Unlock the magic of small spaces with innovative garden designs that transform limited square footage into enchanting … [Read more...]
200+ Garden Design Ideas to Make the Best of Your Outdoor Space
The article titled "200+ Garden Design Ideas to Make the Best of Your Outdoor Space" serves as an expansive resource for … [Read more...]
135+ Best Garden Design Ideas
Dive into a world where creativity meets nature, and practicality embraces beauty. Civil Scoops presents an eclectic … [Read more...]
195+ Best Garden Layout Ideas
In the realm of outdoor aesthetics, your garden is not just an extension of your home but a canvas where nature’s … [Read more...]
200 Best Garden Layout Ideas for Every Size Garden
Creating the perfect garden layout is both an art and a science. Whether you have a sprawling backyard or a tiny … [Read more...]
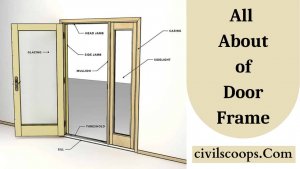
What is Door Frame? | 8 Main Parts of Door Frame | Types of Door Frame used in House
Information of Door Frame Doors are an important part of the building which allows occupants for horizontal movement in … [Read more...]
Soil Hydrometer | How Does a Soil Hydrometer Work | How to Read Hydrometer | What Does a Hydrometer Measure | Advantage, Disadvantages & Uses of Hydromete
Introduction Soil Hydrometer A hydrometer is a type of instrument which is used to gauge the general thickness of a … [Read more...]
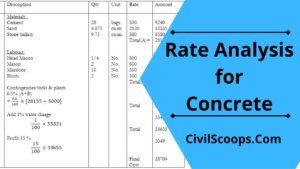
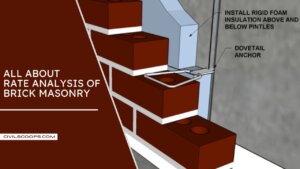
Rate Analysis for Concrete
Introduction of Rate Analysis for Concrete 1st Step - estimation of labour, materials, equipments & … [Read more...]
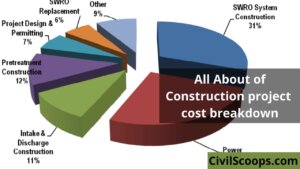
Construction Project Cost Breakdown
Introduction of Construction Project Cost Breakdown In any circumstance, the transparency and rational structure … [Read more...]
Estimate Cost of Construction Per Sq Ft
Introduction of Estimate Cost of Construction Per Sq Ft First, we must understand the asked price of every material … [Read more...]
Types of Crawl Space Insulation | Fiber glass Batt Insulation | Closed Cell Spray Foam Insulation | Open-Cell Foam Spray Insulation | Rigid Foam Insulation and Use|
Information of crawl space insulation There are two types of crawl space insulation that are majorly used. The first … [Read more...]
All About of Mezzanine Floor
Information of Mezzanine Floor The mezzanine floor is an intermediate floor of a building, below the open floor. At … [Read more...]
Reinforced Concrete Frame | Concrete Frame Construction Details | Concrete Building Construction
Reinforced Concrete Frame Reinforced concrete frames comprise of flat components (beams) and vertical components … [Read more...]
Road Gradient | Type of Gradient | All Gradient Advantages and Disadvantages
What Is Road Gradient? The rate of rise and fall with respect to the length of the road is termed as gradient of the … [Read more...]
OPC vs PPC | Difference between OPC and PPC Cement
OPC vs PPC Some Advantages that we get while using OPC in construction sites are. Ordinary Portland cement … [Read more...]
All About of Portland Cement Uses
What Is Portland Cement Uses? Portland cement is the most widely used form of cement in the world. It has been utilised … [Read more...]
Properties of Concrete | What Is the Grade of Concrete
Properties of Concrete There have many properties of concrete that are below- Grades of concrete (M20, M25, M30, … [Read more...]
Types of Wood
Introduction of Wood Wood is one of several renewable natural coffers. It's an important product used in our day-to-day … [Read more...]
What Is Veneer | What Is Laminate | Veneer VS Laminate | Difference Between Veneer and Laminate
What is Veneer? In woodworking, veneer refers to small pieces of wood and sometimes bark, usually less than 3 mm … [Read more...]
What Is Concrete Blocks | Types of Concrete Blocks | Types of Hollow Concrete Block | Advantages & Disadvantages of Using Hollow Concrete Blocks
What Is Concrete Blocks? Concrete blocks are commonly used in the design of buildings. It is less expensive than the … [Read more...]
Steel Is Stronger Than Concrete?
Introduction of Steel Is Stronger Than Concrete Because concrete has a greater compressive strength than steel, steel … [Read more...]
Skeleton Frame | Building Skeleton | Steel Structural Building
What Is Skeleton Frame? A skeleton frame is a framed design regularly utilized for the development of multi-story … [Read more...]
Information About Contractor
Introduction of Contractors Three major parties are committed to each construction design: the holder, the contractor, … [Read more...]
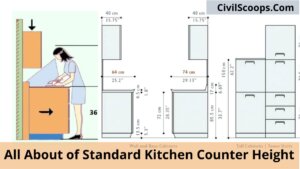
Standard Kitchen Counter Height
Standard Kitchen Counter Height The measurement from the floor to the surface of the counter is called kitchen counter … [Read more...]
What Is Dampness | Causes of Dampness | Effects of Dampness | Damp Proofing Materials | Methods of Damp Proofing
What Is Dampness ? Dampness is a property of a building when the water or moisture is absorbed by the building … [Read more...]
What Is ACP | Applications of ACP Sheet | Advantage of ACP Sheet | Disadvantages of ACP Sheet
What Is ACP Sheet? The ACP is a short form of Aluminum composite panel, it is also known as the sandwich panel. The … [Read more...]
What Is Weep Holes | Function of Weep Holes | Types of Weep Holes
What Is Weep Holes? A weep hole, also known as a weep brick, is a small opening that allows water to drain from a … [Read more...]
Types of Tests on Bricks
Types of Tests on Bricks For construction works to determine the suitability of bricks the following test is … [Read more...]
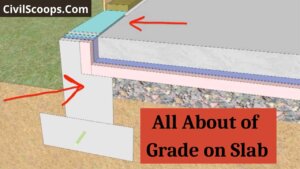
What Is Grade on Slab
What Is Grade on Slab? Grade on the slab is a special type of slab which is constructed on the earth soil. This type of … [Read more...]
Steel Is Stronger Than Concrete | Steel Vs Concrete
Steel Is Stronger Than Concrete? Because concrete has greater compressive strength than steel, steel bars are utilized … [Read more...]
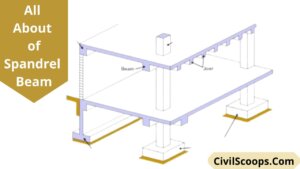
Spandrel Beam | What Is Spandrel | Spandrel Beam Definition | Advantages, Disadvantages, Uses Properties & of Spandrel Beam
Introduction of Spandrel Beam In concrete construction and steel construction spandrel beam is used. Spandrel beams are … [Read more...]
What Is Shell Structure | Types of Shell Structure | Applications of Shell Structure | Advantages & Disadvantages of Shell Structures
What Is Shell Structure? The structure that retains their size and support load, even without frame or solid mass … [Read more...]
Standard Brick Size & Dimensions (Inches & MM)
Standard Brick Size & Dimensions (Inches & Mm) Standard Brick Sizes in England The majority of bricks in … [Read more...]
What is FerroCement| Properties| Materials required| Uses| Advantages| Disadvantages
What is Ferrocement? Ferrocement is a substance of wire meshes & cement mortar. It was 1st developed by P.L.Nervi, … [Read more...]
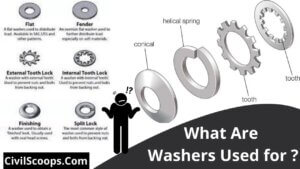
What Are Washers Used for ?
What Are Washers Used for ? The washer seems to be a thin plate with just a concentration hole which is then used to … [Read more...]
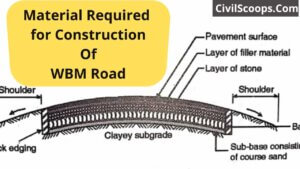
Material Required for Construction of WBM Road
Material Required for Construction Of WBM Road The term macadam at the present time means road surfaces and bases that … [Read more...]
What Is Slip Form? | Slip Form Construction | Slip Form Technique| Types of Slip Form System
What Is Slip Formwork? Formwork is a temporary moulid that is used for the pouring of concrete. The Traditional … [Read more...]
What Is Scaffolding | Types of Scaffolding
What Is Scaffolding? Scaffolding is a temporary platform used to lift, support, and supply materials during a … [Read more...]
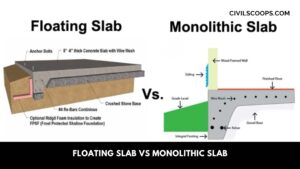
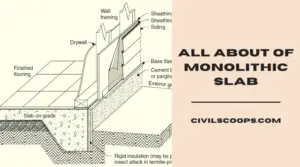
Floating Slab Vs Monolithic Slab | What Is Monolithic Slab | What Is Floating Slab
What Is a Monolithic Slab? The word Monolithic means “all in a single pour” so in construction where Monolithic … [Read more...]
EPDM Flat Roof Installation | Cost of EPDM Flat Roof | How to Install EPDM Rubber Roof | EPDM Flat Roof Installation
What Is EPDM? EPDM, known for its epdm rubber roofing cost effectiveness, is an extremely durable synthetic rubber … [Read more...]
What Are Columns | Types of Rcc Column | Round Column Vs Square Column | Pillar Vs Column
Introduction of Columns The whole structure of a building is comprised of different types of components. The column is … [Read more...]
100 Ways to Save Energy at Home: Energy Saving Tips
100 Ways to Save Energy at Home: Energy Saving Tips There are several ways to save energy at your home. Here are some … [Read more...]
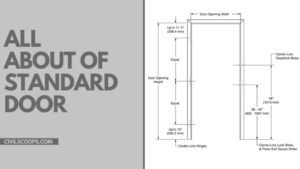
What Is Standard Door Size | Standard Door Height | Standard Door Width | Standard Door Frame Size
What Is Door? The door is the internal part of our house; without the door, we can not access our house or room. A … [Read more...]
How to Spot Hail Damage on Roof | Metal Roof Hail Damage | What Does Hail Damage Do to a Roof | 6 Signs of Hail Damage on a Roof
How to Spot Hail Damage on Roof? Generally, when assessing hail damage metal roof vulnerabilities, it’s evident that … [Read more...]
16 Definition Related for Plastering Work | Tools For Plastering | Preparation of Background for Plastering
Definition Related for Plastering Work Plasterwork is construction or ornamentation done with plaster, such as a layer … [Read more...]
All About Construction Contract
What Is Construction Contract? Contract, especially when we talk about types of contract in construction and types … [Read more...]
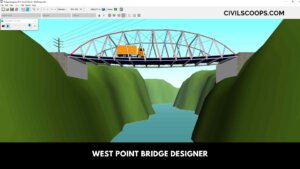
West Point Bridge Designer
What Is West Point Bridge Designer? West point bridge designer software for designing of the bridge. Bridge … [Read more...]
Civil Engineering Software | List of Civil Engineering Software | List of Engineering Software
Introduction of Civil Engineer Software There is a comprehensive civil engineering software list accessible which are … [Read more...]
What Is Staircase | Location of Staircase| Riser and Tread Calculation | How to Calculate Riser and Tread Dimensions
What Is Staircase? The Staircase, or staircase meaning, is basically a structure that is used for the vertical … [Read more...]
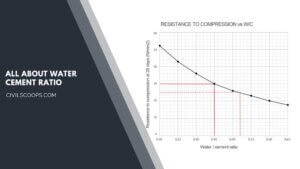
What Is Water Cement Ratio | Water-Cement Ratio and Concrete Strength | Role of Water in Concrete
What Is Water Cement Ratio? It is the ratio of cement and water utilized in the preparation of concrete. The … [Read more...]
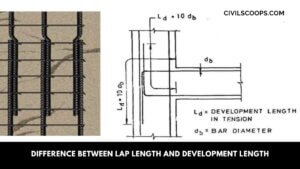
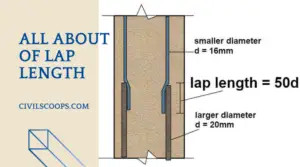
Difference Between Lap Length and Development Length
What is Lap Length? Lap Length is required when bars placed short of their required length (due to nonavailability … [Read more...]
Rotten Egg Smell In Car | Car Smells Like Rotten Eggs
Introduction of Rotten Egg Smell In Car Your senses are always essential when you’re driving your car. It would help if … [Read more...]
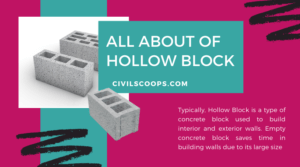
Types of Concrete Blocks
Introduction of Concrete Blocks Concrete blocks, widely known as Concrete Masonry Unit (CMU), encompass various types … [Read more...]
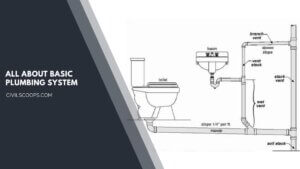
Basic Plumbing System | Drainage System | Supply and Drainage Subsystems
Basic Plumbing System Plumbing follows the basic laws of nature – gravity-pressure, water seeking its own … [Read more...]
Construction Risk Management | Contractor Risk Management | Construction Risk Register | What Is Construction Management at Risk
Information of Construction Risk Management Construction risk management is a long steep process, in which we have to … [Read more...]
Properties of Sand | Physical Properties of Sand | Chemical Properties of Sand
Properties of Sand It can be used as soon as it is obtained from the source. Contains binding content (5-20 per cent), … [Read more...]
What Is Recycled Concrete Aggregate | Importance of Recycled Concrete Aggregate | Crushed Concrete Driveway Pros and Cons
What Is Recycled Concrete Aggregate? Recycled concrete aggregates ( RACs ) are an alternative to the use in … [Read more...]
H-Beam vs I-Beam | What Is H-Beam | What Is I-Beam
H-Beam vs I-Beam H Beam Vs I Beam, Structural steel has been used extensively in the construction of commercial … [Read more...]
What Is Lightweight Concrete | Properties of Lightweight Concrete | Uses of Lightweight Concrete | Advantages & Disadvantages of Lightweight Concrete
What Is Lightweight Concrete? Lightweight concrete can be defined as a type of concrete that includes an expanding … [Read more...]
Specific Gravity Test of Bitumen | Procedure of Specific Gravity Test of Bitumen | Result of Specific Gravity Test of Bitumen
Specific Gravity Test of Bitumen By the specific gravity test on bitumen, we are determining the bitumen specific … [Read more...]
Water Damage in Bathroom | How to Fix a Water Damage Bathroom | Signs of Water Damage in Bathroom
Introduction of Water Damage in the Bathroom In the construction of the foundation of a structure, especially when … [Read more...]
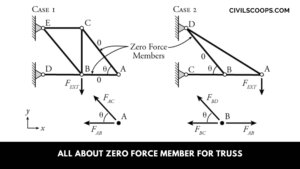
What Is Zero Force Member for Truss | How to Identification of Zero Force Members in Truss
What Is Zero Force Member? In a truss system, some members are not carrying any force. This called a zero-force … [Read more...]
What Is Bridge Abutment | 5 Types of Abutments
Bridge Abutment Means As a component of a bridge, the abutment provides the vertical support to the bridge … [Read more...]
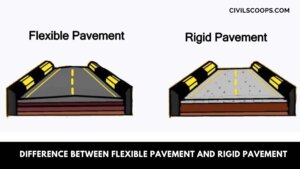
Difference Between Flexible Pavement and Rigid Pavement | What is Pavement | Types of Pavement
What is Pavement? Pavement or carriageway, often referred to as pavement meaning, is that part of the road or … [Read more...]
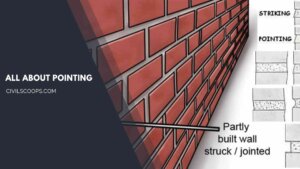
What Is Pointing | 7 Types of Pointing | Keyed Pointing
What Is Pointing? Pointing is the term given to the “finish” that sits between the bricks or stone used to build … [Read more...]
