Material Required for Construction of WBM Road
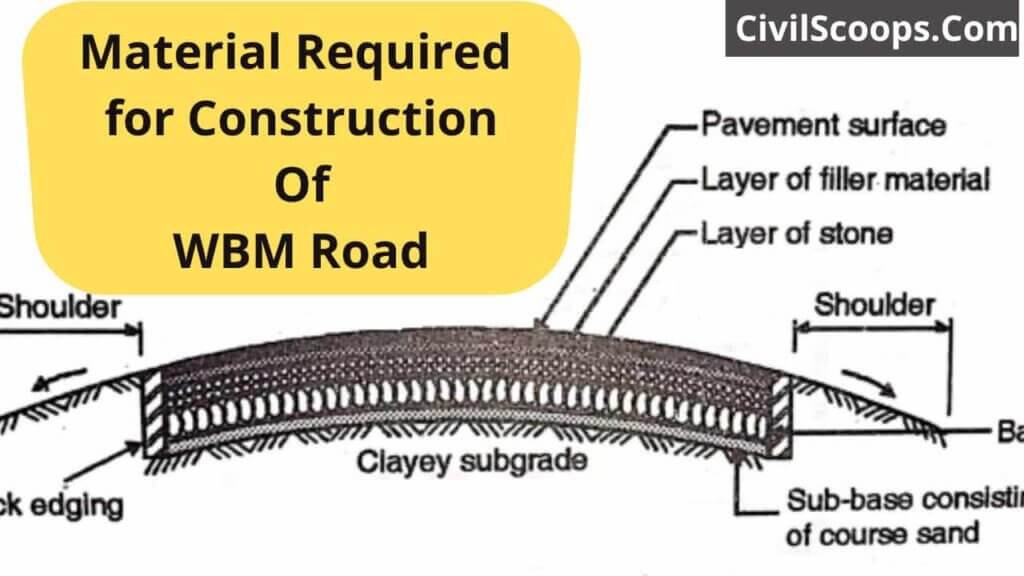
Table of Contents
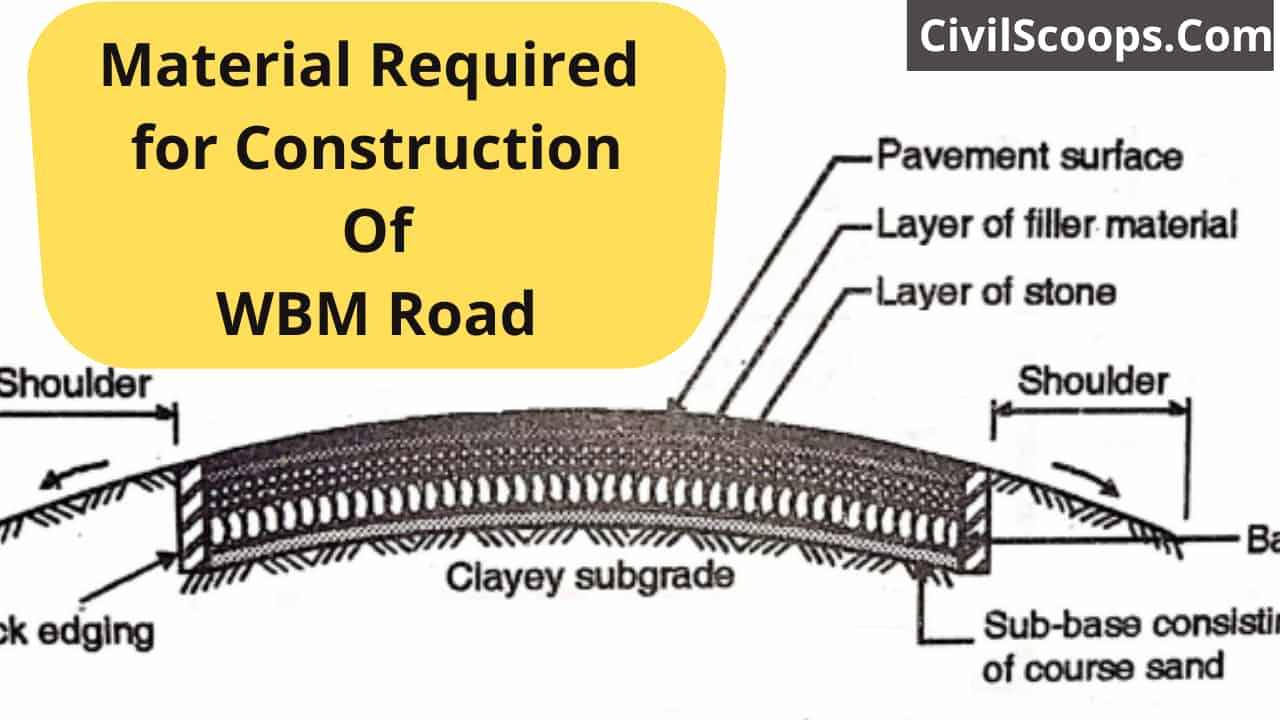
Material Required for Construction Of WBM Road
The term macadam at the present time means road surfaces and bases that form crushed or broken aggregates, cemented together by rolling and water action. WBM road binding action is achieved by the screening of the stone used as a filler in the presence of water. The construction of water-bound macadam varies in thickness from 8 to 10 cm depending on the design
The surface course of WBM deteriorates very quickly as a result of mixed traffic action. Therefore nowadays WBM is used as a base course for better types of pavements such as bituminous or cement concrete surfacing. Typically, layers in WBM are placed in thicknesses of 12 to 15 cm. The total thickness can range from 30 to 35 cm, depending on the design requirements.
Each layer is compressed by a smooth wheel roller to 75 to 80% of its loose thickness. Usually in WBM roads, camels are provided in the order of 1 to 48 in 36.
Materials required for construction of WBM Road
- Coarse aggregates
- Bran
- Filler material
- For WBM construction for the following materials
- Are required.
- Coarse Aggregates
Hard and durable stone are mainly used for coarse aggregate. Traprock is the best stones for road metal with specific gravity ranging from 2.8 to 3.1. There are also hard limestone, dolomite and granite
