What Is Under-Reamed Pile Foundation | Uses of Under-Reamed Piles | Advantages & Disadvantages of Under-Reamed Piles
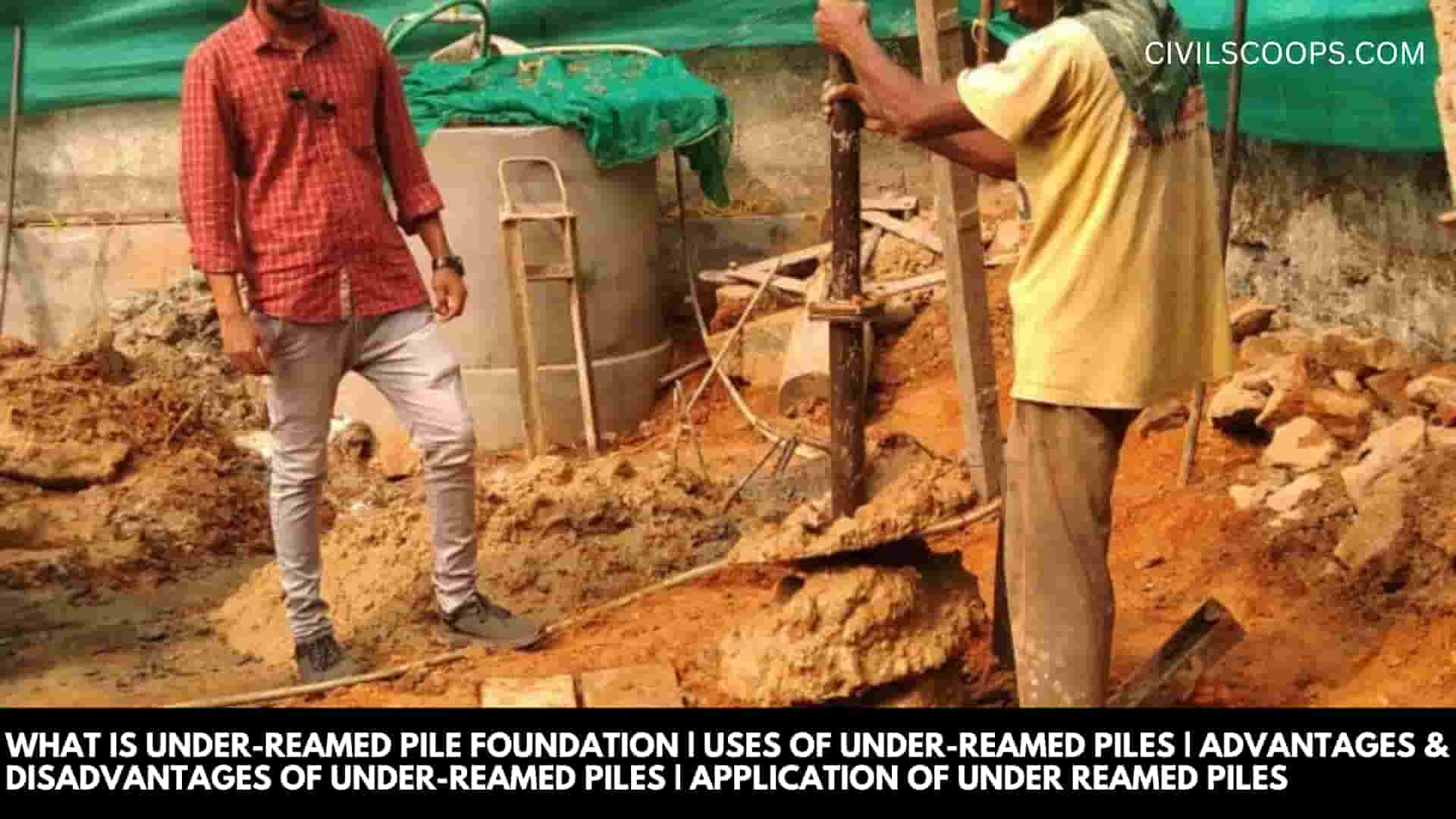

Table of Contents
Reamed Meaning
Reamed is a cutting procedure for which a cutting process creates a very precise hole size.

What Is Under-Reamed Pile Foundation?