Introduction of Gantry Girder | Load on Gantry Girder | Types of Load on Gantry Girder
Introduction of Gantry Girder The gantry girders are girders which supports the loads that are transmitted through the … [Read more...]
What Is Scrap Value and Salvage Value | Types of Value in Civil Engineering
What Is Scrap Value and Salvage Value in Civil Engineering? Scrap Value in Civil Engineering The value of … [Read more...]
Corian Countertops | What Are Corian Countertops | How to Maintain Corian Countertops | How to Clean Corian Countertop
What Are Corian Countertops? Corian is the trade name of a complex plane countertop made by DuPont. This countertop … [Read more...]
All About Repointing Brick | What Is Repointing Brick | When You Need Brick Repointing | Types of Repointing Brick
What Is Repointing Brick? Repointing brick is generally known as repointing of brick or repointing of brickwork. … [Read more...]
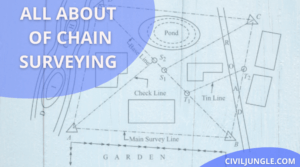
All About Prismatic Compass Surveying
What Is Prismatic Compass Surveying? What is prismatic compass surveying? It is the kind of prismatic compass … [Read more...]
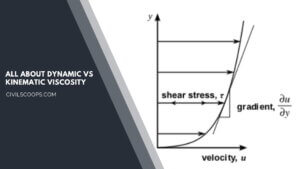
Dynamic Vs Kinematic Viscosity (Difference & Definition)
What Is Viscosity? Viscosity is a basic characteristic property of all liquids. When a liquid flows, it’s an inner … [Read more...]
All About Mix Design
What Is Mix Design? Concrete mix design is a procedure of manufacture of concrete with an ideal proportion of … [Read more...]
Different Types of Stucco | Information of Stucco | Types of Stucco Finishes | Stucco Maintenance
Introduction of Stucco Stucco has been a viral decorative coating for the building. In ancient times, Stucco originated … [Read more...]
All About Wall Putty | What Is Wall Putty | What Is Wall Putty Used For | Disadvantages of Wall Putty | Types of Wall Putty
What Is Wall Putty? Wall putty is basically a substance that is applied to the internal wall of any house to … [Read more...]
Definition Efflorescence | Efflorescence in Concrete
How to Define Efflorescence? Effloresces, often referred to as the efflorescence meaning, is a crystalline set down … [Read more...]
What Is Micro Concrete | How to Apply Micro Concrete | What Are the Benefits of Micro Concrete | How Is Micro Concrete Used
What Is Micro Concrete? Micro concrete is a cement-based coating that is used as a thin layer on different surfaces … [Read more...]
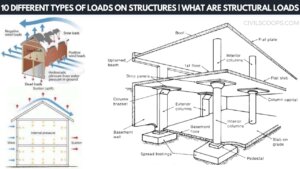
Live Load Vs Dead Load | What Is Load in Civil
What Is Load in Civil? There are different types of load than working on a structure, the design, location, and … [Read more...]
Different Types of Couches for Home
What Are the Couches? Couches are generally known as sofas. It is used for peaceful sleep, relaxing, and sitting … [Read more...]
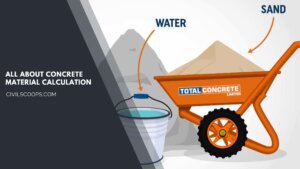
Concrete Material Calculation / Concrete Quantity
What is Material Calculation In Civil? In civil material calculation, especially when it comes to concrete material … [Read more...]
All About Turbidity of Water | What Is Turbidity of Water | Procedure of Turbidity of Water Test
What Is Turbidity of Water? Turbidity of water is a property of water or liquid by which we can measure the … [Read more...]
What Is Moment Frame | Types of Moment Frames
Introduction of Moment Frame The Moment Frames are the fundamentals structure which consists of two-dimensional series … [Read more...]
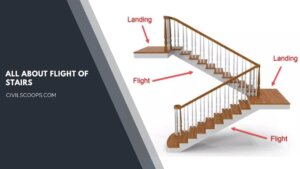
What Is a Flight of Stairs | Types of Stairs | How Many Stairs in a Flight | Some Facts About Stairwells
What Is a Flight of Stairs? A flight of stairs is a set of steps between two floors or two landings. Flight of … [Read more...]
What Is Concrete Forms | Types of Concrete Forms, Uses, Advantage, Disadvantages and Applications
What Is Concrete Form? A concrete form is a system of formwork for reinforced cement concrete which is made with … [Read more...]
New Civil Engineering Technology 2023
New Technology Civil Engineering Here, list of construction inventions are as follows. Self-Healing Concrete … [Read more...]
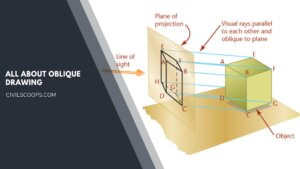
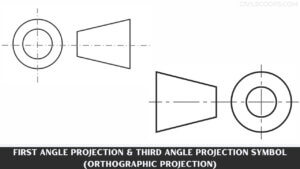
Understanding Oblique Drawing: Techniques, Examples, and Applications
What Is Oblique Drawing? Oblique Drawing is a type of projective drawing in which the frontal lines are given in … [Read more...]
All About No Hot Water in The House
Introduction of No Hot Water in House Dealing with no hot water causes in the house presents several challenges, but … [Read more...]
Repairing a Burst Pipe | Burst Pipe Repair Cost | Fixing a Busted Water Pipe | How to Fix a Burst Pipe | Pipes Burst Under House
Introduction of Repairing a Burst Pipe Burst pipe means bursting of pipe in different circumstances as well as in … [Read more...]
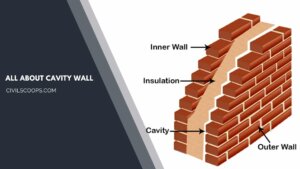
What Is a Cavity Wall | How to Build a Cavity Wall | Cavity Wall Detail | Cavity Wall Thickness | Cavity Wall Insulation Pros and Cons | Brick Cavity Wall
What Is a Cavity Wall? A cavity wall consists of a hollow space between them. The cavity walls normally consist of … [Read more...]
What Is the Best Foundation for a House | Types of House Foundations | How to Build a House Foundation | What Is the Strongest Foundation for a House
Introduction of Foundation for House Foundation, often referred to as house foundation types, is one of the most … [Read more...]
How to Get Wet Blood Out of Carpet?
How to Get Wet Blood Out of Carpet? Wet blood on the carpet is a very problematic thing and blood is type of stain … [Read more...]
What Is Timber | Types of Timber | What Is Mass Timber Products | Type of Mass Timber in Construction
What Is Timber? Timber is a simply wooden structure which is converted into the shape of beams and planks. Another … [Read more...]
All About of Tiles | What Are Tiles | How to Calculate Number of Tiles Needed for a Room
Purpose of Tile Flooring in the House There are some essential purposes behind fitting tiles in the home, It is … [Read more...]
All About Chalk Paint | What Is Chalk Paint | How to Fix the Chalking Paint Problem
What Is Chalk Paint? Initially founded by the common paint variety Annie Sloan, ”chalk paint” is politically an … [Read more...]
How to Remove Paint from Concrete Without Chemicals | Procedure to Remove Paint from the Concrete Surface | How to Get Spray Paint Off Concrete
Instruction of Remove Paint from Concrete Concrete is a widely used building material in the construction industry. … [Read more...]
What Is Water Ponding | Is Standing Water Pooling on Flat Roof a Problem | Common Causes & Solutions for Ponding Water
What Is Water Ponding? As in Construction Industry, National Roofing Contractors Association(NRCA) described Water … [Read more...]
Water Leakage from Ceiling | Water Leakage from Ceiling | How to Stop Water Leakage from Ceiling
Information of Water Leakage from Ceiling Water is one of the most important resource but it is also the biggest enemy … [Read more...]
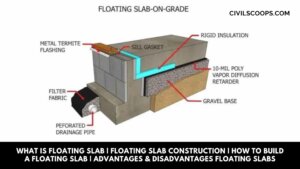
What Is Floating Slab | Floating Slab Construction | How to Build a Floating Slab | Advantages & Disadvantages Floating Slabs
What Is a Floating Slab? These slabs are constructed in two stages. At the first stage, the footings are poured … [Read more...]
Introduction to Stair Landing | What Is Stair Landing | Stair Landing Dimensions
Introduction to Stair Landing Flight of stairs landing is a significant part of a structure giving admittance to … [Read more...]
Types of Wooden Beams
What is Wooden Beam? A wood beam is structural support made from wood. They are most commonly used in wood frame … [Read more...]
What Is Cedar Wood | Is Cedar a Hardwood | Uses of Cedar Wood | Types of Cedar | Red Cedar Wood | Facts About the Cedar Tree
What Is Cedar Wood? Cedar is a very durable wood. It lasts long for decades. Cedar woods have a natural resistance … [Read more...]
What Is Skillion Roof | Types of Skillion Roof | Uses of Skillion Roof | How to Build a Skillion Roof
What Is Skillion Roof? The Skillion roof is a unique type of roof which has just one unvarying isolated surface. … [Read more...]
What Is Gypsum Boards? | Properties of Gypsum Board | Types of Gypsum Board | Advantages & Disadvantages of Gypsum Board
Information of Gypsum Boards There are various new innovative materials are available in the market which enhances the … [Read more...]
What Is Louvered Door? | 10 Different Types of Louvered Doors Available in Market
Induction of Louvered Door Doors are one of the important parts of our home which provides the horizontal movements of … [Read more...]
15 Types of Porch Used for Home | What Is Porch | How to Infer What Porch You Need
Information of Porch The porch is the most important section and front part of the structure whenever we enter the … [Read more...]
What Is an Ice Dam | How to Remove Ice Dam From Roof | What Causes Ice Dams on Roof | How to Remove Ice Dams
What Is an Ice Dam? Generally, ices are very beautiful in nature, but they can also cause many problems like … [Read more...]
Different Types of Roofing Materials | What is Roof Covering
Introduction of Roof Covering Material A roof may be defined as the upmost part of the structure. A roof is a top … [Read more...]
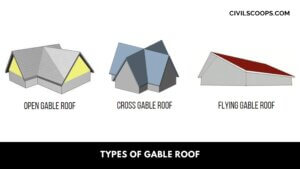
Types of Gable Roof
Types of Gable Roof Here, the different types of gable roof are as follows Box Gable Roofs Front Gables … [Read more...]
What Is Salt Concrete Finish | How to Create a Salt Finish | Rock Salt Concrete Finish Installation Procedure
What is Salt Concrete Finish? As one of the older, more conventional decorative concrete finishes, salt finish … [Read more...]
What Is Stone Masonry | Types of Stone Masonry
Masonry means construction of buildings utilizing building blocks such as stone, bricks, and concrete blocks, etc.. … [Read more...]
What Does Hail Damage Look Like on a Roof | Identifying Hail Damage to Your Roof | Wood Shingles Hail Damage
What Does Hail Damage Look Like on a Roof? Generally, shingles of the roof react differently when they are struck … [Read more...]
All About Marble Flooring | What Is Marble Flooring | Types of Marble Flooring
Information Marble Flooring For thousands of years to create elegant floors Marble has been used widely. And today it … [Read more...]
What Is Asphalt Paving | Types of Asphalt Paving | What Does Asphalt Cost | Hot Mix, Warm Mix, and Cold Mix Asphalt
Introduction of Asphalt Paving Asphalt is also known as bitumen. Asphalt is a sticky, black, largely thick liquid or … [Read more...]
What Is Roof Replacement | What Is Roof Repair | Difference Between Roofing Repair and Replacement
Introduction of Roof Repair Vs Roof Replacement When your roof became older and the water enters the house then you … [Read more...]
Concrete Construction Tools for Construction Sites
Introduction of Concrete Construction Tools for Construction Sites Concrete is one of the most widely used building … [Read more...]
Construction Technology | Types of Construction Technology You Will Use in the Future
Information Of Construction Technology The use of Technology and Digitalization is increasing rapidly in almost every … [Read more...]
What Is Mansard Roof | Mansard Roof Replacement Cost | Advantages and Disadvantages of Mansard Roof
What Is Mansard Roof? Generally, this mansard roof is also known as a French roof or curb roof, which is a combined … [Read more...]
What Is Concrete Screed | Concrete Screed Specifications | Characteristics of Concrete Screed | Advantages & Disadvantages of Concrete Screed
Introduction of Concrete Screed A construction element which is available in a range of thickness to bring forth the … [Read more...]
Fly Ash in Concrete | Advantages & Disadvantages of Fly Ash Concrete | Use of Fly Ash in Concrete | Applications for Fly Ash Concrete | Benefits of Fly Ash Concrete
What Is Fly Ash? Fly ash is a fine powder that would be a by-product of the combustion of pulverized coal in power … [Read more...]
What Is Hail Damage | How to Inspect a Wooden Roof for Hail Damage | Roof Types and Hail Affects on Roof
What Is Hail Damage? In simple words, Hail can be defined as a crystallized piece of snow. Many a time hail is … [Read more...]
Hail Damage to Asphalt Shingles | Introduction of Hail Damage to Asphalt Shingles | What Is Hail and How Does It Damage the Asphalt Shingles
Introduction of Hail Damage to Asphalt Shingles As humans came into this world, at first, they started living in caves … [Read more...]
Built Up Roof with Gravel | Why Do They Put Gravel on Flat Roofs | Purpose of Gravel on a Flat Roof | Added Benefits of Bur Flat-Roof Gravel
Introduction of Built-Up Roof with Gravel BURs (also known as tar and gravel roofs) are a well-known and popular form … [Read more...]
Water Damage from Water Heater | How to Repair Water Damage from a Leaking Water Heater
Water Damage from Water Heater Water damage from a water heater is now a common problem in all residential, … [Read more...]
Roof Leak Detection | What Can a Leaking Roof Due to My Home | What Are the Symptoms of a Leaking Roof | What Causes a Roof to Leak
Roof Leak Detection Here, some sins of 11 different types of roof leak sections are as follows. At first, we … [Read more...]
Residential Roofing | Which Residential Roof Type Is Best for You | Types of Roofing | Find the Right Roof Type for Your Home Based on Design and Price
Introduction of Residential Roofing Residential roofing is different from commercial roofing in the terms of materials, … [Read more...]
Repairing Water Damaged Wall | How to Repairing Water Damaged Wall | How to Fix Water Damaged Wall
Introduction of Water Damaged Wall Sometimes water can be highly destructive to the building materials. At the meeting … [Read more...]
History of Dutch Gable Roof | What Is Dutch Gable Roof | How to Build Dutch Gable Roof | Advantages & Disadvantages of Dutch Gable Roof
Introduction of Dutch Gable Roof The Dutch gable roof is also called a gablet that consists at the top of a roof of a … [Read more...]
All About Exterior Paint | What Is Exterior Paint | Top 10 Exterior Paint Companies in India 2022
What Is Exterior Paint? Exterior paints state that paint is used outdoors in buildings, offices, and other … [Read more...]
How to Fix Damaged Roof Shingles | How Often Should You Replace Your Roof Shingles | Replacing Roof Shingles
How to Fix Damaged Roof Shingles? There are have many steps for the fix to damaged roof shingles that’s are … [Read more...]
How to Reduce Construction Cost (Tips)
How to Reduce Construction Cost ( Tips) By flowing some steps we can reduce the cost of the construction that is … [Read more...]
How to Improve Your Indoor Air Quality at Home?
How to Improve Your Indoor Air Quality at Home? When outside air corruption offers a treat, it must be simple to ignore … [Read more...]
All About Green Concrete | What Is Environmentally Friendly Concrete
Introduction of Green Concrete In the history of the concrete world, green concrete is a revolution topic in Denmark; … [Read more...]
Earthmoving Equipment With Picture
What is Earthmoving Equipment? As the name might suggest, earth-moving equipment generally refers to any piece of … [Read more...]
How to Prevent Home Theft (Tips)
How to Prevent Home Theft (Tips) Home theft is a common problem in recent times, so there are some easy & common … [Read more...]
10 Different Types of Kitchen Sinks | Kitchen Sinks
What Is a Sink? A sink is known by many names like washing basin, washing bowl, and hand basin. Some people just … [Read more...]
Land Moving Equipment
Land Moving Equipment For excavation purposes, earthwork, grading of soil, rock etc. Land-moving equipment are commonly … [Read more...]
Types of Renewable Energy Resources
Types of Renewable Energy Resources In all over the world, scientists have found six number of renewable energy … [Read more...]
