Difference Between Footing and Foundation | What is Footing and Foundation
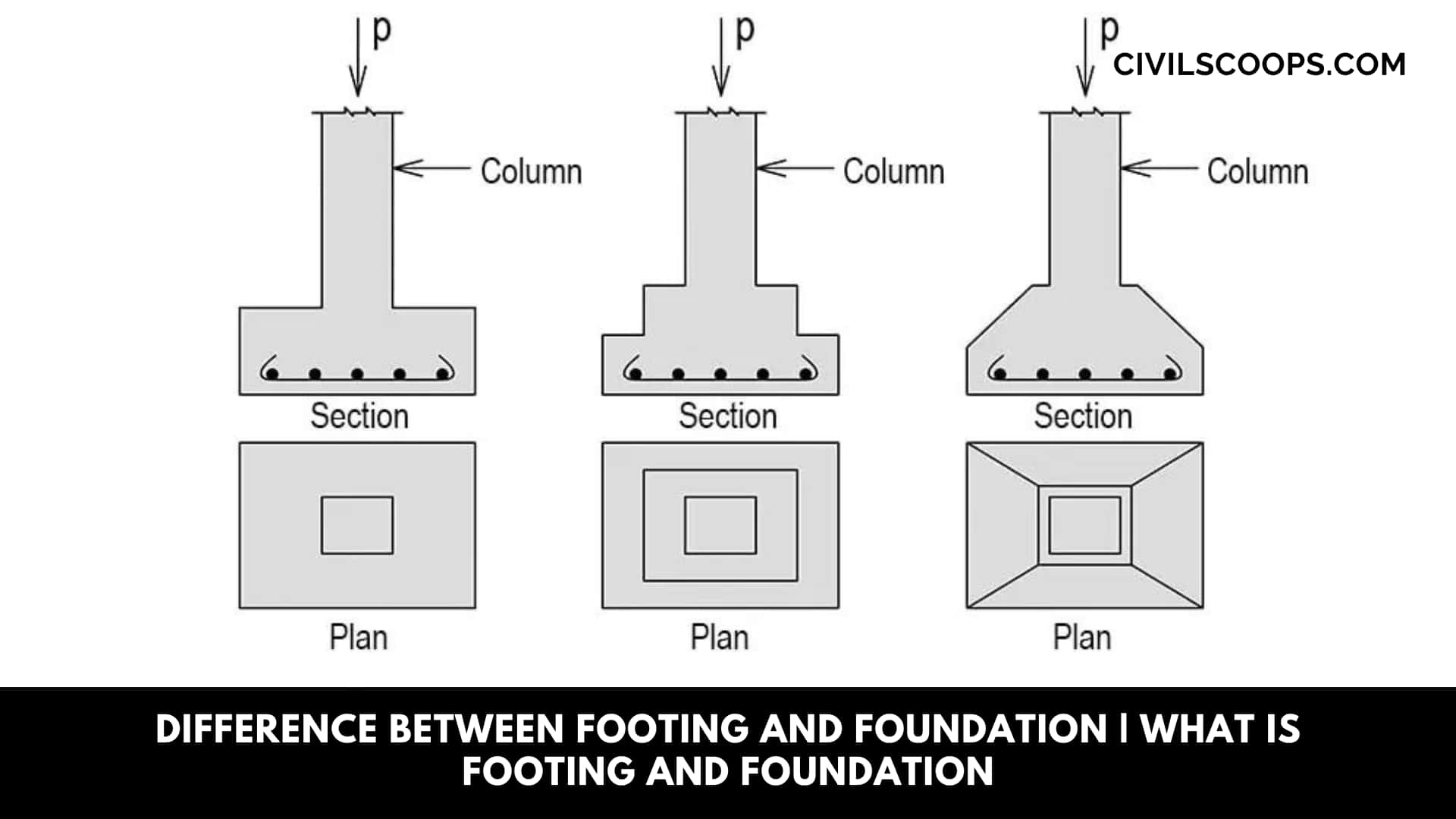
Table of Contents
What is Footing?
Foundation Definition: The footing is generally supporting columns and may be round, square, or rectangular at a plan and in section.
They may be of the slab — stepped or sloping type. Thia stepped footing results at a better distribution of load than a slab footing.
A sloped footing isn’t less economical, although constructional problems are associated with this sloping surface.