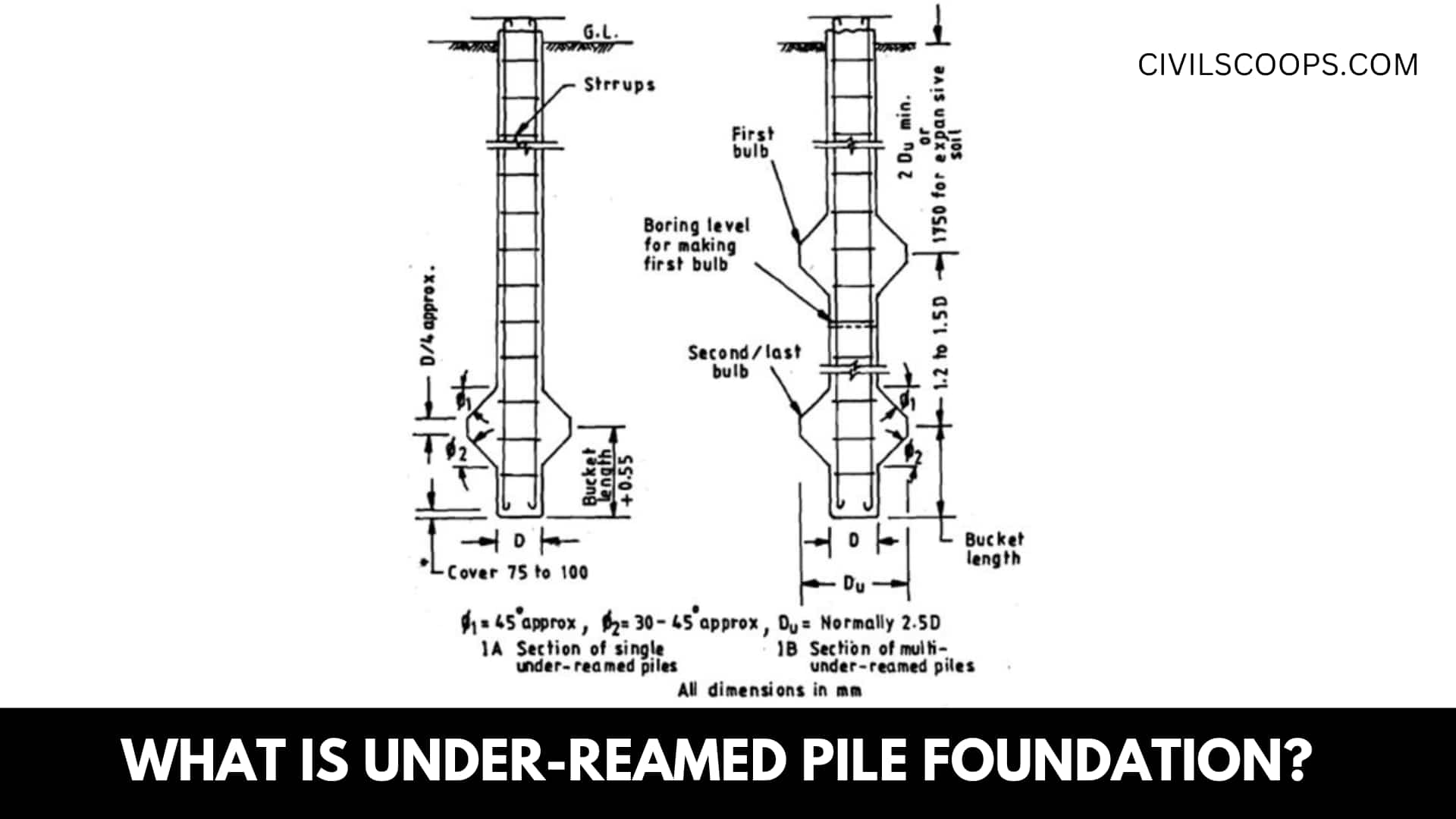
The Under-Reamed Piles Foundation is a response in areas whereby black cotton soil might eventually cause structural instability.
In most instances, soils experience volumetric variations due to fluctuations in moisture below the surface of the soil.
Such expansion as well as shrinkage will cause discomfort, which is quite risky and vital to the bearing of the base. The implication is that Reamed Piles is known to be the safest and most affordable base for certain black cotton soils or expansive soils.
