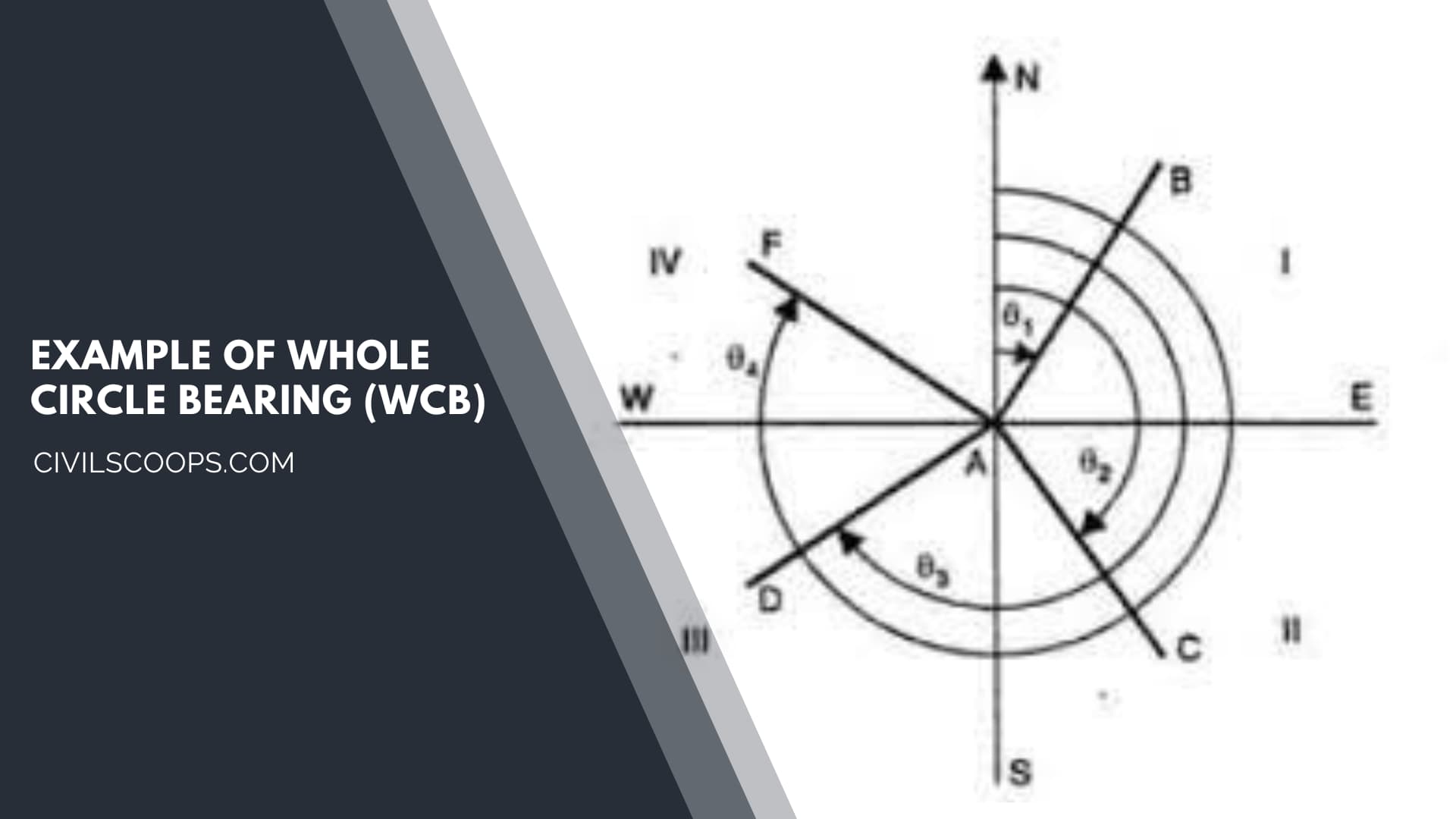
- If the survey line falls between the first quadrant then the Whole Circle Bearing lies between the 0° to 90°.