The isolated spread footing at plain concrete has the advantage that the column had is transferred to the soil through dispersion at the footing.
Foundation detail: In reinforced concrete footings. i.e., pads. This slab is treated as an inverted cantilever bearing this soil pressure and supported by the column.
Where a two-way footing is provided, it can be reinforced at two directions of bending with bars of steel placed in this bottom of the pad parallel to its sides.
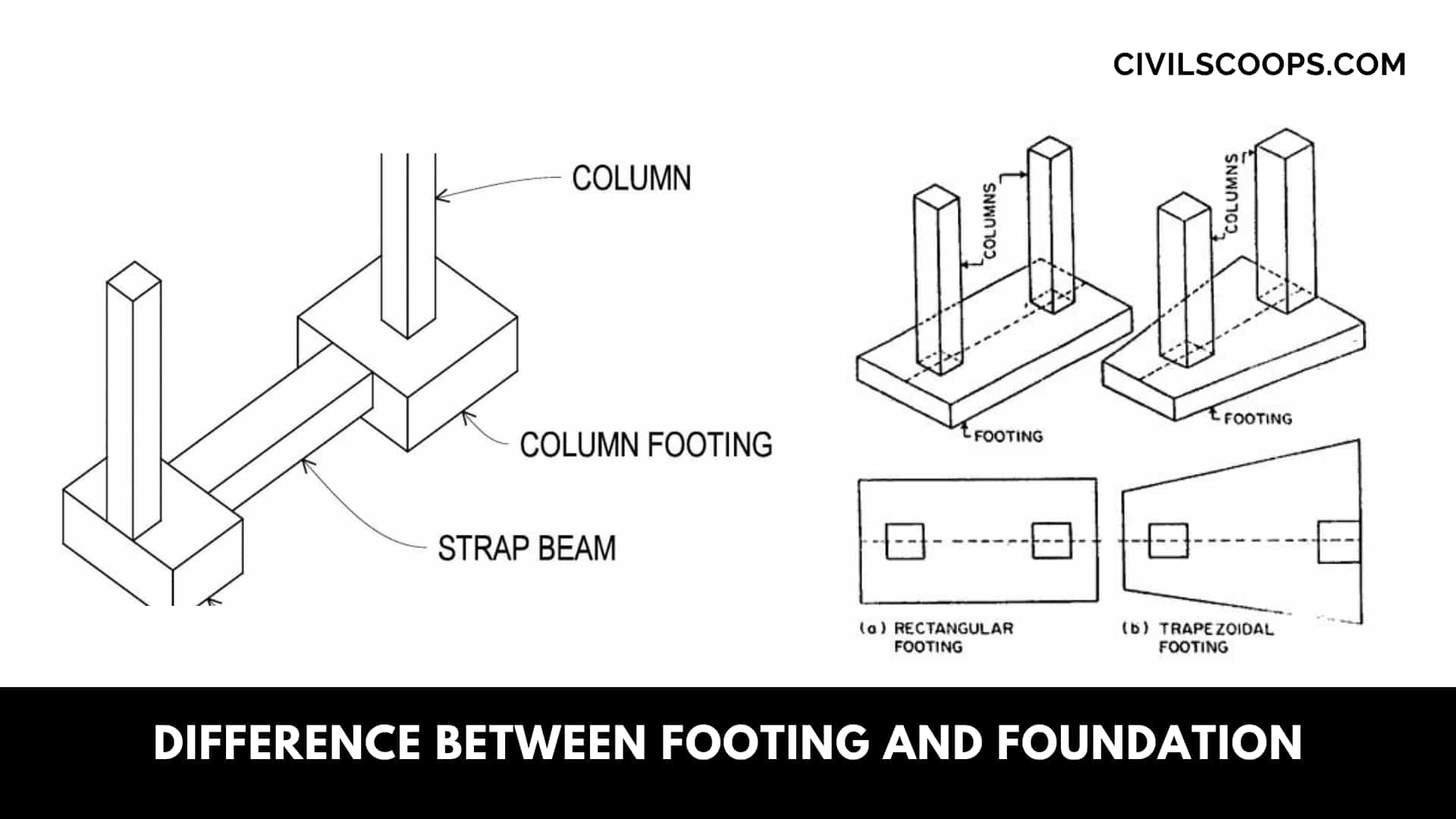
If clearances permit, two-way square footings used to reduce the bending moments. Where not less than one column is placed on pads (combined footing).