Development History of Under-Reamed Pile

The issue of a defect in the composition of the expansive soil is global. Such soils were accessible across all regions. Owing to this, there has been substantial disruption to the built properties.
The disruption to the buildings is primarily due to the expansion and contraction of the soil.
Under-Reamed Piles are being extensively tested by the Central Building Research Institute (CBRI), Roorkee, to be used in black cotton soils which tend to provide a more outstanding response to the rooting problems in expansive soils.
Definition of Under-Reamed Pile
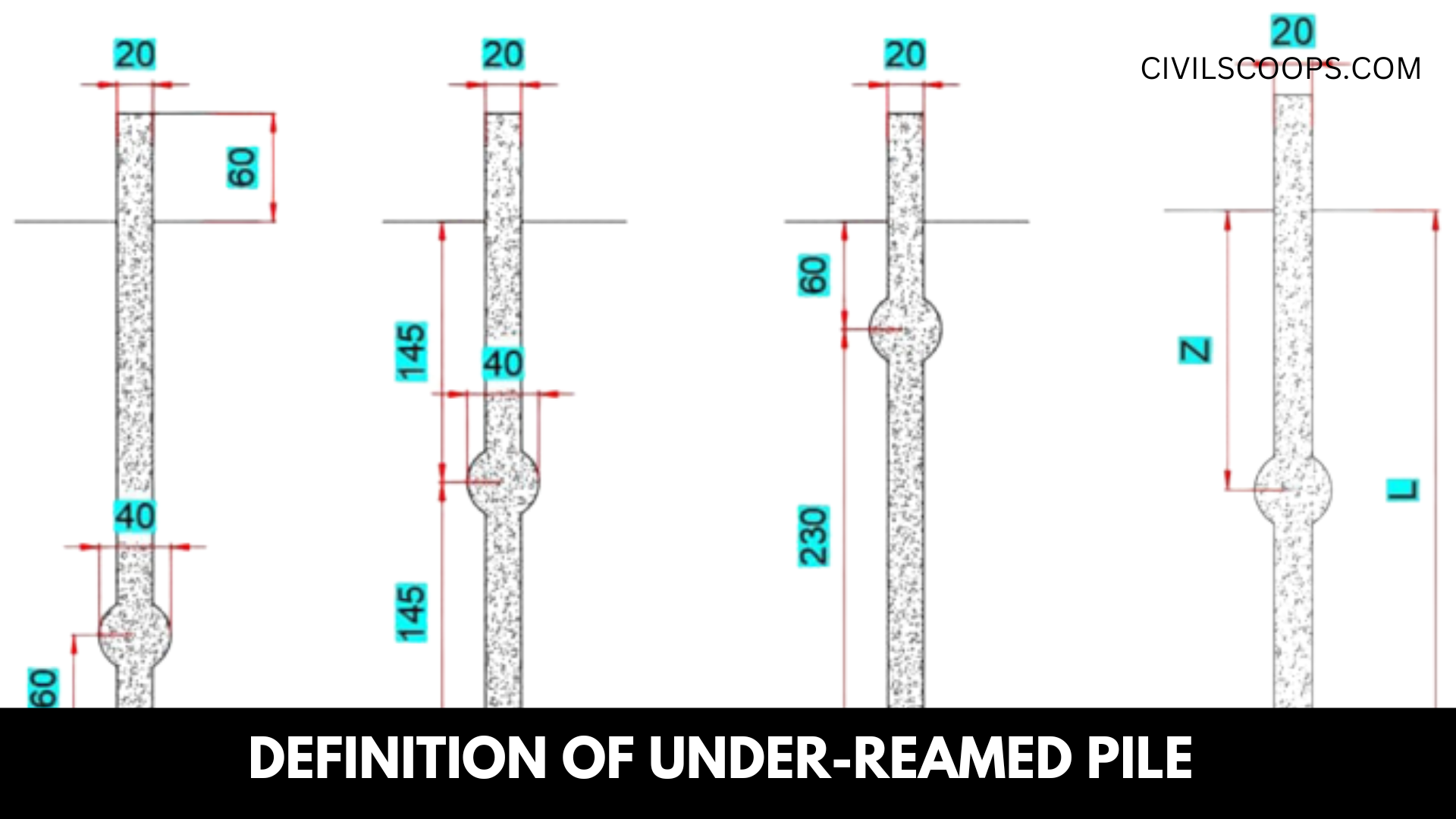
A cast-in-situ concrete pile with such a widened bulb at the bottom, rendered either through cutting or scooping out all the soil or through other appropriate methods, is considered the Under-Reamed Pile. Under-Reamed Piles are often referred to as bored cast-in-situ concrete piles.