- If it lies between the second quadrant then the Whole Circle Bearing of that survey line lies between 90° to 180°. If it lies in the third quadrant then the Whole circle bearing will be between the 180° to 270°.
- And in the fourth quadrant, the Whole Circle Bearing values range between 270° to 360°.
- The Whole circle bearing of any line, can exceed up to 90°, it can be reduced to the corresponding angle which is less than 90°, and has the same numerical value to the trigonometrical functions.
- This type of angle is also known as a Reduced bearing.
- The examples of whole circle bearing are as follows.
- 30°,45°,80°,120°,230°, and 320°, etc
What Is Quadrantal Bearing (QB)
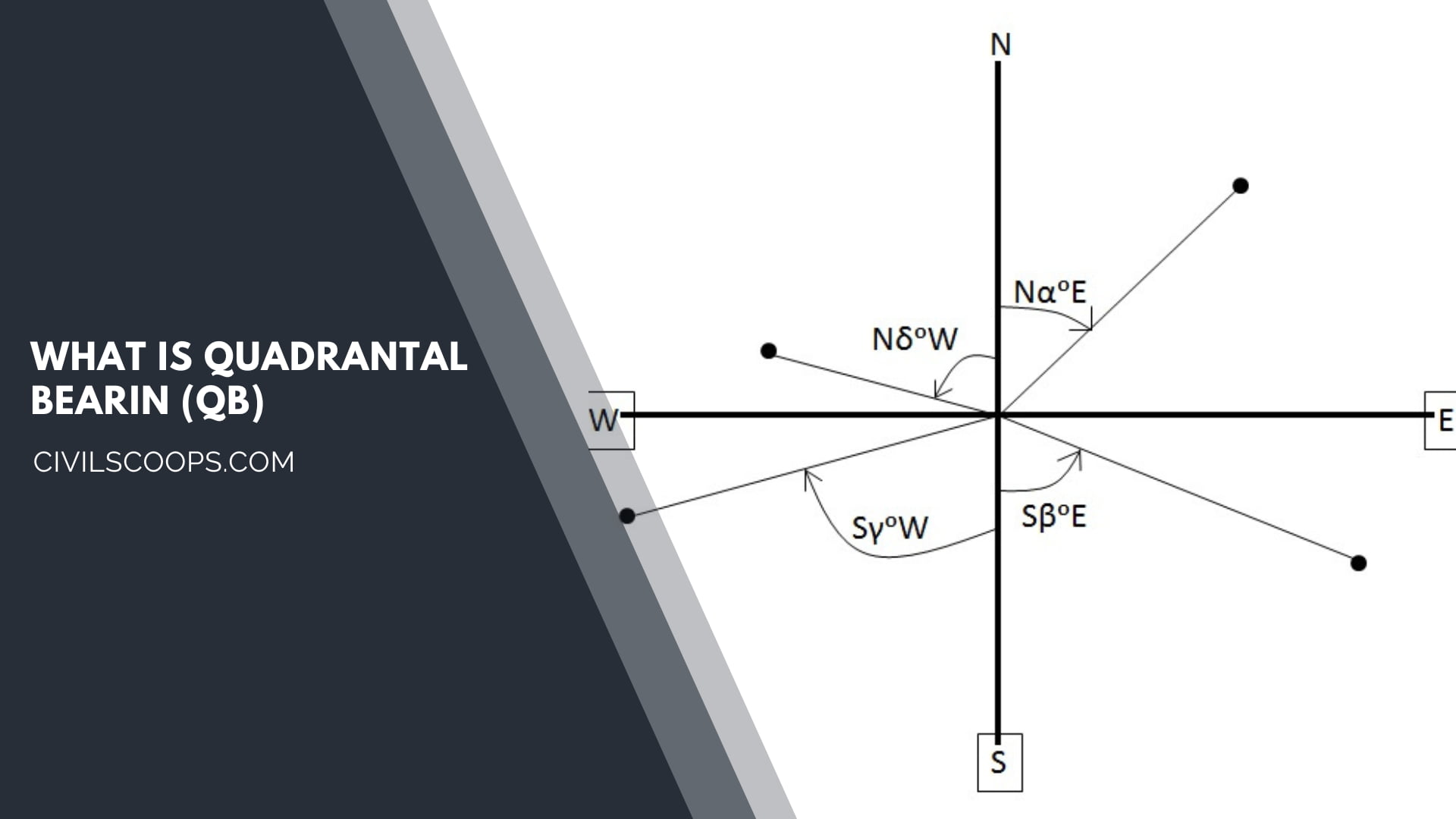
The Quadrantal bearing is also known as a Reduced bearing. Quadrantal bearings are generally measured from the North or South direction towards the East or West direction.
