What Is a Cavity Wall | How to Build a Cavity Wall | Cavity Wall Detail | Cavity Wall Thickness | Cavity Wall Insulation Pros and Cons | Brick Cavity Wall
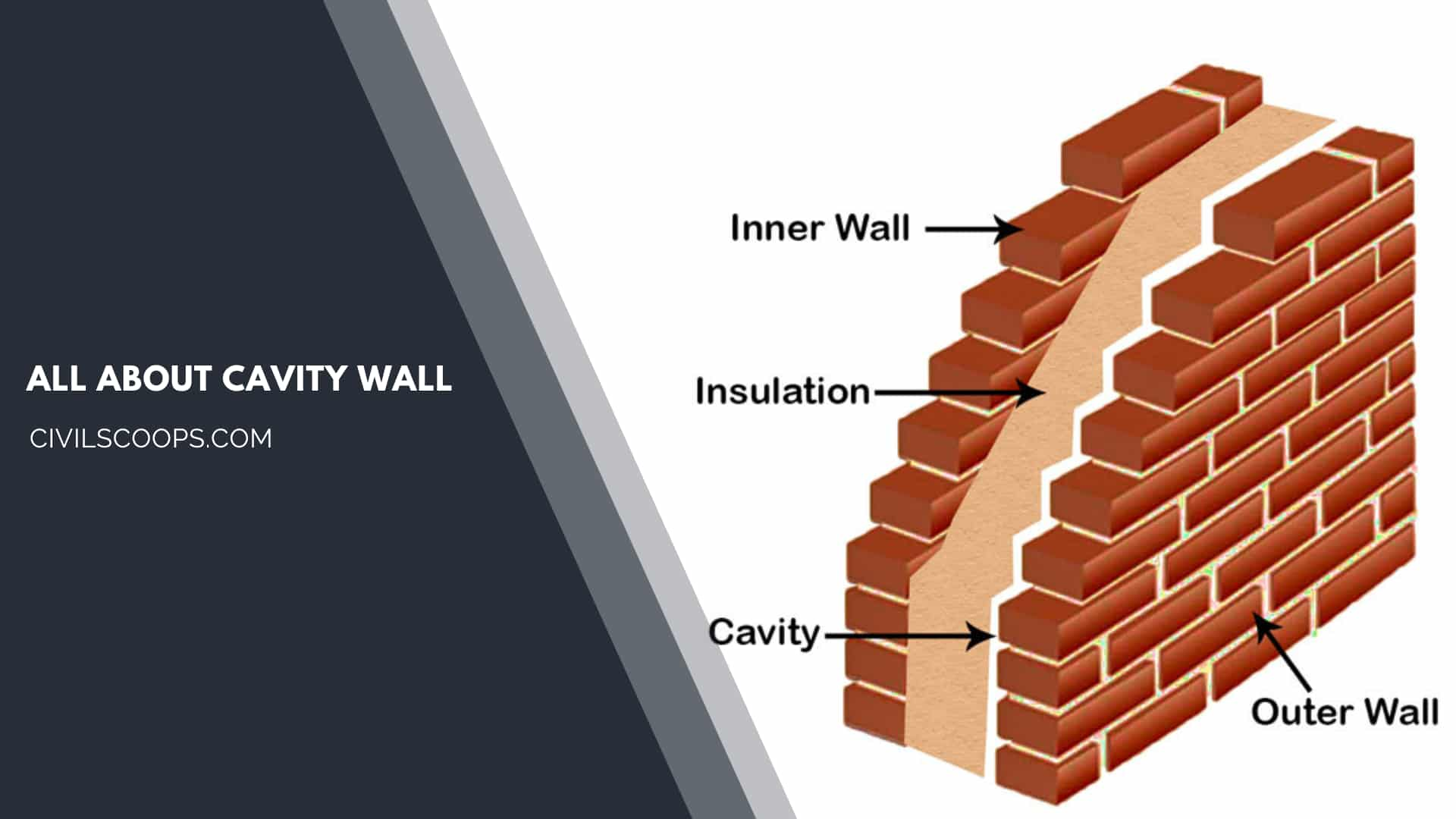
Table of Contents
What Is a Cavity Wall?