All About Site Preparation | What Is Site Preparation | Types of Site Preparation
What Is Site Preparation? Site preparation affects many works such as destruction of old alive design, the gap of … [Read more...]
How to Remove Stains from Wood?
How to Remove Stains from Wood? If you’re renewing your wood products or apparatus, you must remove old wood product … [Read more...]
What Is Pipe Fittings | Types of Pipe Fittings
What Is Pipe Fittings? Pipe fittings are the process where we divert the flow of the water by using piping … [Read more...]
How to Kill Tree Roots?
How to Kill Tree Roots? If it is not necessary then you do not kill the tree roots, because after cutting the tree … [Read more...]
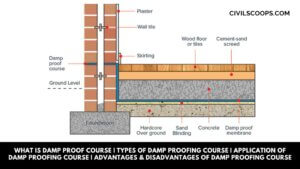
What Is Damp Proof Course | Types of Damp Proofing Course | Application of Damp Proofing Course | Advantages & Disadvantages of Damp Proofing Course
What Is Damp Proof Course? The damp proof course is an important layer for all walls of the building that is … [Read more...]
What Is GIS In Surveying | Definitions of GIS | Parts & Work Flow of GIS | Advantages of GIS
What Is GIS In Surveying? GIS stands for a geographic information system. An information system is a computer … [Read more...]
Waterproof a Concrete Roof | Old Concrete Roof Waterproofing | Concrete Roof Sealant Flat Concrete Roof Waterproofing
Waterproof a Concrete Roof At a first, the concrete roof is only used for commercial buildings, but nowadays to … [Read more...]
How Are Bridges Built | How Are Bridges Constructed | Factors Associated with Building Bridges
How Are Bridges Built? As human beings started to expand across lands and territories, we had a structure to … [Read more...]
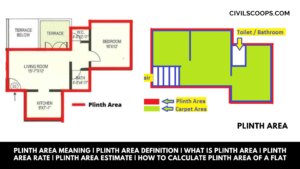
Plinth Area Meaning | Plinth Area Definition | What Is Plinth Area | Plinth Area Rate | Plinth Area Estimate | How to Calculate Plinth Area of a Flat
Plinth Area Meaning: The plinth area means we know the built-up covered area at the floor level of the basement or of … [Read more...]
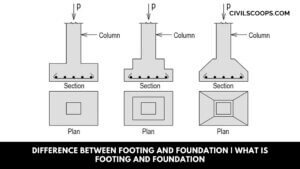
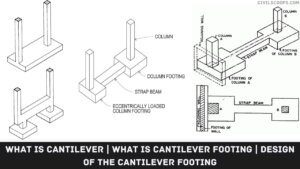
Difference Between Footing and Foundation | What is Footing and Foundation
What is Footing? Foundation Definition: The footing is generally supporting columns and may be round, square, or … [Read more...]
8 Different Methods of Concrete Crack Repair | How to Select Suitable Method of Concrete Crack Repair
Introduction of Concrete Repair Method Concrete is one of the most widely used building materials in the construction … [Read more...]
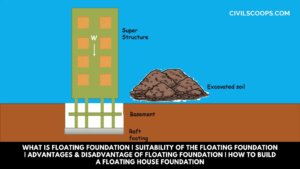
What is Floating Foundation | Suitability of the Floating Foundation | Advantages & Disadvantage of Floating Foundation | How to Build a Floating House Foundation
Introduction of Floating Foundation Foundation is one of the most important parts of the structure which carries the … [Read more...]
All About Wood | Types of Wood | What Is Wood | Advantages of Wood
What Is Wood? Wood is a natural product and one of the most beautiful materials, providing a long-term sustainable … [Read more...]
Top 45 Greatest Constructions of Gothic Architecture in World | What Is Gothic Architecture | Unique Features Of Gothic Architecture
Introduction of Gothic Architecture Since the day the human left caves and started living in houses, the birth of … [Read more...]
What Is Spalling Concrete | Causes of Spalling in Concrete | Repairing Concrete Spalding
What Is Spalling of Concrete? Spalling of concrete at fires is the breaking-off of layers of a concrete surface in … [Read more...]
What Are Curb and Gutter | Types of Curb and Gutter| Advantages & Disadvantages of Curb and Gutter
Introduction of Curb and Gutter There are various types of Curbs and gutters are used in the construction of light and … [Read more...]
9 Curing of Concrete Methods | What Is Curing of Concrete | Why Curing Is Important | Minimum Curing Period for Concrete Cement | How Long Does It Take for Concrete to Dry
What Is Curing of Concrete? Curing performs a crucial role in the growth as well as the resilience of concrete … [Read more...]
Introduction of Bamboo | Advantages & Disadvantages of Bamboo | Bamboo Uses in Construction | Properties of Bamboo as a Construction Material | Bamboo Architecture
Introduction of Bamboo Bamboo is one of the oldest and traditional construction materials used in different … [Read more...]
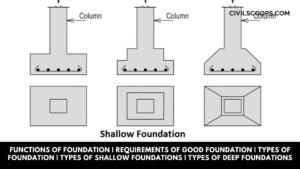
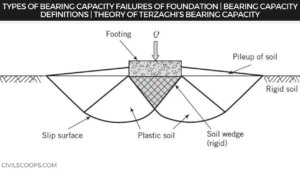
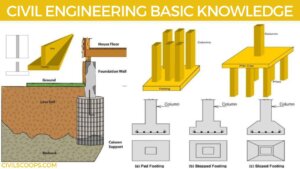
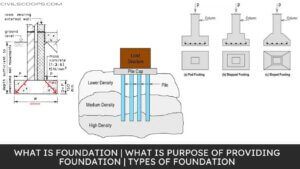
Functions of Foundation | Requirements of Good Foundation | Types of Foundation | Types of Shallow Foundations | Types of Deep Foundations
Introduction of Foundation: Foundation is one of the most important parts of the building. The foundation plays a … [Read more...]
Why Hairline Cracks in Concrete | Types of Cracks in Concrete
Why Hairline Cracks in Concrete? Hairline Cracks in concrete are extremely common but often misunderstood. Once an … [Read more...]
What Is Brutalist Architecture | Brutalist Design | Brutalism Architects Buildings & Houses | What Is Neo-Brutalism
History of Brutalist Architecture: The history of brutalist architecture goes back three years the 1940s to the … [Read more...]
Difference Between Marble and Granite | What Is Marble and How Is It Made | What Is Granite and How Is It Made
Introduction of Marble and Granite Someone busy planning the interior of their home, let me tell you research is very … [Read more...]
What Is Paint Finishes for Walls | Types of Paint Finishes | Types of Paint Finishing
What Is Paint Finishes for Walls? If you have selected a fresh paint color for your home makeover design, you may … [Read more...]
10 Principles of Architecture | What Is Architecture | Why Need Design Principles in Architecture
What Is Architecture? The techniques and art of making the layout of buildings and constructing the building are … [Read more...]
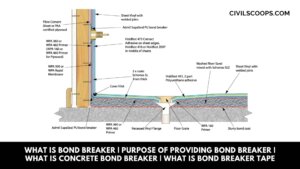
What Is Bond Breaker | Purpose of Providing Bond Breaker | What Is Concrete Bond Breaker | What is Bond Breaker Tape
What Is Bond Breaker? In the modern construction industry, the term “prefabrication” or “precast” holds a significant … [Read more...]
Concrete Batching | Concrete Batching Plant | Types of Batching of Concrete | Various Factors Affecting the Choice of Batching System
All About of Concrete Batching Generally, concrete is a multipurpose, eco-friendly construction material that is … [Read more...]
What Is Superstructures | Difference Between Load-Bearing and Framed Structures
What Is Superstructures? The portion above the ground level and below the ground floor level is known as a plinth. … [Read more...]
What Color Helps You Fall Asleep | Best Bedroom Colors for Sleep 2022
What Color Helps You Fall Asleep? You may apply soft pillows, a glossy blanket, a solid cushion, and slow music … [Read more...]
Difference Between Fat Lime and Hydraulic Lime | What Is Fat Lime | What Is Hydraulic Lime
What Is Fat Lime? Fat lime is also known as Rich lime, High calcium lime, Pure lime, White lime. It is obtained by … [Read more...]
All About Waffle Slab Foundation | What is Waffle Slab Foundation | Waffle Slab Foundation Pros and Cons | Features of Waffle Slab Foundation
What is Waffle Slab Foundation? The waffle slab foundation system is also called a waffle mat foundation. The … [Read more...]
What Is Transportation Engineering | Major Disciplines of Transportation Engineering | What Do Transportation Engineers Do
What Is Transportation Engineering? Transportation plays an important role in the development of the country. … [Read more...]
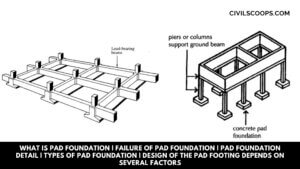
What Is Pad Foundation | Failure of Pad Foundation | Pad Foundation Detail | Types of Pad Foundation | Design of the Pad Footing Depends on Several Factors
What Is Pad Foundation? Pad footing is the type of shallow footing used to spread a concentrated load through … [Read more...]
Types of Roof Tiles | Tile Roof Replacement | Tile Installation Cost | Roofing Tile Price | Ceramic Tile Price Per Square Foot | Tile Installation Factors
Types of Roof Tiles There are various types of tiles that are available in the market. There are mainly twelve … [Read more...]
What Is Mat Foundation | Mat Slab Foundation| Advantage and Disadvantage of Mat Slab Foundation | Types of Mat Foundation | Where Mat Foundation Is Used
What Is Mat Foundation? Mat foundation is also called a raft foundation. Generally, it is a continuous slab laying … [Read more...]
What Is Soil Vent Pipe | How Does Soil Stack Pipe Works | Soil Vent Pipe Material | Types of Plumbing System
Introduction of Soil Vent Pipe The plumbing system and the Drainage of the important aspect of the building because … [Read more...]
Shotcrete Vs Gunite | What Is Gunite | Advantage & Disadvantage of Guniting Process | What Is Shotcrete | Advantage & Disadvantage of Shotcreting
Introduction of Shotcrete Vs Gunite Shotcreting and Guniting are one of the most important and widely used … [Read more...]
What Is Hydraulic Cement | Hydraulic Cement Uses | How to Apply Hydraulic Cement | Advantages & Disadvantages of Hydraulic Cement
Introduction of Hydraulic Cement Water is the biggest enemy of the Civil Engineering Structures. Water can cause great … [Read more...]
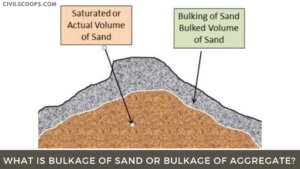
What Is Bulking of Sand | Bulking of Sand Is Caused Due to | Bulking of Sand Graph | Bulking of Sand Formula | Test Procedure to Determine the Bulking of Sand
What Is Bulking of Sand? The free moisture content in the fine aggregate or sand results in bulking of its … [Read more...]
All About Sandbag Cofferdam | What Is Sandbag Cofferdam | Advantages of Sandbag Cofferdam
What Is Sandbag Cofferdam? The cofferdam is a short-term design that supports the building activity behind the … [Read more...]
Top 20 AAC Block Company in India
Introduction Top 20 AAC Block Company in India Best AAC Block Company in India or which AAC Block brand company should … [Read more...]
Detail of Beam Connection | Simple Framing Connection | Semi-Rigid Framing Connection | Rigid Frame Connection
Detail of Beam Connection Beams are connected to the main beams or into the columns. The design of these … [Read more...]
All About Transom Window | What Is a Transom Window | Types of Transom Window
What is a Transom? The transom is blank of the window, but it is one kind of beam which divide the upper of the … [Read more...]
What Is Plumbing Joint | 11 Types of Plumber Joint | Different Types of Pipe Joints and Where Are Use
What Is Plumbing Joint? Pipes are connected with the help of joints. A variety of joints are used in an assembly of … [Read more...]
20 Vastu Tips Before House Construction | Vastu Tips for Different Locations of House | Scientific Facts of Vastu Location of Rooms
Introduction of Vastu Tips for Home If you live in India then you must know about the word ‘Vastu‘. But if you do not … [Read more...]
All About Tile Popping | What Is Tile Popping | Reason for Tile Popping | How to Fix Popped-Up Tiles
What Is Tile Popping? Tile popping is a phenomenon in which the floor tiles pop out, crack, or flex, causing … [Read more...]
Cantilever Bridge | Cantilever Bridge Advantages and Disadvantages | Cantilever Bridge Facts
Introduction of Cantilever Bridge Cantilever Bridge is a special type of bridge which is constructed by using … [Read more...]
What Are Plastic Roads | How to Make Plastic Roads | Who Invented Plastic Roads | First Man Made Plastic Road | Advantages & Disadvantages of Plastic Roads
What Are Plastic Roads? Plastic Roads are roads that are made completely of plastic or composites of plastic made … [Read more...]
20 Types of Construction Materials | What Is Building Materials List | Construction Materials List | Different Materials Used in Building Construction
Introduction of Different Materials Used in Building Construction Building Materials are an essential element in the … [Read more...]
What Is Beam Bridge | Types of Beam Bridges | Beam Bridge Works | Advantages & Disadvantages of Beam Bridges
Introduction of Beam Bridge Bridges are one of the most important parts of the Infrastructure of the country which … [Read more...]
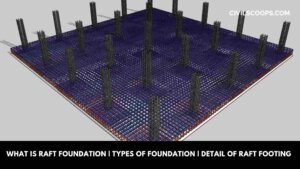
What Is Raft Foundation | Types of Foundation | Detail of Raft Footing
What is a Raft Foundation? A raft foundation, also called a raft foundation, is essentially a continuous slab … [Read more...]
All About Marble Price | What Is Marble | Types of Marble Available in India
Introduction of Marble Price Marble is an easily available material in the market. It is used on floors and tables, … [Read more...]
What Is Inverted Beam | Advantages of Inverted Beam | Purpose of Inverted Beam
What Is Inverted Beam? The Inverted beam is a reinforced concrete beam, different types shape of beam-like I beam, … [Read more...]
All About Door Hinges | 13 Different Types of Door Hinges | What Is Door Hinges | Types of Door Hinges
Introduction of Door Hinges Hinge recreates a vital role in keeping your door in its right position. Hinges are … [Read more...]
All About Load Bearing Wall Construction | How to Tell If a Wall Is Load Bearing | Load Bearing Beam | Non-Load Bearing Wall | Non-Load Bearing Wall Framing
Load Bearing Wall Construction: Load Bearing Wall Construction was most widely used form of construction for large … [Read more...]
Types of Paint Brushes and Their Uses
Types of Paint Brushes and Their Uses Selecting current paint for your house is a great dramatic actor. We can expand … [Read more...]
What Is Guniting | How to Set Guniting Systems | Advantage of Guniting | Disadvantage of Guniting
What Is Guniting? The process was applicable in construction work, where it applied in the stabilization of prone … [Read more...]
All About Floating Houses | What Are Floating Houses | Type of Floating Houses | What Is Floating Building | Floating Architecture Examples
What Are Floating Houses? Floating house is generally a modern type of technology which is very popular in recent … [Read more...]
What Is Calacatta Quartz | 12 Types of Calacatta Quartz
What Is Calacatta Quartz? Calacatta quartz is hardware that features calacatta marmoreal, a model of marmoreal. The … [Read more...]
What Is Pitched Roof | 8 Types of Pitched Roof | Advantages of Pitched Roof
Instruction of Pitched Roof From the beginning of civilization, roofs are one of the essential structural components, … [Read more...]
What Is Bitumen and Bitumens Types?
What is Bitumen? Bitumen is a viscous, solid, or nonvolatile liquid. Bitumen is a complex and complected colloid … [Read more...]
36 Different Types of Plumbing Valve
Plumbing Valve A plumbing valve is a system that is installed in the plumbing system. Plumbing is generally defined … [Read more...]
What Is Sewage Pump | Types of Sewage Pump | Advantages and Disadvantages of Sewage Pump
What Is a Sewage Pump? A sewage pump will apply to move sewage liquids and stability from one place to other. The … [Read more...]
All About Bathroom Accessories | 28 Different Types of Bathroom Accessories
What Are Bathroom Accessories? The bathroom needs every section of the house. Now, bathrooms are essential for us. … [Read more...]