The quadrantal bearing or reduced bearing can be measured either in a clockwise or anticlockwise direction.
The quadrantal bearing varies from 0° to 90°.
In the quadrantal bearing or reduced bearing system, the bearings are taken either from the magnetic North or the magnetic south direction. It will depend on which one is nearer to that line.
In the Quadrantal bearing system, magnetic North and magnetic South lines are considered as a reference line.
Also Read: Carbon Steel vs. Stainless Steel | What Is Carbon Steel | What Is Stainless Steel
Example of Quadrantal Bearing
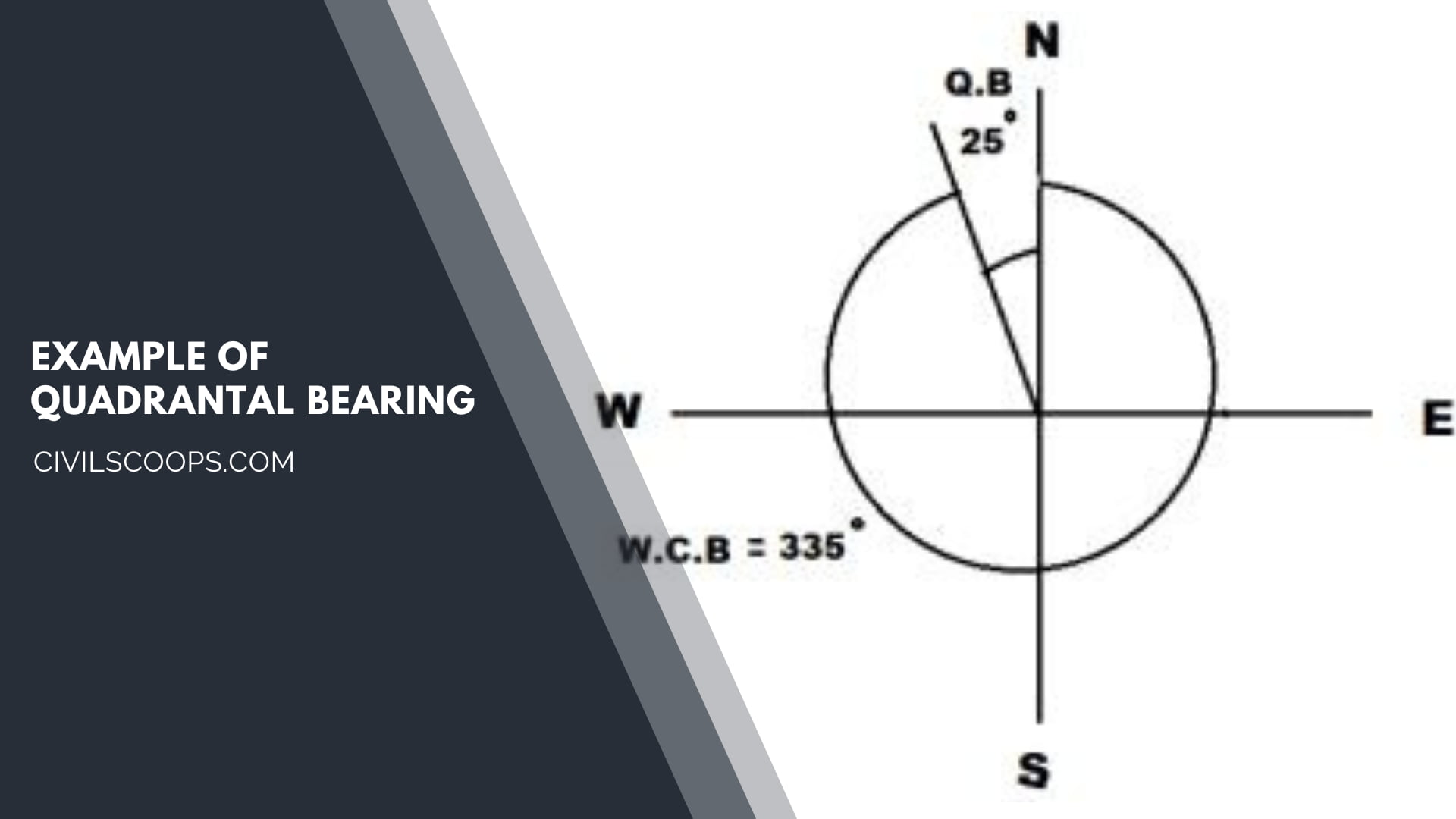
In the quadrantal bearing system, you can take both clockwise as well as the anticlockwise angle from the reference line.