Is satisfactory. The specific gravity of these stones are 2.6 to 2.7. Sandstones and quartz whose specific gravity varies from 2.4 to 2.7 are somewhat less satisfactory, especially for wear.
The frontal part should be flaky, elongated, soft and free of decomposing particles and excess of dirt. Use of coarse aggregates must meet the following specifications:
- Size – 90 to 40 mm or 63 to 40 mm or 50 to 25 mm
- Loss angle friction value 40% max after 500 revolutions
- Screening
- Screening of 10 to 12.5 mm size may be used. They should be properly classified.
- Filler material
The filler material should have sufficient soil content to prevent the uplift of the WBM surface layer. The plasticity index of the filler material can be up to 9.0.
What Is WBM Road?

The full form of WBM road is Water Bound Macadam road. This type of road constructed by broken stone aggregates, stone dust or screening material. In this type of road construction water is applied in the construction time and after that it is compacted with smoothed heavy wheel rollers.
Maintenance of WBM Road

WBM road is the primary road which is planned for improving the road surfacing, this type of roads are damaged quickly due to the heavy traffic load and the adverse climate condition.
This type of road is mainly damaged due to the steel wheel of bullock carts, in the dry season it formed into dust and in the rainy season it converted into the mud. Due to high speed vehicle the upper layer particles are sucked up and the roads get damaged. In the rainy season the aggregates looses and those created ruts and potholes on the road surface.