Their shapes can be rectangular or trapezoidal; the latter produces a more economical design where large differences of the magnitude of the column loads exist or where rectangular footings cannot be accommodated.
This gives pad-type/ combined footings and their behavior under external loads and bearing pressures: typical reinforcement detailing for two different combined footings in sectional elevations and plan.
The specifications and quantities can change depending on the column loads and the spread area.
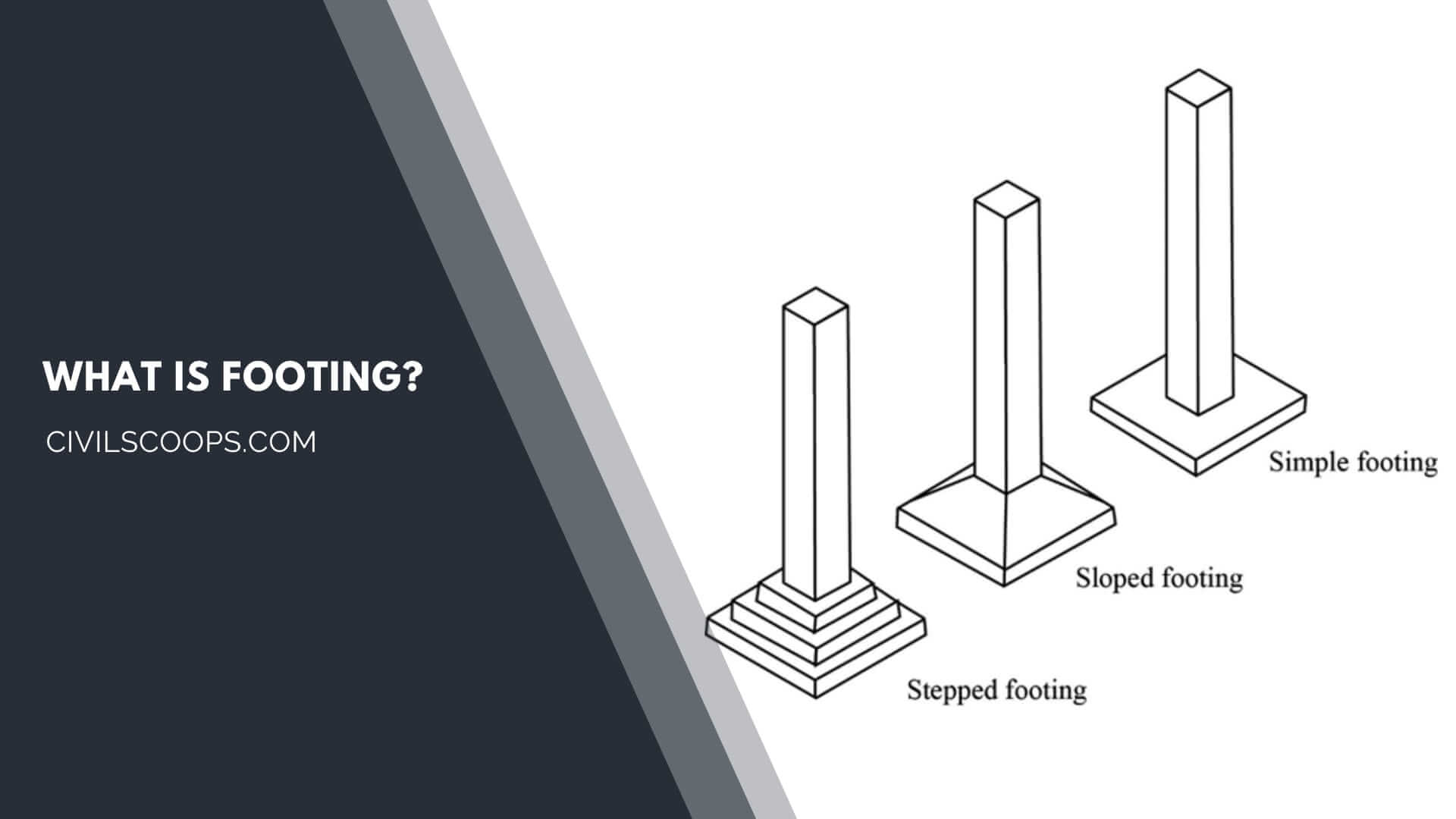
Types of Footing
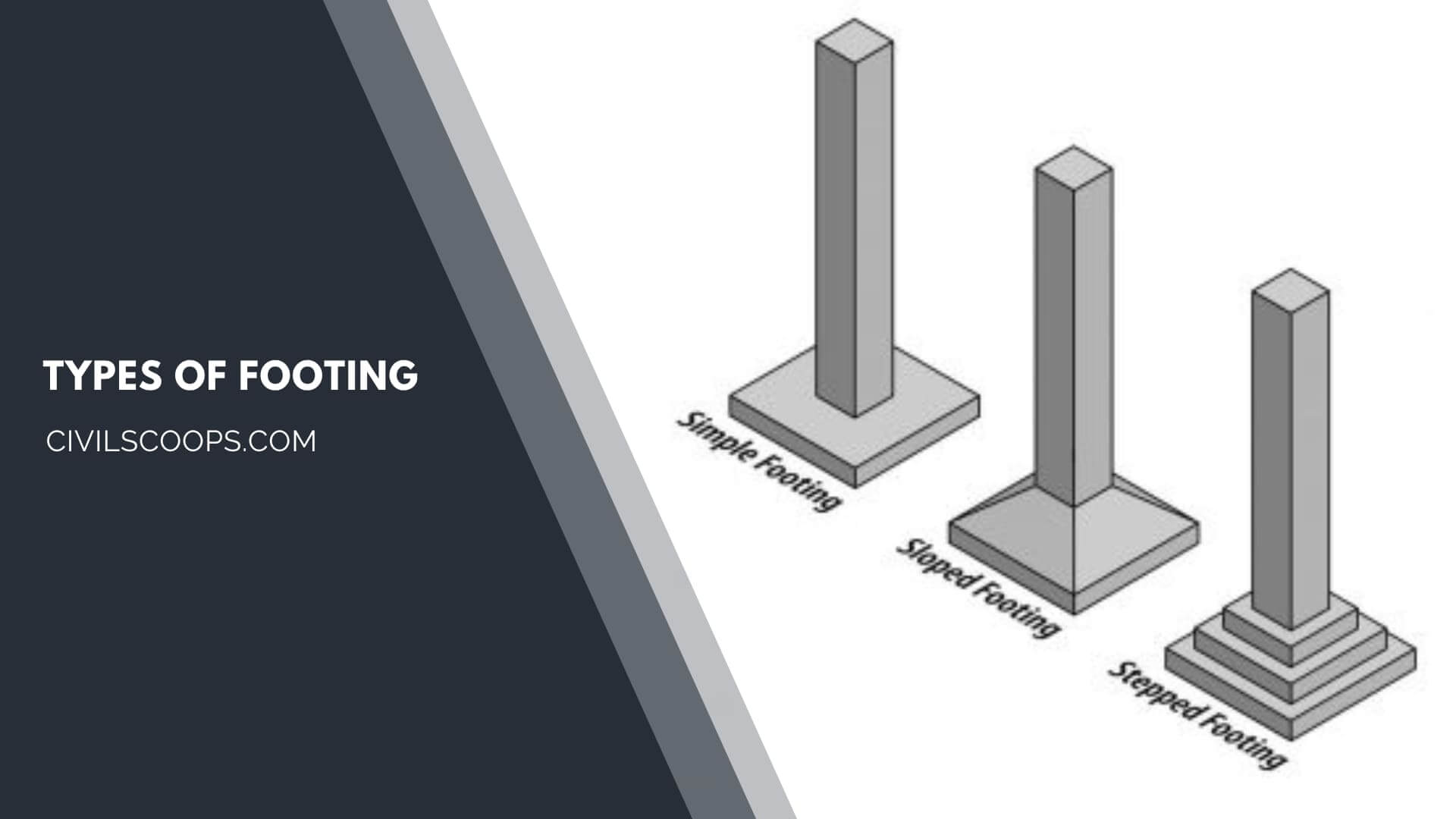
- Isolated Footing:
- Combined Footing:
- Continuous Wall Footing:
- Strap Footing:
- Strip Footing:
- Raft Footing:
- Pile Footing:
- Spread footing
What Is Foundation?