All About Energy-Efficient Homes
Why Are Energy-Efficient Homes Necessary? We are staying in a production where regular energy root will apply at a … [Read more...]
Commercial Building Roof Types | What is Commercial Building Roof
What is Commercial Building Roof? Commercial roofs are available in the marketplace in different types and … [Read more...]
All About Roof Overhangs | 10 Various Types of Roof Overhangs | Standard Roof Overhangs | Overhang Roof Design | Roof Overhangs on Houses
What Is Roof Overhangs? The distance between the house’s siding and the roof determines how much of an overhang … [Read more...]
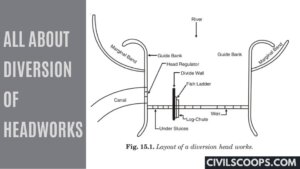
What Is Canal | Classification of Canals | What Is Perennial Canal | Advantages & Disadvantages of Canal Irrigation
Introduction of Canal Canal plays one of the most important roles in transportation and global commerce. The … [Read more...]
All About Transportation of Concrete | What Is Transportation of Concrete | Methods for Transportation of Concrete
What Is Transportation of Concrete? Transportation of concrete is a process where we move freshly prepared concrete … [Read more...]
Bolt Vs Screw | What Is Bolt | What Is Screws
What Is Bolt? A bolt is an externally threaded fastener created for the insertion through holes in the assembled … [Read more...]
Load-Bearing Vs Partition Walls | What Are Walls | Classified of Walls
What Are Walls? Wall is a structural element that divides the space (room) into two spaces (rooms) and also … [Read more...]
All About Gabion Wall | What Is the Purpose of the Gabion Wall | Gabion Wall Construction
What Is the Purpose of the Gabion Wall? A gabion wall is an arresting division designed by mountain rock covered … [Read more...]
Difference Between Rafter and Truss | What Is Rafter | What Is Truss
Introduction of Difference Between Rafter and Truss. The Roof Framing system has undergone a huge revolution over the … [Read more...]
Fineness Modulus of Fine Aggregate | Fineness Modulus of Coarse Aggregate | Sieve Analysis of Fine Aggregate | Sand Zone Classification
Fineness Modulus of Fine Aggregate: The sand fineness module (fine aggregate) is an index number describing the … [Read more...]
What Is Skirting | Types of Skirting | Skirting Replacement Cost | Purpose of Skirting Boards | What Is Skirting Roof | Skirting on Bathroom
What Is Skirting? In civil engineering, skirting is one of the most important part. Skirting is constructed in … [Read more...]
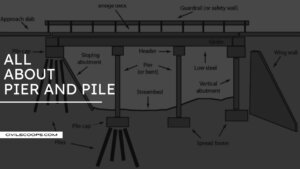
What Is Bridge Pier | Type of Bridge Pier
Introduction of Bridge Human beings have been constructing bridges for about four thousand years. The oldest and … [Read more...]
What Is Bow Window | Types of Bow Windows | Bow Window Sizes | Advantages & Disadvantages of Bow Window
What Is Bow Window? Bow window a type of window which is used to provide extra space to the homeowner. It creates … [Read more...]
Types of Kitchen Faucets
Types of Kitchen Faucets The below kinds of kitchen faucets will checklist. Touchless Kitchen Faucets Pull Out … [Read more...]
Difference Between Beam and Column | What Is Beam | What Is Column
What Is Beam? The beam is a structural element that stands against the bending. Mainly beam carries vertical … [Read more...]
What Is Drywall | Drywall Water Damage | Drywall Water Damage Repair | Cost to Repair Drywall Ceiling Water Damage
What Is Drywall? Drywall is basically a gypsum board which is installed on the interior wall of the house. Drywall … [Read more...]
All About Pony Wall | What Is a Pony Wall | Uses of Pony Wall | Pros and Cons of Pony Wall
What Is a Pony Wall? The pony wall is small. Also, it is known as the ”knee wall,” and this wall is a short design … [Read more...]
Polysulfide Sealant Vs Polyurethane Sealant | Functions of Sealants | What Is Polysulphide Sealant | What Is Polyurethane Sealant
What Is Sealant? The term “Sealant” can be simplified as “sealing elements”. Sealants are the materials, which are … [Read more...]
What Is Mass Concrete | Properties of Mass Concrete | Advantage of Mass Concrete | Disadvantage of Mass Concrete |How Much Mass Density of Concrete
Mass Concrete: Large bridge piers, foundation, and such as dams like the massive structure, the mass concreting … [Read more...]
Nail Vs Screw | What Are Nail | What Is Screw
What Is a Nail? Nail is the most common fasteners used in construction. Up to the end of the Colonial period, all … [Read more...]
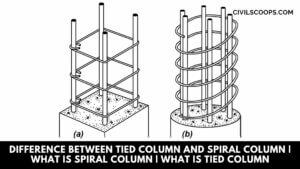
Difference Between Tied Column and Spiral Column | What Is Spiral Column | What Is Tied Column
Introduction of Column The column is one of the most important component parts of the structure. The main … [Read more...]
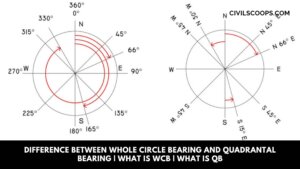
Difference Between Whole Circle Bearing and Quadrantal Bearing | What Is WCB | What Is QB
Introduction of WCB Vs. QB Whole circle bearing(WCB) and Quadrantal bearing(QB) are the two types of bearing which is … [Read more...]
What Is Mezzanine Floor | Types of Mezzanine Floor Construction | Features of Mezzanine Floors | Advantages & Disadvantages of Mezzanine Floors | Uses of Mezzanine Floors | Application of Mezzanine Floors
Mezzanine Floor The mezzanine floor is an intermediate floor of a building, below the open floor. At least twice as … [Read more...]
Types of Concrete Construction Joints | Tips on Placing Joints in Concrete | Tips on Placing Joints in Concrete
Concrete joints are used to compensate when concrete expands or shrinks with changes in temperature. Concrete joints … [Read more...]
13 Types of Houses With Pictures And Advantages and Disadvantages
Types of Houses The types of houses vary from old to new times. Due to turn of people live hood. Now a day’s sum of … [Read more...]
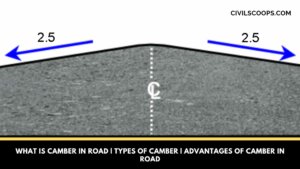
What Is Camber in Road | Types of Camber | Advantages of Camber in Road
What Is Camber in Road? It’s mostly found in the highways the median part of the road surface is elevated with … [Read more...]
What Are Columns | 17 Types of Columns | Different Types of Rcc Columns | Round Column Vs Square Column | Pillar Vs Column
Introduction of RCC Column The whole structure of a building is comprised of different types of components. The … [Read more...]
What are Bay Windows | Different Types of Bay Windows | Bay Window Size | Advantages and Disadvantages of Bay Window
Introduction of Bay Window Bay windows are generally a set of three or more windows that creates an outer angle beyond … [Read more...]
All About Driveways | What Are Driveways | Types of Driveways
What Are Driveways? When there is no offering their knowing factors, driveways can and must will express to be … [Read more...]
Luminous Flux Vs Lumens | What Is Luminous Flux | What Are Lumens | How Bright Is 1000 Lumens
What Is Luminous Flux? Luminous flux, or luminous power, is the measure of the perceived power of light. It … [Read more...]
23 Different Types of Cement Available in India and as Per Is Standards
23 Types of cement that are available and used in India. Ordinary Portland Cement 33 Grade Ordinary Portland … [Read more...]
Best Concrete Mix for Driveway Repair
Best Concrete Mix for Driveway Repair Concrete is the universally applied building object in the universe, and it’s … [Read more...]
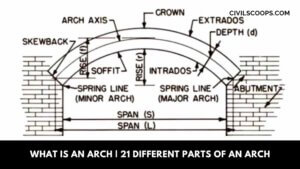
What Is an Arch | 21 Different Parts of an Arch
What Is an Arch? An arch is a design built up in a curved arc with a block arch system, which will connect with … [Read more...]
What Is Building Construction | Steps & Processes of Building Construction | Application of Building Construction | How to Do Planning of Building Construction
Definition of Construction Construction is the methodology of developing a building or infrastructure. … [Read more...]
How to Get Rid of Paint Smell
How to Get Rid of Paint Smell? The paint smell is one of the very annoying things in our house or room. We are … [Read more...]
23 Different Types of Doors
Introduction of Doors Doors are an important part of the buildings which provide entrance and exit in the building. The … [Read more...]
6 Different Types of Concrete Finishes | 7 Types of Wall Finishes | How to Finish Concrete | 3 Types of Concrete Finish Machines | 14 Types of Concrete Finishes for Driveways
Introduction of Concrete Finishing Concrete is a versatile building material which is widely used in the … [Read more...]
What Is Concrete | 31 Different Types of Concrete
What Is Concrete? Concrete is the final product resulting from mixing cement, aggregates (including sand), water, … [Read more...]
17 Types of Properties of Cement | Physical Properties of Cement | Chemical Properties of Cement
Introduction of Properties of Cement Cement is one of the most widely used building materials in the … [Read more...]
What Is Classification of Bricks | Classification of Bricks Different Base
What Is Classification of Bricks? Many types of brick available in the market. All bricks are a different purpose … [Read more...]
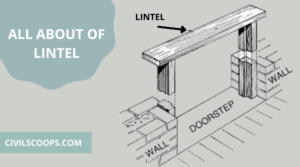
What Is Lintel Beam | Lintel Beam Size | 7 Types of Lintel Beam
What Is Lintel Beam? The lintel is a horizontal flexural member that spans over the openings in the walls for … [Read more...]
What Is Sunken Slab | Advantages & Disadvantages Sunken Slab
What Is Sunken Slab (Sunk Slab)? The sunken slab is one of the familiar and adaptable ways to maintain … [Read more...]
What Is a Concrete Mixer | Types of Concrete Mixer | Specifications of the Concrete Mixer | How to Mix Concrete in a Mixer
Introduction of Concrete Mixer Concrete is one of the main and widely used building materials in construction. Concrete … [Read more...]
What Is Bracing | Types of Bracing | What Does Brace Mean | Advantages & Disadvantages of Bracing Systems
Selection of the right lateral force resisting system has a significant effect on the performance of the structure in … [Read more...]
What Is Caisson Foundation | Types of Caisson Foundation | Advantage, Disadvantage, Application, & Construction of Caisson
What Is Caisson Foundation? Caisson is a watertight structure which it is generally made up of timber, steel, and … [Read more...]
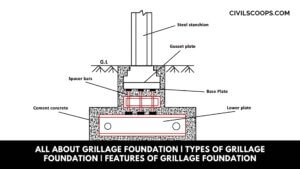
All About Grillage Foundation | Types of Grillage Foundation | Features of Grillage Foundation
Grillage Foundation A foundation consisting of one, two or more layers of beams (typically steel) superimposed on a … [Read more...]
What Is Pier Foundation | Types of Drilled Piers | Advantages and Disadvantages of Drilled Pier Foundations
What Is Pier Foundation? A pier foundation is a collection of large diameter cylindrical columns to support the … [Read more...]
What Is Plaster | Methods of Plastering
What Is Plaster? This id the process of covering rough walls, uneven surfaces in the construction house and other … [Read more...]
All About Asphalt Flooring | What is Asphalt Flooring | Asphalt Flooring Used | Asphalt Flooring Advantages and Disadvantages
What is Asphalt Flooring? This floor is water-resistance, unclean, junction, acid-resistance and charming in look … [Read more...]
All About Drywall Water Damage Repair
Drywall Water Damage Repair What is drywall? A question often asked by many people. So before knowing how to fix … [Read more...]
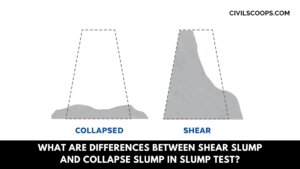
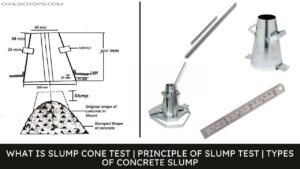
What Are the Differences Between Shear Slump and Collapse Slump in Slump Test?
What Are Differences Between Shear Slump and Collapse Slump in Slump Test? The differences that can be seen between … [Read more...]
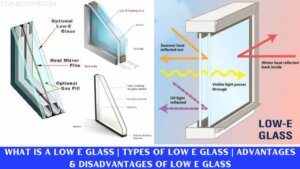
What Is Glass | Types of Glass Used in Construction | Qualities of Glass | Advantages & Disadvantages of Glass
What Is Glass? Glass is generally the oldest material and fancy material which is used in the building industry and … [Read more...]
What Is Hempcrete | Hempcrete Blocks | Advantages & Disadvantages of Hempcrete Blocks | Applications of Hempcrete
What Is Hempcrete? Hempcrete is a bio-composite that is made from the inner wood core of the hemp plant and mixed … [Read more...]
Quality Testing of Sand for Concrete | Quality Testing of Sand for Construction | Types of Sand Test
Quality Testing of Sand at The Construction Site for The Concrete There are different methods for testing the … [Read more...]
All About of Corrosion | What Is Corrosion | 9 Different Types of Corrosion
What Is Corrosion? Corrosion is a native method that transforms pure metals into a robust synthetic form like oxide … [Read more...]
What Is Hard Hat | Hard Hat Colour Definition | Different Hard Hat Colour Codes | Types of Safety Helmets | Classification of Hard Hats
What Is Hard Hat? Hard hats are one of the most important and essential accessories which are widely used on … [Read more...]
How Cement is Made | Cement Ingredients | History of Cement
How Cement Is Made? This Portland cement is a fundamental component of concrete. Concrete is produced when portland … [Read more...]
What Is Pier and Beam Foundation | Advantages & Disadvantages of Pier and Beam Foundations | Pier and Beam Foundation Design | How to Build a Post and Pier Foundation
Introduction of Pier and Beam Foundation The foundation plays important role in the construction of the building. … [Read more...]
What Is Stone | Types of Stone | Uses of Stones
What Is Stone? Stone is a naturally available building material that has been used in the early age of … [Read more...]
All About Soak Pit Design | Health Aspects | Operation and Maintenance of Soak Pit | Applicability of Soak Pit Design
Introduction of Soak Pit Design If there is no intention or need to reuse wastewater, collected rainwater or gray … [Read more...]
All About Undercoat | What Is Undercoat | What Does Undercoat Paint Do | Why Use Undercoat | Difference Between Primer and Undercoat
Introduction of Undercoat Paint plays a crucial role in the appearance of the structure. Paint also protects the … [Read more...]
What Is Septic Tank | How Does A Septic Tank Work | Septic Tank Design based Per User Consumption
What Is Septic Tank? A septic tank collects and treats wastewater in a property that isn’t linked to the mains … [Read more...]
What Is Folded Plate | Folded Plate Structure | Folded Plate Roof Construction Details | Folded Plate Staircase | What Are Folded Plate Roofs
What Is Folded Plate? When assemblies of flat plates are rigidly connected together with each other along their … [Read more...]
What Is Window Glazing | Types of Window Glazing
What Is Window Glazing? Window glazing is one of the best innovations that help to maximize the energy of the … [Read more...]
What Is Shotcrete | Shotcrete & Concrete | Shotcrete Technology | Types of Shotcrete Technology | Advantages of Shotcrete | Disadvantages of Shotcrete
What Is Shotcrete? Shotcrete is a kind of refined concrete drizzled by a gas hose-pipe nozzle at high pressure … [Read more...]
All About Brick Bat Coba | What Is a Brick Bat Coba | Procedure of Brick Bat Coba Waterproofing | Advantages & Disadvantage of Brick Bat Coba Waterproofing
Introduction of Brick Bat Coba We spent a lot of money on the interior and exterior view of our home. But many people … [Read more...]
What Is Linear Measurement Surveying | Types of Linear Measurement Surveying
Introduction of Measuring Distance Distance measurement is usually regarded as the most fundamental of surveying … [Read more...]
What Is DLC (Dry Lean Concrete) | Advantage of DLC (Dry Lean Concrete)
Dry Lean Concrete: Everything You Need to Know About Dry Lean Concrete Dry Lean Concrete is a mixture in which the … [Read more...]
Carbon Steel vs. Stainless Steel | What Is Carbon Steel | What Is Stainless Steel
What Is Carbon Steel? One of the trendy and widely used construction materials in the world contains steel. Steel … [Read more...]