Remedies of Damage WBM Road

In the rainy season the particles are displaced from the road surface, to prevent this problem we can use a thin layer of moist soil to overcome the effect especially in the rainy season. In the dry weather condition the dust can be removed by replacing the road surface by using bitumen layer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of WBM Road

Advantages of WBM Road
Here, the pros of wbm road are as follows.
- The main advantage of WBM road is the construction cost is low.
- The second important advantage is it does not require any skilled labours to construct the road.
- The another most important advantage is we can use local material to construct the WBM road, which is easily available in the locality.
Disadvantages of WBM Road
Here, the cons of wbm road are as follows.
- There are so many disadvantages of WBM road but one of the most important is it requires high maintenance, so the maintenance cost of this road is high.
- This type of roads are less durable, so it requires more maintenance.
- It becomes danger to the traffic if the road is properly maintained.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Road Paving Contractor
Pavement, in civil engineering, durable surfacing of a road, airstrip, or similar area. The primary function of a pavement is to transmit loads to the sub-base and underlying soil.
Road Construction Cost
According to streetsblog’s sources, the costs to completely repave a road usually vary in the range of $100k per mile up to $1 million per mile – with some outliers.
Highway Construction Companies near Me
Construct a new 4-lane highway — $4 million to $6 million per mile in rural and suburban areas, $8 million to $10 million per mile in urban areas. Construct a new 6-lane interstate highway – about $7 million per mile in rural areas, $11 million or more per mile in urban areas.
Asphalt Pavement Construction
Asphalt pavements are made by combining rocks and sand to a particular recipe and then adding asphalt cement as the black sticky glue that holds the pavement together. The combination of rocks and sand is very important to the structure and strength of the pavement.
Road Construction Contractors near Me
Construct a new 4-lane highway — $4 million to $6 million per mile in rural and suburban areas, $8 million to $10 million per mile in urban areas. Construct a new 6-lane interstate highway – about $7 million per mile in rural areas, $11 million or more per mile in urban areas.
Black Top Road Construction Cost
[su_table responsive=”yes” class=”rk”]
| Factor | Average cost |
| stamped or colored asphalt (total) | 5 – $15 per square foot |
| heated driveway (total) |
$12 – $28 per square foot
|
[/su_note]
Highway Contractors near Me
[su_table responsive=”yes” class=”rk”]
| Length | Square Footage | Average Cost |
| 100 feet (one-lane) | 1,200 | $3,500 – $8,500 |
| 500 feet (one-lane) | 6,000 | $17,500 – $42,500 |
| 1,000 feet (one-lane) | 12,000 | $35,000 – $85,000 |
| 1 mile (two-lane) | 126,720 | $370,000 – $900,000 |
[/su_note]
Asphalt Road Construction
- Step 1: Demolition and Removal.
- Step 2: Grading and Sloping.
- Step 3: Prepare the Sub Base.
- Step 4: Proof Roll, Undercutting and Sub Base Repair.
- Step 5: Binder and Surface Course.
- Step 6: Install New Asphalt Surface.
- Step 7: Butt Joints and Transitions.
Rail Road Construction
Our services include excavation, grading, site work, utility installation, structural concrete, building fit-out, building construction and rehabilitation, bridge construction and rehabilitation, roadway construction, and railroad track installation, track maintenance and track removal.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Types of Cement Grades | Difference Between 33, 43 &53 Grade Cement
- What Is Fresh Concrete? | Properties of Fresh Concrete | Factors Affecting Workability
- What Is Panelled Window? | What Is Glazed Window? | Difference Between Paneled Window and Glazed Window
- Hand Level Surveying | What Is Site Level? | What Is Hand Level? | How to Use a Hand Sight Level | Estimating Distances with a Sight Level
- Hollow Block | Hollow Concrete Block | Hollow Concrete Block Size |Hollow Concrete Block Advantage | Hollow Concrete Block Disadvantage | Hollow Concrete Wall | Hollow Block Construction | Size of Hollow Blocks | How to Make Hollow Blocks
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2024-04-05 05:13:58.