Define Footings: Foundation Engineering is a subject built on the basic principles of Soil Mechanics, Soil Hydraulics, and Structural Mechanics.
All these three together may be considered as the pillars of Foundation Engineering.
A wrong application of the principles of any one of the three subjects may lead to a faulty design of the foundation.
Theories have been developed for the design of foundations to suit ideal soil conditions.
However, such conditions rarely exist in nature since soils found in natural conditions are mostly heterogeneous in character.
Theories can have to be modified or adjusted to suit field conditions.
A foundation is a part of a superstructure.
The stresses and strains that are brought to the foundation from the superstructure would lead to interaction between the foundation structural element and the soil surrounding it.
It is this interaction that is very difficult to evaluate, as this is quite a complex phenomenon.
The theories that have been developed for ideal conditions do not take into account all the variables that would lead to the interaction between the soil and the foundation element.
The presence of a water table would make the interaction problem all the more difficult to solve.
It is, therefore, essential that a design engineer should have a thorough knowledge of the theories he wants to use for the design of foundations and also its limitations.
Knowledge of the theories and its limitations by themselves will not lead to the design of a safe and sound foundation if the environmental conditions, the strength and settlement characteristics of the soil are not properly known in advance.
An ideal design engineer, therefore, is the one who has a thorough knowledge of the theories and the field conditions and also who can modify or adjust the design to suit the field conditions.
This requires, therefore, a practical and pragmatic approach to the problem of design and construction while keeping in view the safety and economics of the project.
Also Read: First Angle Projection & Third Angle Projection Symbol (Orthographic Projection)
Types of Foundation

- Shallow foundation
- Individual footing or isolated footing
- Combined footing
- Strip foundation
- Raft or mat foundation
- Deep Foundation
- Pile foundation
- End Bearing Pile
- Friction Pile
- Drilled Shafts or caissons
- Pile foundation
Difference Between Footing and Foundation
[su_table responsive=”yes” alternate=”no”]
| Sr.No. | Footing | Foundation |
| 1 | The foundation is a general expression for structural elements that supports the superstructure as well as the supporting soil |
while the footing is represented the shallow structural element that supports the superstructure.
|
| 2 | A formation which is in contact with the ground. |
A structure which transfers its gravity loads to earth from superstructure.
|
| 3 | A structure which transfers the load from the superstructure to this ground |
the foundation which is in contact with the earth.
|
| 4 | This is a provides support to the entire building |
This provides support to individual columns.
|
| 5 | It analogized with the feet of the leg. |
It can be analogized with the feet of the leg.
|
| 6 | Foundation are of two types, shallow & deep foundation |
This footing is a type of shallow foundation
|
| 7 | This is the basement of the wall |
This is under the foundation wall.
|
| 8 | This Footing includes slab, rebar which are fabricated of brickwork, masonry or concrete. |
Foundation types include piles, caissons, footings, piers, the lateral supports, and anchors.
|
| 9 | Footing reinforces support to an individual column. |
this is Foundation is extensive support because it gives support to a group of footings as an entire building
|
| 10 | the number of footings repose on a foundation. |
This Foundation is the support that bears all kinds of loadings.
|
| 11 | This is Footing transmits loads directly to the soil. |
This is the foundation is in direct contact with the soil and transmits it to the ground.
|
| 12 | All foundations can’t be footing |
But all footings are foundations.
|
[/su_table]
Also Read: What Is Cantilever | What Is Cantilever Footing | Design of the Cantilever Footing
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Difference Between Footing and Foundation
Foundation is a structure which transfers the loads from the superstructure to the ground, while footing is the foundation which is in contact with the earth. A foundation can be shallow and deep, while a footing is a type of a shallow foundation. so, all footings are foundations but all foundations cannot be footings.
Continuous Footing
Continuous footing is footing that supports more than two columns on a wall. When the individual column placed on the strip footing, the load from the column is transferred to the footing slab, which helps create stability for the foundation.
Continuous Footing Foundation
A continuous footing foundation, also known as a continuous strip footing or simply a strip footing, is a type of foundation used in construction to support a load-bearing wall or a row of columns. It is designed to distribute the weight of the structure over a larger area of soil, reducing the pressure exerted on the ground.