It is necessary to state the particular quadrant in which that line lies. The letters N(north), S(south), E(east), and W( west) are used to represent the quadrant.
Reduced bearing is observed by the surveyor’s compass.
The quadrants are represented are as follows.
- 1st quadrant = N – E
- 2nd quadrant = S – E
- 3rd quadrant = S – W
- 4th quadrant = N – W
The example of the quadrantal bearing are as follows
- N35°E,S49°E,N65°W,S25°W etc.
Difference Between Whole Circle Bearing and Quadrantal Bearing
The whole circle bearing and quadrantal bearing or reduced bearing are the two bearings which are usually used in the compass surveying.
In order to choose between the whole circle bearing and quadrantal bearing, you must know the difference between them.
he difference between the whole circle bearing and quadrantal bearing are as follows.
[su_table responsive=”yes” alternate=”no”]
| Sr.No. | Whole Circle Bearing | Quadrantal Bearing |
| 1 | The horizontal angle which is made by the survey line, with the magnetic north in a clockwise direction is known as the Whole circle bearing. |
The horizontal angle which is made by a survey line with the magnetic North or South whichever is near the line in the eastward or westward direction is known as quadrantal wearing or reduced bearing.
|
| 2 | In the whole circle bearing, the magnetic North line is considered as the reference line. |
In the quadrantal Bearing, both magnetic North as well as South lines are considered as a reference line.
|
| 3 | In the whole circle bearing only clockwise angle is taken from the reference survey line |
In the quadrantal bearing both clockwise, as well as the anticlockwise angle from the reference line, is taken
|
| 4 | The value of the whole circle bearing ranges from 0° to 360° |
The value of the quadrantal wearing for reduced bearing ranges from 0° to 90°
|
| 5 | The example of a whole circle bearing are 30°,45°,80°,120°,230°, and 320°, etc |
Example of quadrantal bearing or reduced bearing are N35°E, S49°E, N65°W, S25°W, etc.
|
[/su_table]
Observation of the Bearings
- Consider the bearing of the line is AB to be observed
- Set up the instrument and at station A and then carry out the temporary adjustments.
- Fix one of the ranging rods at the station B.
- Turn the compass box until the ranging rod present at station B is not bisected by the horsehair when seen through the vertical slit above the prism.
- When the needle comes to rest, bisect it by the ranging rod at station B accurately and write down the reading.
- Hence you will get bearing of the line AB.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Whole Circle Bearing
The horizontal angle made by a line with the magnetic north in the clockwise direction is the whole circle bearing of the line. This system is also known as the azimuthal system.
Quadrantal Bearing
A horizontal angle or bearing less than 90 degrees , measured to north, south, east, or west from a survey line.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- What Is Plaster | Methods of Plastering
- All About Drywall Water Damage Repair
- What Are the Differences Between Shear Slump and Collapse Slump in Slump Test?
- What Is Glass | Types of Glass Used in Construction | Qualities of Glass | Advantages & Disadvantages of Glass
- All About Asphalt Flooring | What is Asphalt Flooring | Asphalt Flooring Used | Asphalt Flooring Advantages and Disadvantages
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-04-10 11:10:24.