All About Soffit | What Is Soffit | Different Types of Soffit | What Is Fascia | Advantages & Disadvantages of Fascia and Soffits |
Instruction of Soffits and Fascia The Soffits and fascia play a vital role in the exterior of the structure. Many … [Read more...]
Benchmark in Surveying | TBM in Surveying | GTS Benchmark| Permanent Benchmark | Arbitrary Benchmark
What Is a Benchmark in Surveying? Benchmark is a permanent and temporary reference point in surveying. The term is … [Read more...]
All About FSI and FAR | What Is FSI | What Is FAR | What Is Premium FSI | FSI Full Form | FAR Full Form
What Is FSI? FSI Full-Form Floor Space Index FSI (Floor Space Index) means Floor space index- the ratio of the … [Read more...]
What Are Walls | What Is Interior Walls | 25 Types of Wall | Types of Interior Wall Materials | Types of Wall Construction | Types of Load Bearing Wall
What Are Walls? A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area, carries a load, provides security, … [Read more...]
All About PPC Cement | What Is PPC Cement | Types of Pozzolana Materials | Manufacture of Portland Pozzolana Cement | Uses of Portland Pozzolana Cement
What Is PPC Cement? Portland Pozzolana cement is an incorporated cement produced in that certain ratio by the … [Read more...]
What Is Admixture | 26 Types of Admixtures | Advantages & Disadvantages of Admixture
What Is Admixture? Admixture is artificial or natural materials added to concrete, in addition to cement, water, … [Read more...]
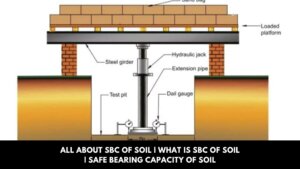
All About SBC of Soil | What Is SBC of Soil | Safe Bearing Capacity of Soil
Introduction of SBC of Soil The first test to be carried out before construction is the soil’s safe bearing capacity. … [Read more...]
14 Types of Plaster Finishes (List of Plaster Finishing)
What is Plaster Finishes? Having your walls up is not the end of the building construction process. If you want to … [Read more...]
20 Types of Construction Beam & Their Uses
Introduction of Construction Beams There are various types of construction beams are used in buildings depending upon … [Read more...]
What Is Pneumatic Structures | Types of Pneumatic Structures | Advantages & Disadvantages of Pneumatic Structures | Uses of the Pneumatic Structures
What Is Pneumatic Structures? Pneumatic Structures are a special type of structure that is generally characterized … [Read more...]
What Is a Concrete Vibrator | 6 Types of Concrete Vibrator | Concrete Vibrator Alternatives | Advantages of Concrete Vibrator | Disadvantage of Concrete Vibrator
What Is a Concrete Vibrator? A concrete vibrator is a machine used for construction purposes in civil projects. … [Read more...]
What Is RQD | Advantages of Rock Quality Designation | Limitations of Rock Quality Designation (RQD)
Introduction of RQD In Civil engineering, different parameters are used to characterize the Quality of the rocks. … [Read more...]
Extra Rapid Hardening Cement | Advantages & Disadvantages of Extra Rapid Hardening cement | Applications, Properties & Uses of Extra Rapid Hardening cement
Introduction to Extra Rapid Hardening Cement Time is one of the most important factors in construction projects. Time … [Read more...]
What Is a Retaining Wall | Types of Retaining Walls | How Retaining Walls Work | Retaining Wall Detail | Retaining Wall Anchoring Retaining Wall Systems
What Is a Retaining Wall? A retaining wall is a design of a structure; it is built when there is a desired change … [Read more...]
RCC Full Form | What Is RCC | Advantages & Disadvantages of Reinforced Cement Concrete | Properties of RCC | What Does RCC Stands for
Introduction of RCC ( Reinforced Cement Concrete) Concrete is a versatile material that is widely used for the … [Read more...]
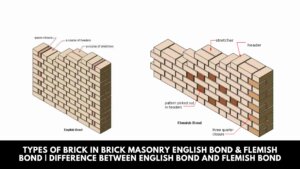
Types of Brick in Brick Masonry English Bond & Flemish Bond | Difference Between English Bond and Flemish Bond
Introduction of English Bond & Flemish Bond Various types of bonds in brick masonry used for wall construction … [Read more...]
Difference Between Formwork, Shuttering, Centering, Staging & Scaffolding
What Is Formwork? The construction of a concrete building requires formwork to support the slabs (horizontal … [Read more...]
What Is Under-Reamed Pile Foundation | Uses of Under-Reamed Piles | Advantages & Disadvantages of Under-Reamed Piles
Reamed Meaning Reamed is a cutting procedure for which a cutting process creates a very precise hole size. What Is … [Read more...]
What Is Chicken Mesh for Plaster | Type of Chicken Mesh for Plaster | Why Use Chicken Mesh for Plaster
What Is Chicken Mesh for Plaster? Chicken wire has specific properties for plastering use. Chicken wire mesh is … [Read more...]
What Is Crane | 19 Different Types of Cranes
What Is Crane? A crane is a significant type of construction machine that’s utilized to move loads horizontally. … [Read more...]
What Is Well Foundation | Component of Well Foundation
What Is Well Foundation? Well Foundation is a type of deep foundation that is generally provided below the water … [Read more...]
What Is Plaster | Types of Plaster As Per Material | Defects In Plastering
What Is Plaster? This is the process of covering rough walls, uneven surfaces in the construction house, and other … [Read more...]
10 Construction Certifications and Where to Get Them
Introduction of Construction Certifications Certification can be a huge addition to a construction worker’s resume, as … [Read more...]
What Is Hardened Concrete | Properties of Hardened Concrete
What Is Hardened Concrete? Hardened concrete is a type of concrete that is strong and have the capacity to bear the … [Read more...]
What Is Fire Escape Staircases | Types of Fire Escaping Stairs | What Is the Importance of Fire Escape in the Building | What Are the Fire Staircase Requirements
Introduction of Fire Escape Staircase Urbanization leads to the Construction of the High Rise building. It is also … [Read more...]
What Are Hollow Bricks | Advantage of Hollow Bricks | Disadvantage of Hollow Bricks | Sizes of Bricks Blocks | How to Make Hollow Bricks
Introduction of Hollow Bricks Bricks are one of the most essential and commonly used Building units in the construction … [Read more...]
What Is Bamboo Flooring | Bamboo Flooring Pros and Cons
What Is Bamboo Flooring? Bamboo flooring is evolving as a popular choice to standard hardwood flooring as it has … [Read more...]
All About Retrofitting | What Is Retrofitting | Why Need Retrofitting | Advantages And Disadvantages of Retrofitting of Building
What Is Retrofitting? Retrofitting is the modern technique or methodology used to increase the structure’s … [Read more...]
Types of Coffered Ceiling | What Is Coffered Ceiling | Coffered Ceiling Cost
What Is Coffered Ceiling? The coffered ceiling is like the baroque style which is invented in the early era of the … [Read more...]
Automation in Construction | Advantages of Automation | Applications of Automation | Where Are Use Automation in Construction Sector
Introduction of Automation in Construction Construction is one of the largest industries all over the world. … [Read more...]
What Is Building | Types of Building
What Is Building? A building is a structure that consists of a roof, floor, walls, foundations, door, windows, etc. The … [Read more...]
Top-Down Construction | What Is a Top-Down Construction | Advantages & Disadvantages of Top-Down Construction
Top-Down Construction The easy description of the top-down construction method will help the storeroom surface of the … [Read more...]
All About Mastic Asphalt Flooring | What Is the Meaning of Mastic Floor | Mastic Asphalt Flooring Cost | Where Is Asphalt Flooring Used
Mastic Asphalt Flooring The surface of your house is another point, and there is no privacy. Its humidity and … [Read more...]
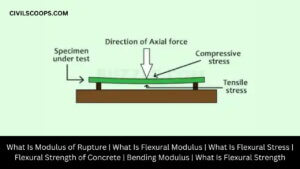
What Is Modulus of Rupture | What Is Flexural Modulus | What Is Flexural Stress | Flexural Strength of Concrete | Bending Modulus | What Is Flexural Strength
Modulus of Rupture of Concrete Beam: Modulus of rupture of Concrete beam indicates the amount of compression and … [Read more...]
Definition of Design Period | Why Design Period is Provided | Factors Affecting Design Period | Design Period Values
Definition of Design Period: The design period could be defined as the number of years in the near future in which … [Read more...]
How Much Does It Cost to Pump a Septic Tank | Why Septic Tanks Required Pumping | Typical Problems Leading to Septic Tank Pumping
Information of Septic Tanks System A septic tank is basically an underground structure that is made from concrete, … [Read more...]
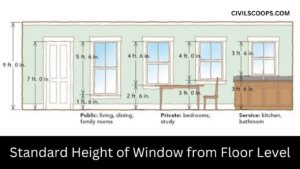
Standard Height of Window from Floor Level | Window Sill Height from Floor
Standard Height of Window from Floor Level To the base of the window from the floor level up, the height is known as … [Read more...]
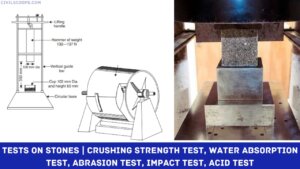
Properties of Stones | Requirements of Good Building Stones
Properties of Stones The following properties of the stones should be looked into before selecting them for … [Read more...]
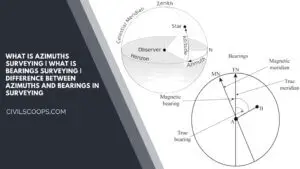
What Is Azimuths Surveying | What Is Bearings Surveying | Difference Between Azimuths and Bearings in Surveying
What Is Azimuths Surveying? Azimuths are defined as horizontal angles that are measured from the reference meridian … [Read more...]
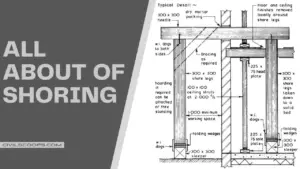
What Is Falsework | Types of Falsework | Causes of Falsework Failures
Falsework Means The temporary structure is used to support a permanent structure, material, plant, equipment, and … [Read more...]
Alignment of Road | Alignment in Design | Horizontal Alignment of Road | Vertical Alignment of Road
Alignment of Road: Alignment is the center line position of the highway on the ground; it is also termed highway … [Read more...]
Mortar Vs Grout | What Is Mortar and Grout | Type of Mortar and Grout | Difference Between Mortar and Grout
What Is Mortar? The term mortar is used to indicate a paste prepared by adding the required quantity of water into … [Read more...]
What Is a Classified Road | Classification of Roads in India
Introduction of Indian Road India is a very vast country and where the economic development of the country mainly … [Read more...]
What Is Levelling in Surveying | Types of Levelling in Surveying | Advantages & Disadvantages of Levelling in Surveying
Introduction to Levelling Levelling is one of the most important parts of surveying before starting the construction of … [Read more...]
What Is Dressing of Stone | Types of Dressing of Stone
What Is Dressing of Stone? Dressing of stone is a process of providing a proper shape, size and smooth finish to the … [Read more...]
What Is Injection Grouting | Types of Injection Grouting | Different Types of Grouting Materials
What Is Injection Grouting? Injection Grouting is defined as the process of filling the cracks, and voids under … [Read more...]
15 Difference Between Bridge and Culvert | What Is Bridge | What Is Culvert
What is Bridge? A Bridge, a connecting structure, create bonding between different disconnected parts of a country, … [Read more...]
Skeleton Frame | What Is Building Skeleton | What Is Steel Structure Building | Use of Steel Frame Structures| Advantages & Disadvantage of Steel Frame
What Do You Mean by Skeleton Frame? A skeleton frame is a framed structure often used for the construction of … [Read more...]
Plasticizer Vs Superplasticizer | What Is Plasticizer In Civil | What Is Superplasticizer In Civil
What Is Plasticizer In Civil? Plasticizers us in concrete for the workability, Strength, and Durability of … [Read more...]
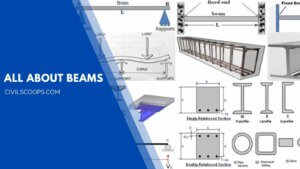
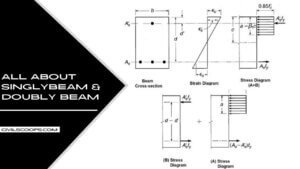
22 Types of Beams | Standard Size of Beams
Introduction of Beam The Beam is the horizontal structural member which is used to resist the loads which are … [Read more...]
What Is Bridge | Components of Bridge and Their Function
What Is Bridge? A bridge is a system for transporting road traffic and perhaps other moving loads across a deep … [Read more...]
What Is Honeycomb in Concrete | Cause of Honeycomb in Concrete| Cure of Honeycomb in Concrete | Types of Grouting
What Is Honeycomb In Concrete? This takes place when the mortar doesn’t fill the distance between the coarse aggregate … [Read more...]
What Is Dampness | Requirements of an Ideal Material for Damp-Proofing | Materials Used for Damp-Proofing
What Is Dampness? The most common source of dampness is due to the capillary attraction of sub-soil water in the … [Read more...]
All About Bond Beam Block vs Lintel Block | What Is Bond Beam | What Is a Lintel Block | Bond Beam Detail | Advantages & Disadvantages of Bond Beam Blocks
Introduction of Bond Beam Block vs Lintel Block: Bond beam is a horizontal structural element that is generally … [Read more...]
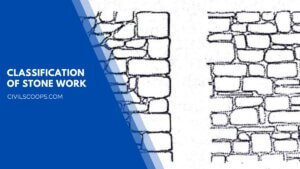
Classification of Stone Work | What Is Stone Masonry
What Is Stone Masonry? The construction of stones bonded together with mortar is termed stone masonry. Where the … [Read more...]
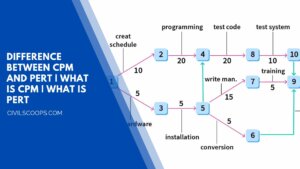
14 Difference Between CPM and PERT | What Is CPM | What Is PERT
The network technique is a major advance in management science. This technique is based on the basic characteristics … [Read more...]
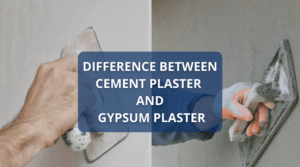
All About Gypsum Plaster | What Is Gypsum Plaster | 15 Advantage of Gypsum Plaster | Disadvantage of Gypsum Plaster
History of Gypsum Plaster Gypsum plaster has been used as an interior wall and ceiling finish for thousands of … [Read more...]
All About M Sand | What Is M Sand | Properties of Manufactured Sand | Advantages & Disadvantages of Manufactured Sand
What Is M Sand? Manufactured sand (M-Sand) is an additional river sand for concrete structures. Manufactured sand … [Read more...]
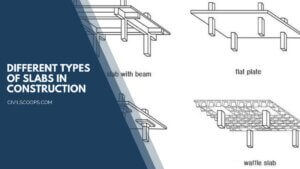
19 Different Types of Slabs in Construction | What Is a Slab | Types of Slabs
What Is a Slab? Slabs are structural elements manufactured from concrete constructed to produce flat surfaces, … [Read more...]
All About Sand | What Is Sand | 29 Types of Sand | Composition of Sand
What Is Sand? Sand could be a blend of bijou grains of rock & granular materials, which is distinctly defined … [Read more...]
All About Uscs | Which Test Gives a Better Estimation of the Friction Angle | Introduction of USCS ( Unified Soil Classification System )
Which Test Gives a Better Estimation of the Friction Angle? Usually, the economics of the project dictates the type of … [Read more...]
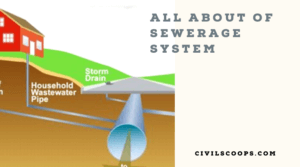
What Is Sewerage | What Is Storm Drain | Household Drain Systems | House Drainage Parts and Components | Types of Sewer Pipes | Sanitary Pipework
What Is Sewerage? A sewerage system, or waste product assortment system, maybe a mesh of pipes, pumping stations, … [Read more...]
What Are Defects in Painting | 18 Types of Defects in Painting | How to Prevent Defects in Painting
What Are Defects in Painting? Painting is one of the important finishing works used in structural construction in … [Read more...]
Top 10 Companies for Environmental Engineers to Work For
With climate change upon us, we are counting on engineers like you to help save the planet so no pressure. Environmental … [Read more...]