Is Footing and Foundation Same?
The footing is what’s actually in contact with the ground, while the foundation is the structure that transfers the load to the earth. A simple way to visualize the difference when comparing it to the human body would be to view the footing as the actual feet of the legs and the foundation being the legs themselves.
What Are Footings and Foundations?
Footings are horizontal elements that support and distribute the load from a building to the ground, while foundations encompass the entire system that supports and anchors the building, including footings and other below-grade components.
Continuous Wall Footing
A continuous wall footing, also known as a strip footing or continuous strip footing, is a type of footing used to support a load-bearing wall or a continuous line of closely spaced columns. It is a long, continuous concrete footing that runs along the length of the wall or column line.
Continuous Strip Footing
A continuous footing, which is also called strip footing or wall footing, is used to support walls along their length. Sufficient overhangs are provided to ensure adequate footing bearing area. Continuous footing is usually placed concentrically beneath walls.
Continuous Wall Foundation
A wall footing or strip footing is a continuous strip of concrete that serves to spread the weight of a load-bearing wall across an area of soil. It is a component of a shallow foundation.
Continuous Strip Foundation
Strip foundations (or strip footings) are a type of shallow foundation that are used to provide a continuous, level (or sometimes stepped) strip of support for linear structures such as walls or closely-spaced rows of columns that are built on top of the foundation, placed centrally along their length.
Continuous Pad Foundation
This is where the pad foundations are combined together as a single long structural element. This is often the case where the pads and the columns they support are closely spaced.
Pile Footing
They are typically used for large structures, and in situations where soil is not suitable to prevent excessive settlement. As pile foundations carry a lot of load, they must be designed very carefully.
Spread Footing Foundation
Spread footing is a form of foundation designed and built to hold up superstructure elements like steel or concrete columns, walls, and so on. It is the most general construction used to keep a structure from sinking into the earth.
Isolated Footing Foundation
Isolated footings (also known as Pad or Spread footings) are commonly used for shallow foundations in order to carry and spread concentrated loads, caused for example by columns or pillars. Isolated footings can consist either of reinforced or non-reinforced material.
What Is Foundation?
foundation, Part of a structural system that supports and anchors the superstructure of a building and transmits its loads directly to the earth.
Types of Foundation
- Basement Foundation.
- Crawlspace Stem Walls.
- Concrete Slab Foundations.
- Wood Foundations.
- Pier and Beam Foundations.
Pile Foundation
Pile foundation, a kind of deep foundation, is actually a slender column or long cylinder made of materials such as concrete or steel, which are used to support the structure and transfer the load at desired depth by either end bearing or skin friction.
What Is Footing and Foundation?
A footing is a horizontal element that supports and distributes the load from a building to the ground. A foundation encompasses the entire system that supports and anchors a building, including footings and other below-grade components.
What Is Footing?
The bottom part of a foundation is called the footing. Footings in construction are critical, as the footing distributes the weight of the building evenly across the entire structure so that it doesn’t sink into the ground.
Types of Footing
The 4 Different Types of Footings
Most building contractors will decide between four different types of footings in construction: individual footings, combined footings, strip footings, and raft or mat foundation. Their choice depends on the soil, the weight of the building, and what type of build they’re doing.
Strip Footing
Sometimes referred to as a strip footing, a strip foundation is a type of shallow foundation often used within low to medium-rise residential buildings. Suitable only where the ground conditions are stable and with good load-bearing capacity, strip foundations are fast and cost-effective to build.
Raft Footing
A raft foundation is a reinforced concrete slab under the whole of a building or extension, ‘floating’ on the ground as a raft floats on water. This type of foundation spreads the load of the building over a larger area than other foundations, lowering the pressure on the ground.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- All About Wood | Types of Wood | What Is Wood | Advantages of Wood
- What Is Spalling Concrete | Causes of Spalling in Concrete | Repairing Concrete Spalding
- 8 Different Methods of Concrete Crack Repair | How to Select Suitable Method of Concrete Crack Repair
- Top 45 Greatest Constructions of Gothic Architecture in World | What Is Gothic Architecture | Unique Features Of Gothic Architecture
- What is Floating Foundation | Suitability of the Floating Foundation | Advantages & Disadvantage of Floating Foundation | How to Build a Floating House Foundation
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-06-03 07:54:51.