A pile built mostly in the field to transfer the load of the foundation to the soil by resistance produced as in its tip along the top, or even both, is referred to as a bearing pile.
When the piles are predominantly provided by resistance formed at the point or base of the pile, they are related to it as the “End-Bearing Pile” and even if the load is mostly assisted by friction along its top, the pile is related to it as the Friction Pile.
When this is intended primarily to avoid uplifting or pulling, it’s considered an “Anchor Pile.”
Under Reamed Pile Design
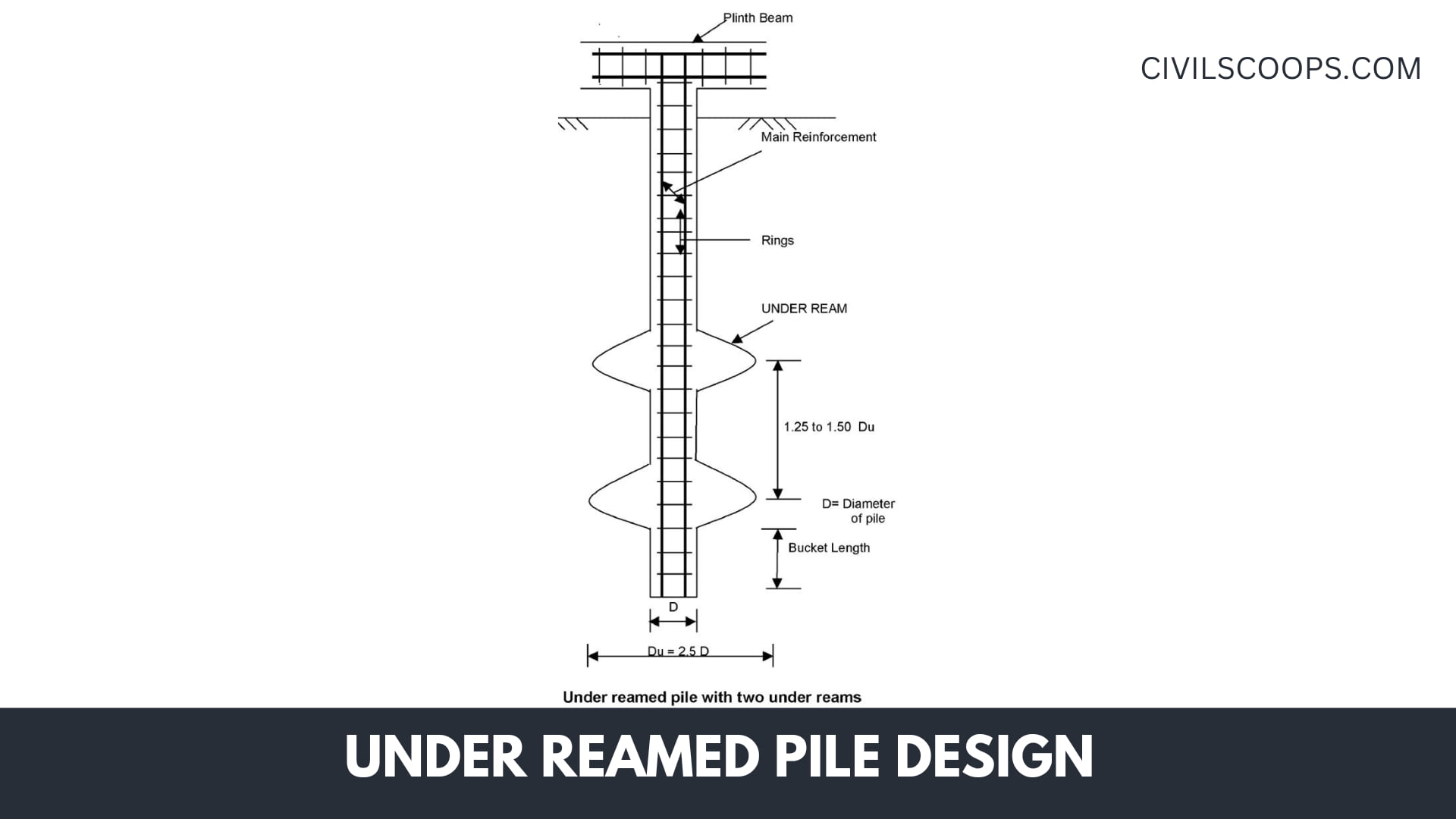
- The concrete used during under-ream piles should have a slump of 10-15 cm for concrete in water-free unlined holes drilled. For concrete formwork, the concrete required must have a slump of 15-20 cm with efficient outcomes. M-15 or M-20 concrete with a minimum cement content of 350 or 400 kg/m3 can also be used.