What Is Consistency of Cement | What Is Initial Setting Time of Cement | What Is Final Setting Time of Cement
What Is Consistency of Cement? Any Cement paste requirement of minimum water in cement paste to initiate the chemical … [Read more...]
All About Glass Block Floor | Glass Block Floor | Advantages of Glass Blocks | Disadvantages of Glass Blocks
Introduction of Glass Block Floor Glass blocks are one of the unique construction materials which were developed in … [Read more...]
All About Reinforced Brick Masonry | What Is Reinforced Brick Masonry | Construction of the Reinforced Brick wall
What Is Reinforced Brick Masonry? Reinforced brick masonry is totally different from the normal method of brick … [Read more...]
All About Slab Construction | What Is Slab Construction | Types of Slab Design
Introduction of Slab Construction The concrete slab is a horizontal surface of a residential building or commercial … [Read more...]
All About Vitrified Tiles | What Are Vitrified Tiles | Advantages of Vitrified Tiles
Introduction of Vitrified Tiles Tiles are one of the most important parts of the interior of the building. Tiles give a … [Read more...]
Steel Is Most Trusted TMT Bar in India?
Introduction of Shyam Steel Industries Ltd. Shyam Steel Industries Ltd started its journey in 1953 with a small factory … [Read more...]
All About Roller Compacted Concrete | What Is Roller Compacted Concrete | Roller Compacted Concrete Process
Roller Compacted Concrete Roller Compacted Concrete also known as RCC. Roller Compacted Concrete takes its name … [Read more...]
All About Plaster | What Is Plaster | Requirement of Good Plaster | Types of Plasters
What Is Plaster? This is the process of covering rough walls, uneven surfaces in the construction house, and other … [Read more...]
All About Aggregates | How do Shape and Size Matter in Aggregate | Fine Aggregate Vs Coarse Aggregate
Aggregates Aggregates are inert granular, substances like either sand gravel or crushed stone which are an important … [Read more...]
All About Mix Design of Concrete | What Is Mix Design of Concrete | Nominal Mix | Design Mix
What Is Mix Design of Concrete? Concrete mix design involves a process of preparation in which a mix of ingredients … [Read more...]
What Is Seasoning of Timber | Type of Seasoning of Timber | Benefit Seasoning of Timber
What Is Seasoning of Timber? The wood spice process is the process by which the moisture in the wood is reduced to the … [Read more...]
What Is Unit Weight | What Is Density | What Is Unit Weight Material | Unit Weight Building Materials
What Is Unit Weight? The ratio of the weight of a material to its volume is its unit weight, sometimes termed specific … [Read more...]
Joints of Stone Masonry | Type of Joints of Stone Masonry | General Principles Which Are Used in the Construction of Stone Masonry
Joints of Stone Masonry The construction which is done with the help of stones and bonded together with mortar is … [Read more...]
WPC Board Vs Plywood | Which Should Be a Better Choice | What Is WPC Board | What Is Plywood
Introduction of WPC Board Vs. Plywood The Interior of the structure plays a vital role in improving the aesthetical … [Read more...]
What Is Dry Pack Mortar | Advantages of Dry Pack Mortar | Disadvantages of Dry Pack Mortar
Introduction of Dry Pack Mortar Dry pack mortar is simply a mixture of cement, sand, and water in the appropriate … [Read more...]
What Is Shell Structure | 11 Types of Shell Structure | Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages of Shell Structure
Introduction to Shell Structure Nowadays there is a need for construction of the buildings which are in closed-form … [Read more...]
Forces Acting on a Gravity Dam | Construction of Gravity Dam | Advantages & Disadvantages of Gravity Dam | Applications of Gravity Dam
Introduction of Gravity of Dam The Gravity dam is defined as a structure that is designed and constructed such that the … [Read more...]
Stone Masonry vs Brick Masonry | What Is Brick Masonry | What Is Stone Masonry
What Is Brick Masonry? It is constructed by placing the bricks in the mortar in an orderly manner to produce solid … [Read more...]
Difference Between Flyover and Bridge | What Is Flyover | What Is Bridge
What Is Flyover? Flyovers, over a flyover, underpasses, overpasses, etc. are some examples of engineering marvels … [Read more...]
What is CBR Test in Civil
What is CBR Test? CBR Test Full Name is California Bearing Ratio (CBR) In the year 1930, this test was developed by … [Read more...]
What Is Quarrying of Stones | Methods of Quarrying | Selection of a Site for Quarrying of Stones
What Is Quarrying of Stones? You must have heard the words mine and quarry. The operations of taking out the materials … [Read more...]
First Angle Projection & Third Angle Projection Symbol (Orthographic Projection)
What Is Orthographic Projection? Orthographic views consist of one, two, or more separate aspects of an object taken … [Read more...]
Piling for Foundation | Use of Pile Foundation | Characteristics of Pile Foundation
What Is Foundation? All engineered construction work resting on the earth must be carried by some interfacing element … [Read more...]
What is Soft Flooring | Types of Soft Flooring | Advantages & Disadvantages of Soft Flooring | Use of Soft Flooring | Maintenance of Soft Flooring
What is Soft Flooring? Soft flooring is defined as a secondary floor to some extent sort of hard flooring. The adding … [Read more...]
What Is a Buttress Dam | Types of Buttress Dam | Advantages & Disadvantages of Buttress Dam | Application of Buttress Dam
What Is a Buttress Dam? The buttress dam is a variation or improvisation of the Gravity Dam. Buttresses are just like … [Read more...]
What Is a Low E Glass | Types of Low E Glass | Advantages & Disadvantages of Low E Glass
What Is a Low-E Glass? Low-E Glass full name Low-Emissivity Glass, glass was created to minimize the amount of … [Read more...]
What Is Soundness of Cement Test
What is the Soundness of Cement Test? The soundness of the cement test Changes in volume after completion of the mold … [Read more...]
What Is Varnish | Types of Varnish | Classification of Varnishes | Advantages & Disadvantages of Varnish | Application of Varnish | How to Apply Varnish to Wood
What Is Varnish? Varnishes are very much translucent substances that had a safe surface layer in almost the same … [Read more...]
Difference Between Timber And Wood | What is Wood | What is Timber
Difference Between Timber And Wood: What What Is Wood? Wood is a tough and fibrous substance which forms a major … [Read more...]
Stepped Footing | House Foundation on Slope | How to Build a Foundation on the Slope
Introduction of Stepped Footing The main function of the foundation is to give support to the Structures and … [Read more...]
What Is Weirs | Types of Weirs | Advantages & Disadvantages of Weirs | Operation & Limitations For Weir | Limitations of Weirs | Location of Weirs
What Is Weirs? Weir is characterised as a barrier through which water flows into an open channel. The edge or surface … [Read more...]
What Is Sealing Brick Work| Advantages of Brick Sealer | Types of Brick Sealer
What Is Sealing Brick Work? Although brick is hard and sturdy, however, it is additionally abysmally porous, thus it … [Read more...]
15 Different Types of Cement and Their Uses
Types of Cement and Their Use Mainly cement is classified into two categories based on setting time and hardening; … [Read more...]
10 Different Between Mortar And Concrete | What Is Mortar & Concrete | Types of Mortar & Concrete
What Is Mortar? Mortar is a mixture in varying proportions of binding material like cement or lime and an inert … [Read more...]
Types of Bearing Capacity Failures of Foundation | Bearing Capacity Definitions | Theory of Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity
Bearing Capacity Definitions Bearing capacity: It is the loading capacity of the soil. Ultimate bearing capacity (qu): … [Read more...]
Civil Engineering Basic Knowledge
Abbreviation, Full Forms, and Terminology. Construction Materials 1. Cement: Cement is essentially attained by … [Read more...]
Difference Between Heartwood and Sapwood | What Is Sapwood | What Is Heartwood
Difference Between Heartwood and Sapwood The main difference between the heartwood and the sapwood is that the … [Read more...]
Difference Between Mat Foundation and Spread Footing | What Is Mat Footing | What Is Spread Footing
Introduction of Mat Foundation Vs Spread Footing Mat foundation is also called a raft foundation. Generally, it is a … [Read more...]
11 Difference Between Silt and Clay
Silt and clay both are the result of the chemical as well as a physical breakdown of the minerals which are present in … [Read more...]
What Is Frost Wall | Types of Frost Wall | Requirements for Frost Wall Construction | Application of Frost Wall | Advantages of Frost Wall | Uses of Frost Wall
What Is Frost Wall? The Frost wall or frost-protected wall structure is built to keep soil below the building against … [Read more...]
What Is Plate Load Test | Method of Plate Load Test | Limitations of Plate Load Test | Advantages & Disadvantages of Plate Load Test
What Is Plate Load Test? The Plate Load Test is a field method to identify the ultimate bearing capacity of the … [Read more...]
What Is Isolated Foundation | Types of Isolated Foundations | Shape of Isolated Foundations | Design of Isolated Foundation | Advantage & Disadvantageof Isolated Foundation
What Is Isolated Foundation? Isolated foundations are structural components often used to distribute and deliver loads … [Read more...]
What Is Tunel | Types of Tunnels | What Are Tunnels Used for | Classification of Tunnel | How Are Tunnels Built |Advantages & Disadvantages of Tunnels
What Is Tunel? Tunnels are artificial underwater tunnels that are built without damaging the surface of the earth. … [Read more...]
What Is Stone | Classification of Stones | Application of Stone | Advantages of Stone | Disadvantages of Stone
What Is Stone? Stones were some of the essential construction materials in civil engineering. Stones are formed of … [Read more...]
Difference Between Coarse-Grained Soil and Fine-Grained Soil | What Is Coarse-Grained Soil | What Is Fine-Grained Soil
Introduction of Coarse-Grained Soils Vs Fine-Grained Soils Soil is one of the most important components which should be … [Read more...]
How to Calculate Steel in RCC Slab
Introduction of Calculate Steel in Rcc Slab The slab is one of the most important structural elements in the … [Read more...]
What Is Vacuum Concrete | Application of Vacuum Concrete | Advantages & Disdvantages of Vacuum Concrete
What Is Vacuum Concrete? Vacuum concrete is that type of concrete where the extra water is removed for increasing the … [Read more...]
What Is Earthen Dam | Types of Earthen Dam | Failure of Earthen Dam | Application of Earthen Dam | Advantage & Disadvantage of Earthen Dam
What Is Earthen Dam? The dam which is constructed fulfilled by the earth is known as the earthen dam. The earthen dam … [Read more...]
What Is Inverted Arch Footing | Where Are Uses Inverted Arch Footing | Advantages of Inverted Arch Footing | Disadvantages of Inverted Arch Footing
What Is Inverted Arch Footing? The Inverted Arch Footing is built in areas where the carrying or bearing capacity … [Read more...]
10 Different Types of Loads on Structures | What Are Structural Loads
Introduction of Structural Loads Structural analysis is a salient feature of a design of buildings as structural loads … [Read more...]
What Is Kelly Ball Test | Test Procedure of Kelly Ball Test | Use of the Kelly Ball | Advantages & Disadvantages of Kelly Ball Test
Definition of Kelly Clamp Kelly clamp is defined as a vertically movable pinch clamp fastened to a graduated stick to … [Read more...]
What Is Composite Masonry | 6 Different Types of Composite Masonry
What Is Composite Masonry? Composite masonry is the one that is constructed out of two or more types of building units … [Read more...]
What Is a Concrete Surface Retarder | Types of Retarders | Advantages & Disadvantages of Retarder in Concrete
What Is a Concrete Surface Retarder? Surface retarders, also know surface “deactivators,” are applied to fresh concrete … [Read more...]
Which of the Following Is a Way That Slopes Fail | Types of Slope Failure | Types of Slopes in Geography | Causes of Slope Failure
Which of the Following Is a Way That Slopes Fail? The large block falls from cliffs. Rocks, soil, sediment & ice … [Read more...]
How Pre Engineered Building Is Better Than Conventional Building | Advantages & Disadvantages of Pre Engineered Buildings | Use of Pre Structure
Introduction of PRE Engg Building The Steel industry is growing rapidly all over the world. Steel is widely used … [Read more...]
Difference Between Pier and Abutment | What Is Pier | What Is Abutment
What Is Pier? These Piers provide vertical supports for spans at intermediate of different points and perform both … [Read more...]
What Is Flyover | Types of Flyover | Flyover Design | Flyover Construction
What Is Flyover? A Flyover is a bridge that carries one railroad or road over another. Flyover can also be described as … [Read more...]
Pile Cap Design | Pile Cap Construction | Piles Structure | Pile Cap Foundations | Square Piling Caps | Pile Cap Reinforcement
Introduction of Pile Cap The pile cap is a type of thick concrete mat-like structure which rests on the pile (timber or … [Read more...]
What Is Diversion of Headworks (Rivers) | Types of Diversion Headworks
What Is Diversion of Headworks (Rivers)? For direct irrigation from the river, a structure constructed across a … [Read more...]
Structural Audit Definition | Structural Audit of Residential Building | Why Structural Audit | Need of Structural Audit | When to do Structural Audit
Structural Audit Definition Structural Audit can be defined as a very important approach to understanding the distress … [Read more...]
How to Build a Suspension Bridge | Suspension Bridge Facts | Suspension Bridge-Strength & Weaknesses | Advantages and Disadvantages of a Suspension Bridge
Introduction of a Suspension Bridge Suspension bridges are one of the most popular choices in Bridge construction … [Read more...]
Kani’s Method | Advantages of Kani’s Method | How to Use Kani’s Method for Analysis | Procedure of Kani’s Method
Kani’s Method Structural analysis is one of the most important parts of civil engineering. The construction of high … [Read more...]
Grey Water vs Black Water | What Is Grey Water | What Is Black Water
Water is a crucial asset – without it, we simply would not survive. Every day we use it, and most of it is collected as … [Read more...]
Difference Between Mild Steel and Stainless Steel | What Is Stainless Steel | What Is Mild Steel | Mild Steel Properties
What Is Stainless Steel? Stainless steel is the form a steel alloy with a chromium content of 11.5 percent by weight. … [Read more...]
What Is Cantilever | What Is Cantilever Footing | Design of the Cantilever Footing
What Is Cantilever? Cantilever is basically a structural element that extends horizontally and has supported at only … [Read more...]
Kerbs In Roads | 4 Different Types of Kerbs | Shape of Kerbs | Materials of Kerbs in Roads | Kerb Height | What Is Kerb Stone | Materials of Kerb Stone | Road Kerb Details
Kerbs In Roads The top of the kerbs should be 100 mm above the road surface. With the pavement, the kerb is laid on … [Read more...]
What Is Concrete Resurfacing | How to Resurface Concrete | Concrete Resurfacing Material | Concrete Repair and Resurfacing
What Is Concrete Resurfacing? Concrete resurfacing is the process to provide a brand new look to damaged … [Read more...]
Difference Between Lime and Cement | What Is Lime (Hydraulic) | What Is Cement
What Is Lime (Hydraulic)? It is an important binding material used in building construction. Lime has been used as the … [Read more...]
What Is Rolling Margin | Procedure of Rolling Margin
What is Rolling Margin? The rolling margin is the difference between the actual weight of round bars … [Read more...]
What Is False Ceiling | Why We Need False Ceiling | Types in False Ceilings | Advantages & Disadvantage of False Ceiling | False Ceiling Installation Steps by Step
Introduction of False Ceiling The ceiling is the first thing which a person noticed whenever we entered the room. The … [Read more...]
Difference Between Bitumen and Tar | What Is Bitumen | What Is Tar
What Is Bitumen? The bitumen is the binding material that is present in asphalt. It also sometimes called mineral tar. … [Read more...]
Different Types of Washers | When to Use Washers | How to Use a Washers | Shapes of Washers
Introduction of Washers A washer may be a disk formed plate (made of metal, rubber, or plastic) used to garrison the … [Read more...]
Is Steel Stronger Than Concrete | Steel and Concrete Construction Costs | Steel Vs Concrete | How Strong Is Concrete | Concrete Vs Steel Building Cost
Is Steel Stronger Than Concrete? Steel has more lightweight and higher strength than concrete. And also steel built a … [Read more...]
What Is Cinder Block | Cinder Block Properties | Shapes of Cinder Blocks | Advantages of Cinder
What Is Cinder Block? Cinder blocks are totally different from concrete blocks. Concrete and cinder blocks are made … [Read more...]