A cavity wall consists of a hollow space between them. The cavity walls normally consist of two skins, which should be brick, cinder blocks, or reinforcement concrete blocks, etc.
The absorbent materials are used in cavity wall construction to that draw out the rainwater and consist of humidity in the wall. The weep hole is constructed above the window or base the wall to draw out the rainwater.
It is joined together by metal ties and at suitable intervals and separating by an air space. The cavity wall generally is an exterior wall but sometimes it’s used as an interior wall.
The weep holes provide an air circulation system in the cavity walls that help to Come out of the evaporated water outside of the cavity.
Approximately two meters apart at the base of each story, a weep hole is created by separating several vertical joints.
Also Read: Concrete Construction Tools for Construction Sites
How to Build a Cavity Wall?

- To leaves of the masonry wall separated by an air gap and tides by ties is known as a cavity wall.
- The cavity walls normally consist of two skins, which should be brick, cinder blocks, or reinforcement concrete blocks, etc.
- It is joined together by metal ties and at suitable intervals and separated by an air space.
- When it is construed as a non-load-bearing wall then the two skins of the cavity wall are maybe the equal thickness.
- As required, sometimes the inner wall is thicker than the outer wall.
- The weep holes provide an air circulation system in the cavity walls that help to Come out of the evaporated water outside of the cavity.
- Approximately two meters apart at the base of each story, a weep hole is created by separating several vertical joints.
Useful Article for You
- How Much Does Hempcrete Cost
- How to Build a Lean to Roof
- How Dense Is Sand
- How to Make Mortar from Scratch
- How Tall Is a Kitchen Counter
- How to Use a Hand Sight Level