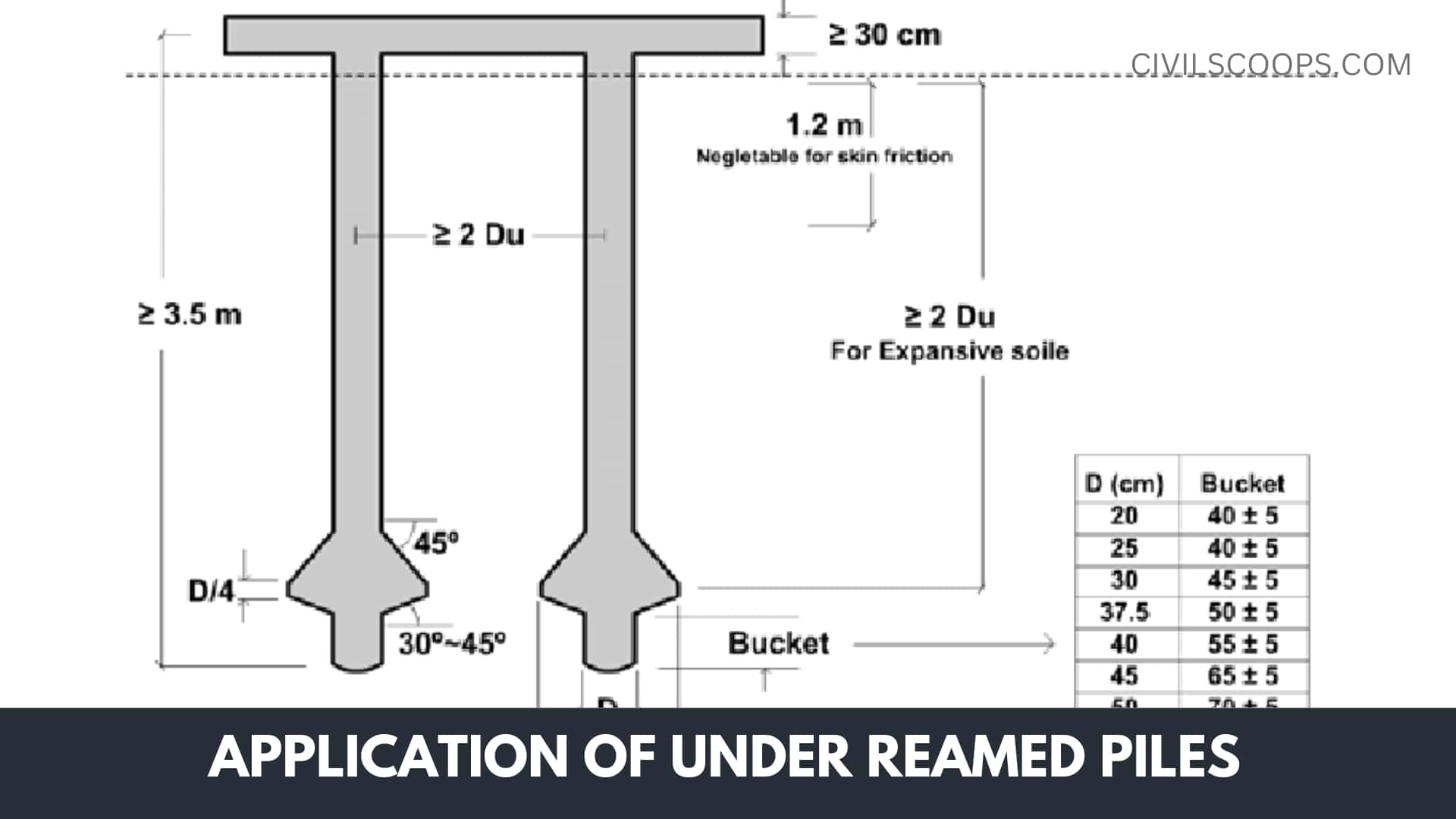
- The minimum length of under-ream piles in dense layers of expansive soils ought to be 3.5 m below the surface level.