Core Cutter Method | What is Compaction of Soil
What is Compaction of Soil? Compaction of soil is area compacted by mechanical method for remove air voids in compacted … [Read more...]
What Is Plaster | Plaster Ratio | History of Plastering | Requirements of Good Plaster
What Is Plaster? Plastering is the process of covering uneven surfaces and rough walls in the construction of … [Read more...]
What Is Self Compact Concrete | What Is Slump Flow Test | Equipment for Slump Flow Test | Procedure of Slump Flow Test
What Is Self Compact Concrete? Making concrete structures without vibration has been done in the past. For example, the … [Read more...]
Tests on Stones | Crushing Strength Test, Water Absorption Test, Abrasion Test, Impact Test, Acid Test
Tests on Stones To determine the required properties of stones, the following tests Could be conducted: Crushing … [Read more...]
What Is Drip Irrigation | Drip Irrigation Advantages | Types of Irrigation | Drip Irrigation System
What Is Drip Irrigation? Drip irrigation is a type of micro-irrigation system that has the potential to save water and … [Read more...]
What Is Clay Product | Types of Clay Product
What Is Clay Product? There is a wide variety of structural clay products, broadly classified as facing materials, … [Read more...]
Requirements of Good DPC | Prevention of Dampness | Methods of Damp proofing
Requirements of Good DPC Here, the list of requirements of a good DPC are as follows. Totally impervious and … [Read more...]
21 Difference Between Gypsum Plaster and Cement Plaster | What Is Gypsum Plaster | What Is Cement Plaster
What Is Gypsum Plaster? Gypsum plaster is made by heating gypsum at low temperatures to drive off water, to produce … [Read more...]
What Is Passometer & Pedometer | Advantage of Passometer & Pedometer | Passometer Vs Pedometer
What Is Passometer? Passometer is an electromechanical and portable instrument, which count the number of paces or … [Read more...]
What Is Pedestal | Functions of Pedestal | Methods of Construction: Pedestals | Advantages and Disadvantages of Pedestal
What Is Pedestal? The term “Pedestal”, so far in the Civil Engineering field is concerned, is a compressive … [Read more...]
Procedure for RCC Concrete
Purpose of RCC Concrete The purpose of this procedure is to provide a methodology for active surveillance of various … [Read more...]
What Is Sand Blasting | Concrete Sand-blasting Equipment | Key Benefits of Sand Blasting
What Is Sand Blasting? Commonly called abrasive blasting, grit or sand-blasting can be used to expose the aggregates … [Read more...]
Testing for Silt Content in Sand
Why We Measure the Silt Content from the Sand? Silt content is a fine material that’s less than 150 microns. It’s … [Read more...]
What Is Bleeding In Concrete | What Is Segregation In Concrete
What Is Bleeding In Concrete? Bleeding in concrete is sometimes referred to as water gain. This is a special form … [Read more...]
What Is Waterproofing | Types of Waterproofing
What Is Waterproofing? This is the process of making a structure water-resistant or impervious to the ingress of … [Read more...]
Difference Between Carpet Area and Built-up Area
What Is Carpet Area? Carpet area means it is an accurate area that can freely be covered by a carpeted inner a … [Read more...]
21 Different Types of Arches Construction
Introduction of Arches Construction An Arch is basically a structure that is constructed of a wedge-shaped unit. The … [Read more...]
Difference Between Veneer and Laminate | What Is Veneer | What Is Laminate
What Is Veneer? A veneer is a very thin piece of wood that is attached to particleboard or other types of … [Read more...]
What Is Fresh Concrete | 8 Properties of Fresh Concrete
What Is Fresh Concrete? When concrete is its plastic state, it is known as fresh concrete. Fresh concrete can be … [Read more...]
What Is Slump Cone Test | Principle of Slump Test | Types of Concrete Slump
What Is Slump Cone Test? A Slump cone test or concrete Slump test is to determine the workability or consistency of the … [Read more...]
What Is Foundation Repair | Foundation Techniques | Effects of Foundation Damage | What Foundation Repair Techniques Are Available
What Is Foundation Repair? Foundation renovation is required when the foundation of a home, building, or structure … [Read more...]
What Is Foundation | What Is Purpose of Providing Foundation | Types of Foundation
Foundation in Civil Engineering In engineering, a foundation is the element of a structure which connects it to the … [Read more...]
History of Remote Sensing | Application of Remote Sensing
History of Remote Sensing In the past time, the only way to store records was photography. The contemporary era of … [Read more...]
What Is Mortar | Test of Mortar | Process for Compressive Strength
What Is Mortar? Mortar is an intimate mixture of binding material, fine aggregate, and water. When water is added … [Read more...]
What Is Building Bye-Laws | How Essential Building By Laws
According to the definition, building bye-laws are the norms set forth by the government authorities such as Gandhinagar … [Read more...]
What Is Quick Setting Cement | Uses of Quick Setting Cement
What Is Quick Setting Cement? Quick setting cement is one of the types of cement. This cement setting time very … [Read more...]
What Is Structural Settlement | Causes For Structural Settlement | What Is Soil Settlement & Foundation Structural Settlement
What Is Structural Settlement? The term Structural Settlement is defined as the vertical displacement of the base of a … [Read more...]
Well Point System | Types of Well Point System | Well Point Dewatering | PVC Well Point | Well Point Installation | Well Point for Shallow Well
What Do You Mean by Term Well Point? A Well Point is also known by the term Drive point. Well Point is a well of small … [Read more...]
Different Between Clamp Burning and Kiln Burning | What Is Clamp Burning | What IS Kiln Burning
What Is Clamp Burning? A typical clamp is shown below figure The bricks and fuel are placed in alternate layers. … [Read more...]
What Is Self Compacting Concrete | What Is U Box Test | Equipment U-Box Text | Procedure U-Box Text
What Is Self Compacting Concrete? Making concrete structures without vibration has been done in the past. For … [Read more...]
Total Station in Surveying | Operations of Surveying | Advantage & Disadvantage of Surveying | Types of Surveying | Uses of Surveying
What Is a Total Station in Surveying? The most frequently used surveying instrument today is the total station (As … [Read more...]
18 Difference Between Compaction and Consolidation | What Is Compaction | What Is Consolidation
What Is Compaction? compaction of soil is area compacted by the mechanical method to remove air voids in compacted … [Read more...]
PVB Vs SGP | What Is Limited Glass | What Is PolyVinyl Butyral (PVB) | What Is Sentry Glass Plus (SGP)
What Is Limited Glass? Laminated Glass is a type of safety glass that holds together when shattered. In the … [Read more...]
What Is Survey Levelling | Important Terms Related to Levelling | What Are Different Types of Levelling | Types of Trigonometric levelling
Introduction of Survey Levelling Survey levelling is the method by which we measure the elevation of one land with … [Read more...]
Concreting in Construction | Classification of Concreting | Properties of Concreting | Grades of Concreting in Construction | Advantage & Disadvantage Concreting
Introduction of Concreting in Construction Concrete is most frequently used man-made construction material in the … [Read more...]
What Is Self Compact Concrete | What Is J-Ring Test | Equipment of J-ring Test | Procedure of the J-Ring Test
What Is Self Compact Concrete? Making concrete structures without vibration has been done in the past. For example, the … [Read more...]
What Is Rebar | Why use Reinforcement in Concrete | Types of Steel Reinforcement Bars
We know that Rebar. It is known as reinforcement steel and reinforcing steel. This is a steel bar or mesh bar of steel … [Read more...]
How is Concrete Made | What is Concrete | Components of Concrete | How to Mix Concrete
How Is Concrete Made? Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a … [Read more...]
All About Waffle Slab | What is Waffle Slab | Waffle Slab Details | Advantages & Disadvantages Waffle Slab | Waffle Slab Design | Construction of Waffle Slab
What is Waffle Slab? Slabs required supports which is given in the form of columns so that the load coming on the … [Read more...]
What Is Granolithic Floors | Construction Method | Advantages аnd Disadvantage
What Is Granolithic Flooring? Granolithic is also known as granolithic paving and granolithic concrete is a type of … [Read more...]
Emulsion Paint Vs Oil Based Paint | Purpose of Providing Paints | Properties of Good Paint | Properties of Good Paint | What Is Oil Based Paint
Introduction to Paints Paints are commonly used for the decoration of the Structure. Paints are one of the … [Read more...]
Septic Tanks Are Back In! Here’s What You Need to Know About How They Work
Introduction of Septic Tanks In a city, houses and apartments are designed to follow a sewage system. Many houses and … [Read more...]
Mivan Shuttering | Merit & Demerit Mivan Technology | Mivan Formwork Assembly Process
Mivan Shuttering: Mayan Technology Mivan shuttering is a fast-paced construction technique that offers strength and … [Read more...]
7 Types of Rollers | Advantages & Disadvantages of Roller Compacted Concrete | Advantages & Disadvantages of Road Roller
Introduction of Roller Most construction sites require an anchored ground to perform. One of the principal common kinds … [Read more...]
What Is Shear Wall | Classification of Shear Walls |Advantages of Shear Wall | Functions of Shear Wall | Important Point Shera Wall
What is a Shear Wall? Shear wall is a structural member used to resist lateral forces, i.e., parallel to the plane … [Read more...]
Room Soundproofing | What Is Room Soundproofing | Cost to Soundproof a House | Fully Soundproof Room
Introduction of Room Soundproofing Room soundproofing means blocking the sound from getting in or out of the room. Some … [Read more...]
Different Types of Pavers for Driveways
What Are Pavers? Pavers are generally blocks or slabs which made from different materials like concrete, marble, … [Read more...]
What Is Bulkage of Sand (Fine Aggregate )
What is Bulkage of Sand or Bulkage of Aggregate? Bulkage in the sand when dry sand contact atmosphere moisture. … [Read more...]
What are Traps | What Does Trap do | 14 Types of Traps In Plumbing
What are Traps In Plumbing? As the name suggests, traps simply trap the water and sewer gas. A trap is a plumbing … [Read more...]
What Is Shovel | Types of Shovels
What Is a Shovel? A shovel is a working tool by which we can move any type of materials like sand, ore, soil, … [Read more...]
What Is Fine Aggregate | Types of Fine Aggregates (Classification)
What Is Fine Aggregate? Fine aggregates are essentially any natural sand particles won from the land … [Read more...]
All About Rat Trap Bond | What Is Rat Trap Bond | How to Use | Advantage & Disadvantage of Rat Trap Bond
What Is Rat Trap Bond? This is one of the wall constructing method of brickwork on wall construction. This method … [Read more...]
All About Fish Ladder | What Is Fish Ladder | Types of Fish Ladder | Fish Ladders in Dams
Fish Ladder A fish ladder is a structure that allows migrating fish passage over or around an obstacle on a river. Fish … [Read more...]
All About Pier and Pile | Difference Between Pier and Pile | What Is Pier | What Is Pile
Introduction of Pier and Pile The pile and the piers are two different types of deep foundations which are widely used … [Read more...]
All About Flooring | What Is Flooring | 11Types of Flooring.
What Is Flooring? The purpose of flooring is to get a good hard, level, and beautiful surface for living. The … [Read more...]
All About Polymer Concrete | Why Is Polymer Concrete | Types of Polymer Concrete
Why Is Polymer Concrete? Polymer concrete is a combination material in which the binder consists entirely of synthetic … [Read more...]
How to Calculate Staircase Qty | Concrete & Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) | Staircase Reinforcement Details
Parts of Stairs Parts Names & Details A various part of Stair: Step: A flat surface, especially one in a … [Read more...]
Mortar Vs Cement | Types of Cement | Types of Mortar
Mortar Vs. Cement The difference between mortar and cement is that cement is the bonding agent, while the mortar is a … [Read more...]
All About Formwork Failure | What Is Formwork Failure | Causes of Formwork Failure
What Is Formwork Failure? The construction of a concrete building needs formwork to support. Specific forms are … [Read more...]
All About Rate Analysis | What is Rate Analysis | Rate Analysis of Earth Work, Brick, Concrete and Plaster
What is Rate Analysis? The basis of arriving at a correct and reasonable rate per unit. work or supply for a … [Read more...]
All About Flagstone | Introduction of Flagstone | What Is Flagstone | What Is a Flagstone Patio | Types of Flagstone
Introduction of Flagstone Flagstone is the extreme flagstone lead describing and clarifying your choices when it … [Read more...]
All About M-Sand And River Sand | What is M-Sand | M-Sand Bonding Strength | What is River Sand |
What is M-Sand? M- Sand full name is Manufacturer Sand. M Sand is nothing but artificial sand made from crushing of … [Read more...]
All About Roof Vent | What Is a Roof Vent | Different Types of Roof Vents | Advantages of Roof Ventilation
What Is a Roof Vent? Completely, roof ventilation is a system that promotes air to ventilate via the vent. Roof … [Read more...]
All Abot Parts of Stairs | Stairs Parts Names & Details | Parts of Stairs Parts Names & Details
Parts of Stairs Parts Names & Details A various part of Stair: 1. Step: A flat surface, especially one in a … [Read more...]
All About Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry | Introduction of Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry | Important Point in Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry | Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry
Introduction of Rate Analysis of Brick Masonry Rate analysis of brick masonry used of reference book IS Code … [Read more...]
Important Factors to Consider When Building a New Home
Important Factors to Consider When Building a New Home Having one's own home is the dream of many of us. But very … [Read more...]
All About Painting | What Is Painting | Painting Area Calculation for Evan Surface & Uneven Surface |How Much Paint Do I Need
How to Calculate Square Feet for Paint? For most home improvement projects, knowing how to calculate square feet is … [Read more...]
All About Consider | When Building a New Home | Important Factors to Consider When Building a New Home
Important Factors to Consider When Building a New Home A home is a place where everyone spends most of the time of … [Read more...]
All About Plywood | What Is Plywood | What Is Plywood Used For | What is Plywood Made From
What Is Plywood? Considering all the building materials, Plywood has become one of the most eye-catching materials … [Read more...]
All About Soil Compaction | What Is Soil Compaction | Different Types of Soil Compaction Equipment
What Is Soil Compaction? Soil compaction occurs when soil particles are pressed together, reducing the pore space … [Read more...]
All About Tremie Pipe | What is Tremie Pipe | Tremie Method of Underwater Concrete | Critical Features of Tremie Pipe Concreting
What is Tremie Pipe? A tremie is a pipe that can use for pouring concrete underwater. Its standard function is in … [Read more...]
Hempcrete Vs Concrete | What Is Hempcrete | What Is Concrete
What Is Hempcrete? Hempcrete is a bio-composite that is made from the inner wood core of the hemp plant and mixed … [Read more...]
Cellar Vs Basement | What Is Cellar | What Is Basement
What Is Cellar? A cellar is a part of a building that is present entirely below the level of the curb. The cellar … [Read more...]
What Is Geodetic Surveying | What Is Plane Surveying | Geodetic Surveying Vs. Plane Surveying | Difference Between Plane Surveying and Geodetic Surveying
What Is Geodetic Surveying? The geodetic surveying is that type of surveying which takes into account the … [Read more...]
All About Singly Beam & Doubly Beam | What Is Singly Beam | What Is Doubly Beam | Based on Implanted Reinforcement |
What Is Singly Beam? A singly beam is the beam which is provided with longitudinal reinforcement in the tension … [Read more...]
All About Of Pavement Markings | What Is Pavement Marking | Types of Pavement Marking and Their Meaning
Introduction of Pavement Markings For road users, road marking or pavement marking is a component of an … [Read more...]
All About of Window | What Is Window | Selection Criteria for a Window | Types of Windows
What Is Window? The word 'window' is considered to be derived from an old Norse word 'Vindauga'. 'Vinduga' is made … [Read more...]
Information About Roof | What is the Roof | Different Types of Roofs | The Details in the Design of a Roof Are
Introduction of Roofs The roof is an integral element of the surrounding structure. It protects the top portion of the … [Read more...]
All About of Shoring | What is Shoring | Types of Shoring | Types of Shoring in Construction
What is Shoring? Shoring is a short-term figure applied to stop settling the major incomplete work. It is necessary … [Read more...]
All About of Plumbing Fittings | What Are Plumbing Fittings | Types of Plumbing Fittings
What Are Plumbing Fittings? Plumbing fittings are water systems that perform ingredients that support turning the … [Read more...]
All About of Tort and Contract | What is tort | What Is Contract | Difference between Tort and Contract | Tort law definiti on
What Is Tort? The word reference's meaning of the word tort is any wrongful act that leads to legal liability. It … [Read more...]