- How to Resurface Concrete
- How to Layout a Building
- How Is the Skeleton Similar to the Frame of a House
- How to Seal a Brick Wall
- How to Use Portland Cement
- How to Form a Monolithic Slab
- How to Get Rid of Gloss Paint Fumes
- How Are Bridge Foundations Built
- How to Calculate Fineness Modulus
- How to Measure Slump in Concrete
- How Does a Cantilever Bridge Work
- How Much Is Flagstone Per Square Foot
- How to Build a Post and Pier Foundation
- How to Construct Building
Cavity Wall Detail:
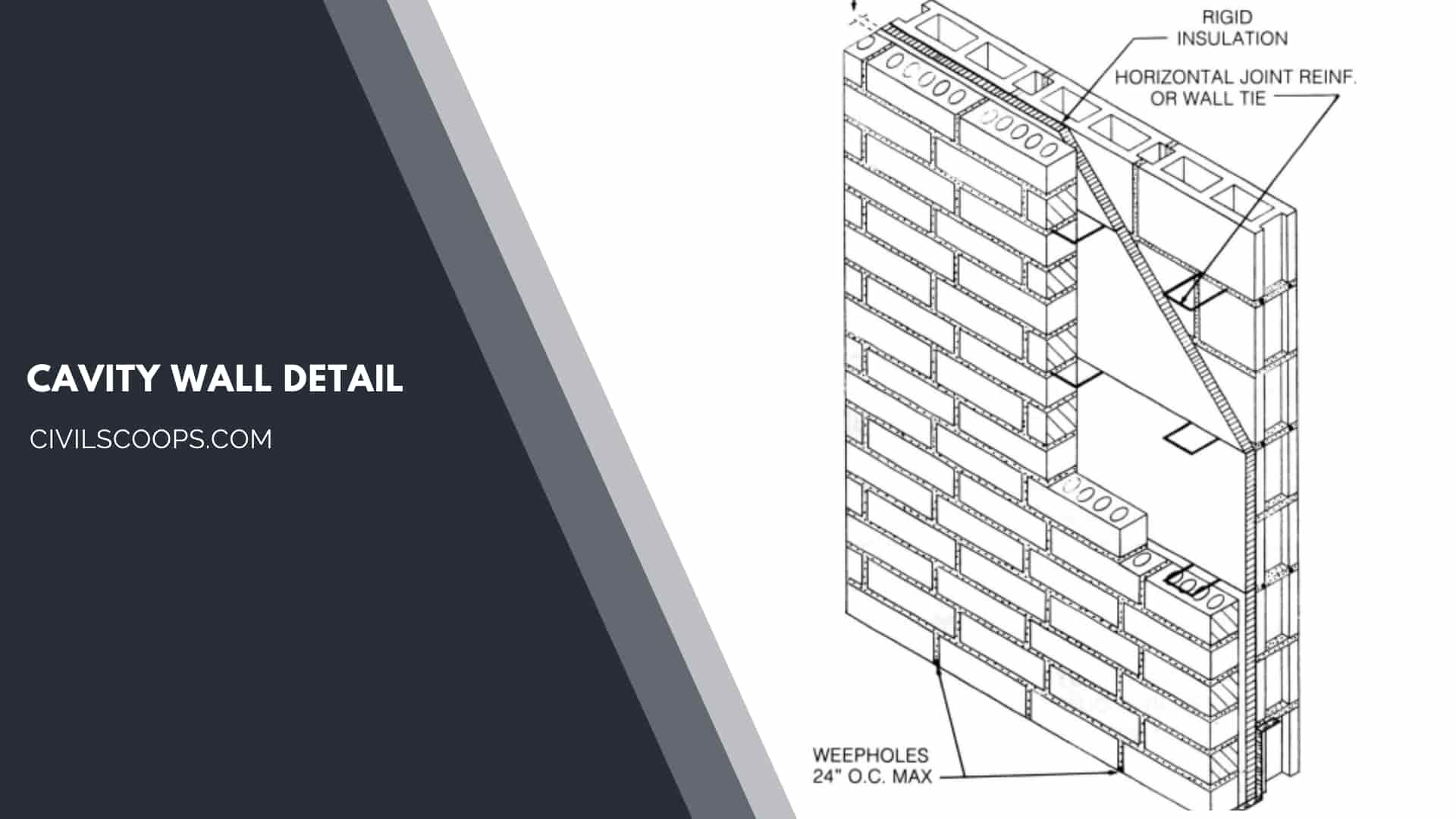
- The cavity wall is termed as skin. It is contained two layers of masonry like a bricklayer or concrete layer reinforcement concrete etc.
- It is joined together by metal ties and at suitable intervals and separating by an air space.
- The cavity wall generally is an exterior wall but sometimes it’s used as an interior wall.
- If it is a non-load bearing wall then the two skins of the cavity wall are maybe the equal thickness.
- To fulfill the structural requirements sometimes the internal skins are thicker than the external skins.
- At least four to five ties are used at each square meter to provide an adequate bond between the inner and outer skins of the cavity wall.
- A flexible vertical damp proof course should be provided at the doors and windows reveals to prevent the entry of moisture in the room.
- The width of the cavity wall should not more than 100 mm and not less than 40 mm.
- To protect from rust the mild Steel is used that is galvanized or dipped into hot tar or sanded.
- The vertical distance and a horizontal distance of ties should not exist 450 mm and 900 mm.
- Sometimes a DPC should be provided to prevent the damp between the walls.
- The damp-proof course was made of lead, pitch, asphalt, and slate.
- At regular intervals at the steel or wrought iron wall ties are used to tide two half of the walls.