- The diameter of the substrate is holding 2.5 times the diameter of the stem.
- The overall vertical spacing here between under-reams is 1.5 times the depth of the under-reams for piles up to 0.3 m in diameter. In large-diameter stacks, the spacing can be decreased to 1.25 times the diameter of the stem.
- The maximum bulb will be at a minimum size of twice the diameter of the bulb. In the case of vast soils, this depth should never be below 1.75 m ground level.
- Generally, the amount of bulbs issued does not exceed 2.
- The minimum central distance of the under-ream piles in a group is 1.5 times the diameter of the under-ream and is normally maintained at double the under-ream diameter.
- Throughout the case of a pile group with a pile spacing of 2 Du, the size of the group can be assumed to be equal to the amount of the load-carrying strength of the specific piles in the category.
Throughout the case of a pile group with such a 1.5 Du pile spacing, the safer load allocated per pile should really be decreased by 10%.
Increasing Load-Carrying Capacity of Under-Reamed Piles
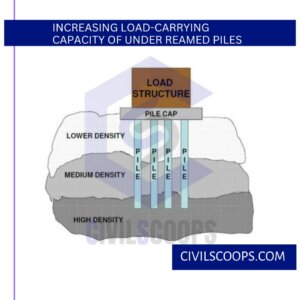
- By putting more bulbs
- By increasing the dia. of the bulb
- By increasing the length of the pile
- Providing proper reinforcement
Features and Details of Under-Reamed Piles

- Pile Diameter = 20 cm to 50 cm
- Bulb Diameter = two to three times the diameter
- Pile Length: 3 m to 8m
- Space between two piles = 2 – 4 m
- Spacing between Two bulbs = 1.25 – 1.5 times the bulb diameter.
- Load-carrying capacity = 20 to 40 tonnes
Those are all drilled cast-in-situ concrete piles that have one or even more bulbs shaped toward their base by expanding the borehole of the pile stem.
Enlargements aid in including significant bearings or anchorages. These piles are being proven to be helpful in expansive soils including such black cotton soil, as bulbs offer uplifting anchorage owing to swollen pressure.
The diameter of the bulbs under reamed bulbs maybe two to three times the diameter of the stem. The spacing of the bulbs is 1.25 – 1.5 times the diameter of the stem.
The uppermost bulbs must be at a sufficient depth of 2 times the size of the light.
Boring for the piles is done in the usual way. The bulbs are then shaped via an underside reamer rotating by a drill rod. Bowls are being used to extract dug-up earth.
The reinforcing cage would then be dropped as well as the pile is concreted. The amount of cement as well as the concrete slump should be as suggested in the case of bored cast-in-situ piles.
Also Read: 11 Difference Between Silt and Clay
Uses of Under-Reamed Piles

Under-Reamed Piles are commonly used during various soil types, including sandy soils, clay soils as well as expansive soils. Under-Reamed Piles are supposed to be taken to that depth due to the following factors.
- To prevent adverse effects of seasonal moisture variations in vast soils like black cotton soils.
- To get to the rough strata.
- To achieve a sufficient potential for the forward, downward, and lateral loads as well as moments.
- Taking the foundations just below scour mark
- These have been shown to be suitable for factory buildings, including machine foundations.
- Under-Reamed Piles are often used in cases where friction and noise generated by pile construction are minimized.
If the soil filling is not carried out professionally, namely the in such a layer of 20 cm thick with such an optimal moisture content, it is willing to deal.
Therefore, in order to take care of the very same, the grade slab was established on a set of Under Reamed Pile spaced around 3 m center to center.
Where the grade slab is constructed as a flat slab assisted by Under Reamed Piles, where even the pile cap serves as a column pedestal as with a flat slab, but no beams are given for cost reductions.
This has really performed and seems to be doing so well for ages. This has already been achieved in terminal buildings for Surat and Amritsar International Airports along with several other public buildings.