All About of Drapes Vs. Curtains | Difference Between Drapes and Curtains | What Are Drapes | What Is Certain
Drapes Vs. Curtains Windows considers the elegant pattern most essential drapes and curtains that give a current … [Read more...]
All About of Standard Door | What Is the Standard Door Size | Standard Size of the Door Frame
What Is the Standard Door Size? In the U.S.A, two kinds of door sizes are highly applied for house inside and outside … [Read more...]
All About of Parking Space | What Is a Parking Space | Standard Parking Space Dimension
What Is a Parking Space? Parking for the motor vehicle is the foremost essential thing for each taxi owner. … [Read more...]
All About of Wall Texture | What Is Wall Texture | Uses of Texture Paint | Types of Wall Texture Paint
What Is Wall Texture? The wall texture painting offers an excellent appearance to your house. The texture is a … [Read more...]
All About of Shear Force and Bending Moment | What Is Shear Force | Shear Force Formula
What Is Shear Force and Bending Moment? Internal forces such as shear force and bending moment are representations … [Read more...]
All About of Lean-To Roof | What Is a Lean-To Roof | Lean-To Roof Design | Advantages And Disadvantages of the Lean-To Roof
What Is a Lean-To Roof? A lean-to roof is called construction in which the roof leans opposite to another wall, and … [Read more...]
All About of Underwater Concrete | What Is Underwater Concrete | Advantages & Disadvantages of Underwater Concrete
What Is Underwater Concrete? Underwater concrete is a special type of construction material which in used certain … [Read more...]
All About of Retention in Construction | What Is Retention in Construction | Retention in Construction
What Is Retention in Construction ? Retention is security held by an obtaining worker for hire to ensure the … [Read more...]
All About of Mortar | What Is Mortar | How to Make Mortar | How to Mix Mortar | Mortar in Construction | Functions of mortar
What Is Mortar? Cement and water, or lime, Suki, and water are used to make mortar. The mortar's joining … [Read more...]
All About of Fence | What Is Fence | Different Types of Fences | Advantages of Fence
What Is Fence? Creating a barricade that can be permanent or temporary alongside the boundary line of land or a … [Read more...]
Building Estimation Step by Step In Excel Sheet
Dear friend, we work building quantity calculation in manual in a paper, So now going we area in how to Calculate in … [Read more...]
Top 10 Tiles Companies in India 2021
Top 20+ Tiles Brand Name List [table responsive="yes" alternate="yes" fixed="no" class=""] Sr.No. Tiles Brand … [Read more...]
Difference Between Plane Surveying and Geodetic Surveying
Definition of Plane Surveying The Plane surveying is defined as a survey technique wherein the Earth's surface is … [Read more...]
What Is Traffic Rotaries? | Rotary Intersection | What Is Rotary Island? | Advantages & Disadvantages of Traffic Rotary
What Is Traffic Rotaries? Traffic rotaries or intersections are a special type of intersection designed by civil … [Read more...]
What Is Tie Beam? | Tie Beam Details | Ties in Column | Tie Beam Design | Concrete Tie Beam | Tie Beam Reinforcement Details
What Is Tie Beam? Tie beams are beams that link two or more columns or rafters in a roof or truss, or at some height … [Read more...]
Types of Curing | Concrete Curing Time | How to Cure a New Concrete Slab | What Is Curing of Concrete | How Long Does Concrete Take to Dry | How Long Does It Take for Cement to Dry
What Is Curing of Concrete? Too kept within the recommended temperature range and the concrete is protected against … [Read more...]
What Is Sheepsfoot Roller? | Characteristics of Sheepsfoot Rollers | Difference Between Padfoot and Sheepsfoot Rollers
What Is Sheepsfoot Roller? Sheepsfoot rollers are vibratory compacting devices that are mostly used for soil and … [Read more...]
Monolithic Slab I Monolithic Definition I Monolithicfooting I Monolithic Slab Foundationl Monolithic Slab Foundation Design L What Is a Monolithic Slab L How to Form a Monolithic Slab
Monolithic Slab Monolithic means “all single pouring,” so the foundation is made of a single layer of a concrete slide … [Read more...]
What Is a Spillway | Types of Spillway | Definition Spillway | Spillway Design
What Is a Spillway? To control the release of water from a dam or levee downstream, A spillway is a structure used to … [Read more...]
What Is Workability | What Is Workability of Concrete | Types of Workability of Concrete | Factors Affecting Workability of Concrete
What Is Workability? Workability is an essential property of concrete that is related to compaction as well as … [Read more...]
What Is Sewerage System? | Types of Sewerage System | Why We Need a Partially Separate System? | How Does a Sewer System Work? | How Does a Sewage Treatment Plant Work?
What Is Sewerage System? A sewage system is a pipeline network, pumps, and power to force the collection of … [Read more...]
What Is Seasoning of Timber? | Methods of Seasoning of Timber | Purpose of Seasoning of Timber
What Is Seasoning of Timber? Seasoning of timber is a process that is applied on the wood piece to reduce the moisture … [Read more...]
What Is Gradient of Road? | Limiting Gradient of Road | Types of Gradient of Road | Exceptional Gradient of Road | The Gradient of Road | Purpose of Providing Gradient of Road | Importance of Gradient in Roads
What Is Gradient of Road? The gradient is the rise and fall of the gradient with respect to the horizontal line. … [Read more...]
What Is Lap Length? | Lap Length in Beam | Why Lapping Is Provided? | How to Calculate Lap Length? | Lap Length as Per Is Code 456 | What Are the General Rules for Lap Length? | Lapping Zone
What Is Lap Length? Lap length is specified as the length given to enable the overlapping of two reinforcement … [Read more...]
Hollow Block | Hollow Concrete Block | Hollow Concrete Block Size |Hollow Concrete Block Advantage | Hollow Concrete Block Disadvantage | Hollow Concrete Wall | Hollow Block Construction | Size of Hollow Blocks | How to Make Hollow Blocks
Introduction Hollow Block Typically, Hollow Block is a type of concrete block used to build interior and exterior … [Read more...]
What Is Heat Resistance Concrete? | Reinforcement in Heat Resisting Concrete | Properties of Heat Resisting Concrete | Application of Heat Resisting Concrete | Advantages & Disadvantages of Heat Resisting Concrete
Heat Resisting Concrete Introduction: Innovative products are produced from the industry day by day, and they also … [Read more...]
Hand Level Surveying | What Is Site Level? | What Is Hand Level? | How to Use a Hand Sight Level | Estimating Distances with a Sight Level
Hand Level Surveying Grading contractors and land surveyors also use the hand level as a tool. To find a height … [Read more...]
Types of Cement Grades | Difference Between 33, 43 & 53 Grade Cement
Introduction of Cement Cement is the foremost vital module of engineering construction jobs. Concrete is created … [Read more...]
What Is Panelled Window? | What Is Glazed Window? | Difference Between Paneled Window and Glazed Window
Introduction of Panelled Window and Glazed Window The window is one of the vital building components. By the window … [Read more...]
What Is Fresh Concrete? | Properties of Fresh Concrete | Factors Affecting Workability
What Is Fresh Concrete? Fresh Concrete - Fresh concrete is often molded to a sturdy structural module. Fresh … [Read more...]
What Is Flyash Brick? | Fly Ash Bricks Cost | Properties of Flyash Bricks | Fly Ash Bricks Manufacturing Process | Compressive Strength of Fly Ash Brick | Fly Ash Brick Size | Advantages & Disadvantages of Fly Ash Bricks
What Is Flyash Brick? The ash created during coal combustion is known as fly ash. It's a crystalline dust made from … [Read more...]
What Is Estimate? | Types of Estimate | Advantage of Estimate | Disadvantage of Estimate
What Is Estimate? An estimate is an anticipated or probable cost of job & is generally prepared before the … [Read more...]
What Is Epoxy? | What Is Epoxy Flooring? | Types of Epoxy Flooring | Advantages of Epoxy Flooring | Disadvantages of Epoxy Flooring | Uses of Epoxy Flooring | Application Process of Epoxy Flooring
Introduction of Epoxy Flooring Usually, chemical resins are a group of short-chain polymers that contains epoxide … [Read more...]
Difference Between Short Column and Long Column
Difference Between Short Column and Long Column There are many differences between the Short column and the Long … [Read more...]
What Is Plastering | What Is Pointing | Difference Between Plastering and Pointing |
Introduction of Plastering and Pointing Basically, we know that a cement sand paste which is used after brickwork … [Read more...]
What Is Timber ? | What Is Lumber ? | What Is Lumber Used for ? | Lumber Vs Wood | Difference Between Lumber and Timber | Standard Wood Size | What Is Timber Used for ?
What Is Timber? Timber is a phrase that has numerous meanings and is often used interchangeably with the phrase lumber … [Read more...]
Concrete Slump Test | Principle of Slump Test | What Is Slump Test ? | How to Measure Concrete Slump? | Slump Test Results | Concrete Slump Test Procedures |
Concrete Slump Test The aim of a concrete slump test or slump cone testing is to measure the workability or quality of … [Read more...]
Difference Between Coarse Aggregate and Fine Aggregate | What Is Coarse Aggregate? | What Is Fine Aggregate? | Advantage of coarse aggregates | Advantage of Fine Aggregate
Introduction of Coarse Vs Fine Aggregate :- In construction the coarse aggregates are larger size filler … [Read more...]
Concrete Vs Cement | Definition of Cement and Concrete | Composition of Cement and Concrete | Types of Cement and Concrete | Properties of Cement and Concrete | Uses of Cement and Concrete | Advantages of Cement and Concrete | Disadvantages of Cement and Concrete
Concrete Vs Cement Definition of Cement and Concrete Definition of Cement Cement is the greatest significant … [Read more...]
Concrete Release Agent | Concrete Form Release Agent | Concrete Formwork Release Agent | Concrete Form Release Oil | Concrete Mold Release Agent | Homemade Concrete Release Agent | Concrete Release Agent for Wood | How to Keep Concrete from Sticking to Wood | Fiberglass Release Agent |
Concrete Release Agent:- The concrete release agent is a combination of plant oil, mineral oil, and paraffin … [Read more...]
What Are Conceptual Sketches | Concept Sketch Definition | Use of Concept Sketches in Class | Using Concept Sketches in the Field | Architecture Concept Drawings | Difference Between Sketches and Drawings
What Are Conceptual Sketches A concept sketch is more than just a diagram of labels. We've included a few samples of … [Read more...]
What Is Ceramic Tiles? | Advantages & Disadvantages of Ceramic Tiles | What Is Vitrified Tiles? | Advantages & Disadvantages Vitrified Tiles | Differences Between Ceramic Tiles and Vitrified Tiles
Introduction of Ceramic and Vitrified Tiles: What Is Ceramic Tiles? Ceramic is a term that is used to refer to all … [Read more...]
What Is Gable Roof | History of Gable Roofing | Gable Roof Design | Parts of Gable Roof | 7 Types of Gable Roofs | How Long Can the Roof Last? | Gable Roof Advantages and Disadvantages | Cost of Gable Roof Construction |
What Is Gable Roof? The gable roof is also called a pitched roof. In this type of roof, two sloping sides peak at the … [Read more...]
Building Layout | How to Building Layout | Construction Layout Techniques
Building Layout The true intention and intent of setting out (layout) are to move the plan, length, and width of the … [Read more...]
How a Building Is Constructed | Components of Building
How a Building Is Constructed In the building construction process, there have two main part that’s are below- 1. … [Read more...]
What Is Bituminous Road? | Bituminous Road Construction | Bituminous Road Layers | Bituminous Macadam | Bituminous Road Construction Process | Advantages of Bitumen Road | Disadvantages of Bitumen Road | Application Road
What Is Bituminous Road? Bitumen is dark viscous material which is sticky in nature, it mainly founds in natural … [Read more...]
What Is Super Elevation? | Superelevation Definition | Purpose of Providing Superelevation in Roads | Calculation of Superelevation in Roads | Minimum and Maximum Superelevation in Roads | Method of Providing Superelevation to the Roads
What Is Super Elevation? The banking of highway horizontal curves to support the operator by countering the … [Read more...]
What Is Lintel? | Function of Lintel | Types of Lintel
What Is Lintel? To support the load from the structure above from the building, the lintel is a beam that is placed … [Read more...]
What Is Grouting | Type of Grouting | Experiment of Grouting | Characteristics of Grouting | Types of Grout for Ceramic Tile | Advantage of Grouting | Disadvantage of Grouting
What Is Grouting To increase the load-bearing capacity of the concrete, masonry structure, rock mass, or soil the … [Read more...]
What Is Grade of Concrete | Concrete Mix Ratio | Type of Concrete Mix | Different Types of Concrete Grade with Concrete Mix Ratio and Compressive Strength | Uses of Different Grades of Concrete
What Is Grade of Concrete By the composition and strength of the concrete, the grades of concrete are defining. … [Read more...]
What Is Hidden Beam | Why Is It Used | Where Is It Used in Buildings | How to Design a Hidden Beam | Purpose of Hidden Beam | Advantages of Hidden Beam | Disadvantages of Hidden Beam
What Is Hidden Beam? A Hidden beam could be a reinforced concrete beam, additionally referred to as concealed beam … [Read more...]
What Is Combined Footing | Types of Combined Footing | Advantage & Disadvantage of Combined Footing | Application of Combined Footing
Introduction of Combined Footing Combined footings are developed when two or more columns are close to one another … [Read more...]
Density of Cement Sand and Aggregate | Density of Cement | Density of Sand | Density of Aggregate
Density of Cement Sand and Aggregate We know the density which is also known as unit weight, its mass per unit … [Read more...]
What Is Mortar | Uses of Mortar | Advantages & Disadvantages of Mortar | Applications of Mortar | Properties of Mortar
What Is Mortar? Mortar is an aggregate paste made by sand, cement (binding material) & water or by lime, surkhi … [Read more...]
What Is Steel | Types of Steel | How to Calculate Unit Weight of Steel Bars | Calculation of Weight of Steel Bar for 1-Metre Length | Self Weight of Steel
What Is Steel? Steel is the most adaptable and widely used construction material. Steel is made up of the important … [Read more...]
What Is Chain Surveying | Principle of Chain Surveying | Procedure of Chain Surveying | Error in Chain Surveying | Advantages & Disadvantagesof Chain Surveying
Introduction of Chain Surveying Chain surveying is a branch of surveying where only accurate measurements are made in … [Read more...]
Difference Between Cement Plaster and Gypsum Plaster
Introduction Between Cement Plaster Vs Gypsum Plaster The cement plaster is an intimate mixture of Portland cement, … [Read more...]
What is WPC Boards | WPC Board Characteristics | Advantages & Disadvantages of WPC Boards | Uses of WPC Boards | Applications of WPC Boards
What Is WPC Board? The term "wood plastic composite" refers to a panel or lumber component constructed from recycled … [Read more...]
What Is Development Length | Why We Provide Development Length | How to Calculate Development Length | Development Length for Single Bars
What Is Development Length? Development length is defined as the minimal size of the bar that must be set in concrete … [Read more...]
How to Calculate Quantity of Material For Plaster | Measurement of Plastering Quantities | Material for 20 mm Thick Plastering in Wall for 100 Sq.m.
How to Calculate Quantity of Material for Plaster? Plastering is the practice of coating rough walls and uneven … [Read more...]
10 Difference Between One way and Two way Slab | What Is the Slab | What Is a One Way Slab | What Is Two Way Slab
What Is the Slab? A slab is an important structural feature that provides flat surfaces in buildings. Slabs are commonly … [Read more...]
What Is Contour Interval | How to Find the Contour Interval | Uses of Contour Intervals in Surveying | Reading Contour Lines | What Is Importance of Topographic Maps
What Is Contour Interval? A contour interval may be a perpendicular distance or dissimilarity in altitude between two … [Read more...]
What Is Plinth | What Is Plinth Beam | What Is Plinth Protection | Purpose of the Plinth Beam in a Structure | Advantages & Disadvantages of Plinth Beam
What Is Plinth? In construction between the ground floor level and ground-level portion of the building is known as a … [Read more...]
What Is Plum Concrete | Purpose of Plum Concrete | How to Prepare Plum Concrete | Advantages & Disdvantages of Plum Concrete
What Is Plum Concrete? Plum concrete is created mostly by the participation of large and medium rocks of usual size … [Read more...]