Also Read: Load-Bearing Vs Partition Walls | What Are Walls | Classified of Walls
Cavity Wall Construction Details:
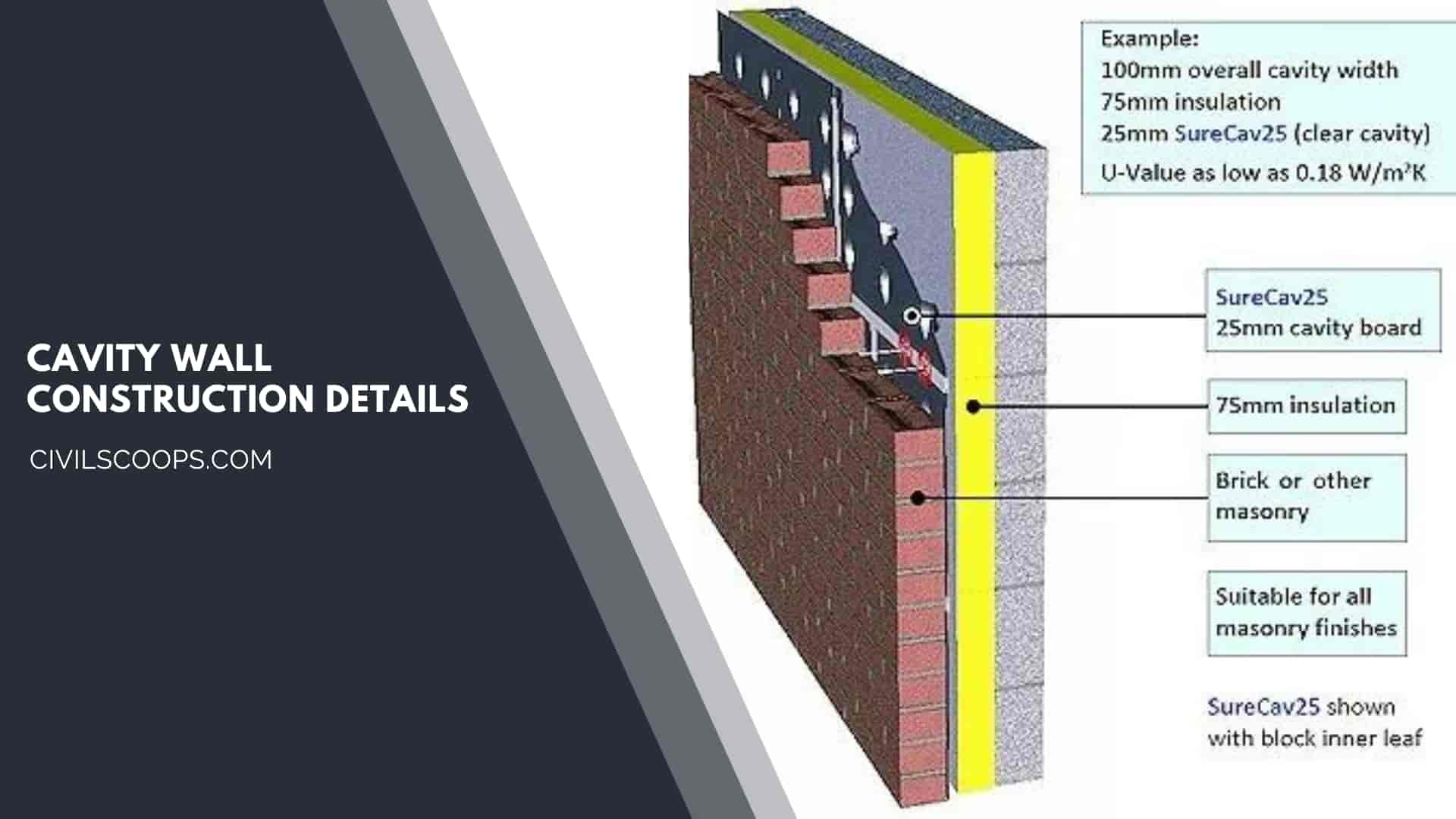
- When an air space or hollow area is exits between the two walls, then it is called a cavity wall.
- The inner wall is generally made of masonry, like bricks, cinder blocks, concrete blocks, reinforcement blocks, etc.
- The humidity into the wall and the rainwater slowly draw by the masonry because it is an absorbent material.
- Another system of the cavity is to drain water through the weep holes lies above the window or base of the wall.
- The weep holes provide an air circulation system in the cavity walls that help to Come out of the evaporated water outside of the cavity.
- Approximately two meters apart at the base of each story, a weep hole is created by separating several vertical joints.
- The cavity holes are provided above the window because it prevents dry rot of wooden window frame.
- It is commonly referred to provide both sides of the cavity walls.