Advantages of Under-Reamed Piles

- It tends to decrease the vertical settlement as well as the differential settlement.
- It has been used as soil appears to expand and shrink in response to fluctuations in moisture or the expansive structure of the soil.
- A requirement of under-reams or bulbs does have the benefit of increasing the ability of bearings and bulbs.
- As the number of bulbs is raised between one and two, the load-carrying capacity of the Under-Reamed Pile is raised.
- A requirement of bulbs is of particular benefit for under-reamed bulbs to prevent uplifting and being used as anchors.
- The cost benefits of the Under-Reamed Piles are due to the smaller depth of the pile pipe, which means that less concrete is used to replace the excavated material.
Disadvantages of Under-Reamed Piles

- In a depth for which components of the soil differ depending on the climatic situation, the under-reamed piles weren’t ideal for waterlogged soil since they seize over by friction.
- These batteries require stringent quality control and constant monitoring during production.
- For much of the period, Under Reamed Piles, are worked manually using a hand-operated pump. It is also very important to protect the plumbing of the pile since because they’re not in the plumbing, the entire load transfer process will shift.
Application of Under Reamed Piles
- As black cotton soil has properties that grow as it interacts with moisture or water and then contracts because it is drying off. There might be a risk of cracking in the system due to this factor.
- In order to prevent disruption caused by a change in soil depth, the reamed pile is being used.
- Often, where the soil base just doesn’t have enough bearing space, it is used under reamed piles to maximize the capacity.
- Underlying reamed piles are appropriate whenever the water level of sandy soil is large.
- It is to be included. Whenever the lifting powers are behaving
Is Code for Pile Foundation

- Indian Standard IS code 2911 (Part III) – 1980 includes the design and construction of under-reamed piles with one or more bulbs.
- As per the code, the diameter of the bulbs under the ream will range from 2 to 3 times the diameter of the stem based on the viability of the construction and design specifications.
- The coding indicates a spacing of 1.25 to 1.5 times the lamp diameter for the lamps.
- An angle of 45 with such a horizontal angle is suggested for all bulbs underneath. This code specifies mathematical expressions for the calculation of bearing and lifting capacities.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
What Is Pile Foundation in Construction?
Pile foundations are long, thin elements generally made of steel or reinforced concrete. They transfer the load through weak, compressible material onto more compact, less compressible stiffer soil or rock at greater depth.
What Are Pile Foundations Used for?
Pile foundations are underground structures that support a building. Piles are long pillars that extend downwards into the ground to keep the building above them stable. They are typically used in situations where the top layer of soil is weak and unable to hold the weight of the building.
What Is a Concrete Pile?
A concrete pile is a foundation driven deep into the ground to support the structure, unlike shallow or wide foundations such as Isolated Footings or Combined Footings. They are usually much thinner in diameter or width than in length.
Under Reamed Pile Foundation
A cast-in-situ concrete pile with an enlarged bulb at bottom made by either cutting or scooping out soil or by any other suitable process is called Under-Reamed Pile. Under-Reamed Piles are also called bored cast-in-situ concrete piles.
What Is Under Reamed Pile?
Under reamed piles are bored cast-in-situ concrete piles having one or more number of bulbs formed by enlarging the pile stem. These piles are best suited in soils where considerable ground movements occur due to seasonal variations, filled up grounds or in soft soil strata.
Pile Foundation Is Code
Following are the Indian Standard Codes on Pile Foundations: IS 2911 : Part 1 : Sec 1 : 1979 Driven cast in-situ concrete piles. IS 2911 : Part 1 : Sec 2 : 1979 Bored cast-in-situ piles. IS 2911 : Part 1 : Sec 3 : 1979 Driven precast concrete pile.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- 10 Construction Certifications and Where to Get Them
- What Is Hardened Concrete | Properties of Hardened Concrete
- What Is Plaster | Types of Plaster As Per Material | Defects In Plastering
- What Are Hollow Bricks | Advantage of Hollow Bricks | Disadvantage of Hollow Bricks | Sizes of Bricks Blocks | How to Make Hollow Bricks
- What Is Fire Escape Staircases | Types of Fire Escaping Stairs | What Is the Importance of Fire Escape in the Building | What Are the Fire Staircase Requirements
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-03-20 10:43:03.