Cavity Wall Foundation Detail:
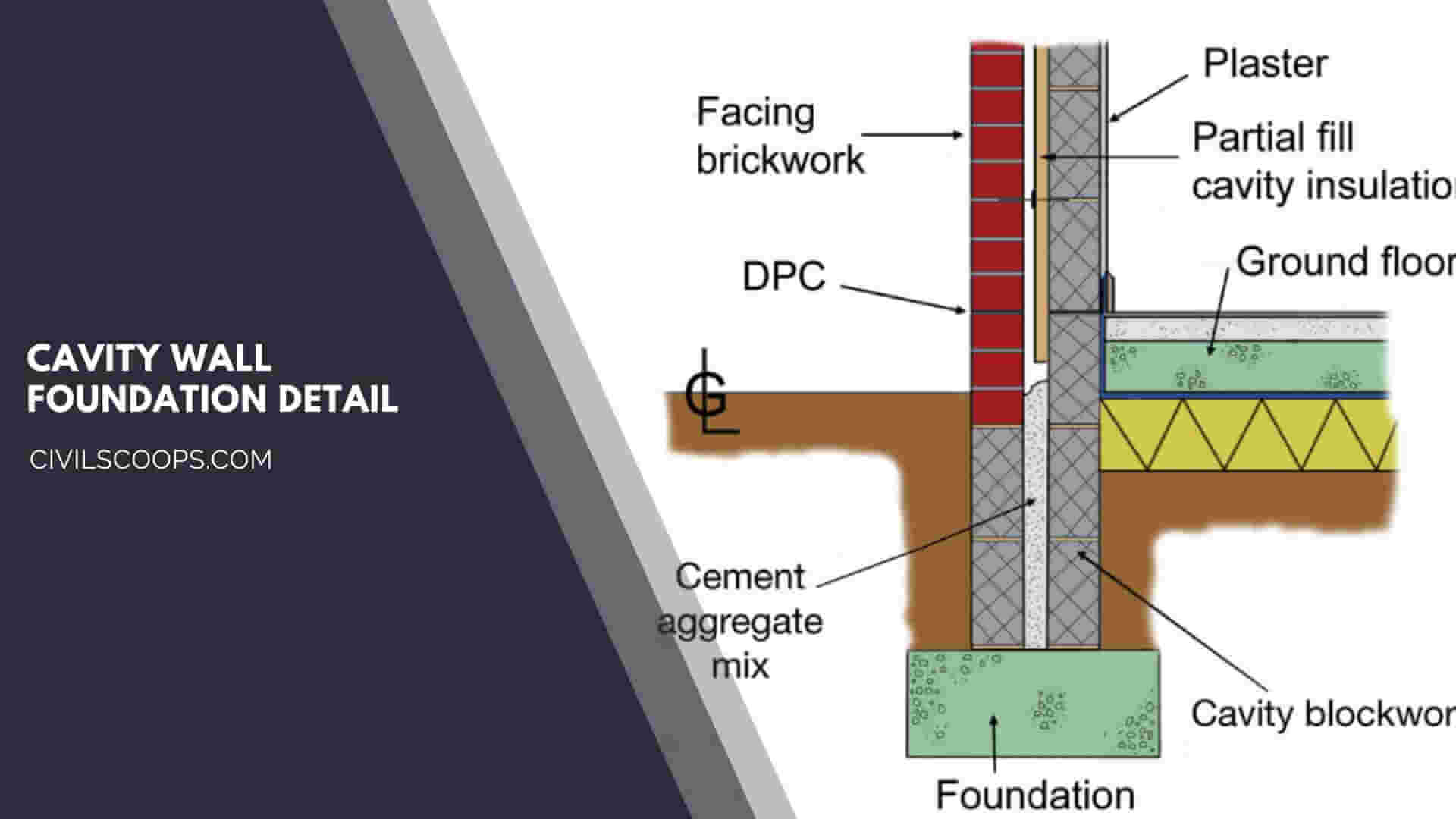
- The cavity portion between the top of the foundation concrete and the ground level is filled with 1:2:4 at least 150 mm below DPC.
- Under the two leaves separately, DPC is provided.
- The rainwater has access to drain out the outside of the leaves by the weep holes.
- The cavity walls are existing up to the concrete bed.
- Just below the floor level with a damp-proof course, the cavity extent up to the base of the footing.
- If the brickwork below the ground level is not correctly done, then the water enters from the joints and reaches up to the cavity causes dampness in the wall.
Cavity Wall Thickness:
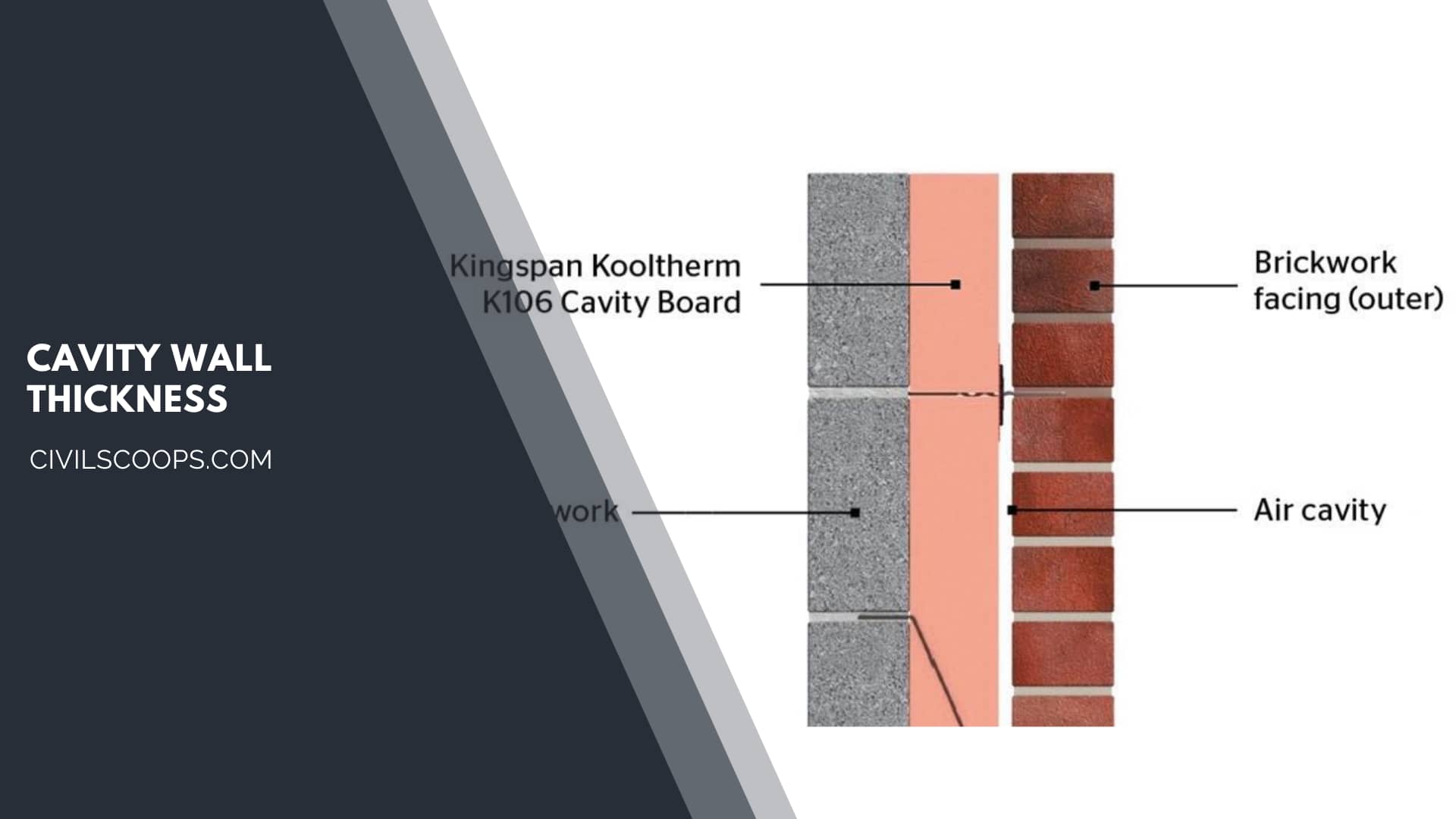
- The wall that is provided as a non-load bearing wall and that walls are hollow is called a cavity wall.
- The two leaves of the cavity wall are equal thickness. Sometimes the inner wall is thicker than the outer wall.
- The double walls of the cavity wall are 260 or 275 mm thick according to the building codes.
- The inner and outer walls of the cavity wall approximately 102.5 mm thick, consider 65 to 70 mm thick.
- Sometimes the inner wall should be increased to 215 mm or more when the floor is to be supported, or a heavier load is acting.
Internal Walls Construction:
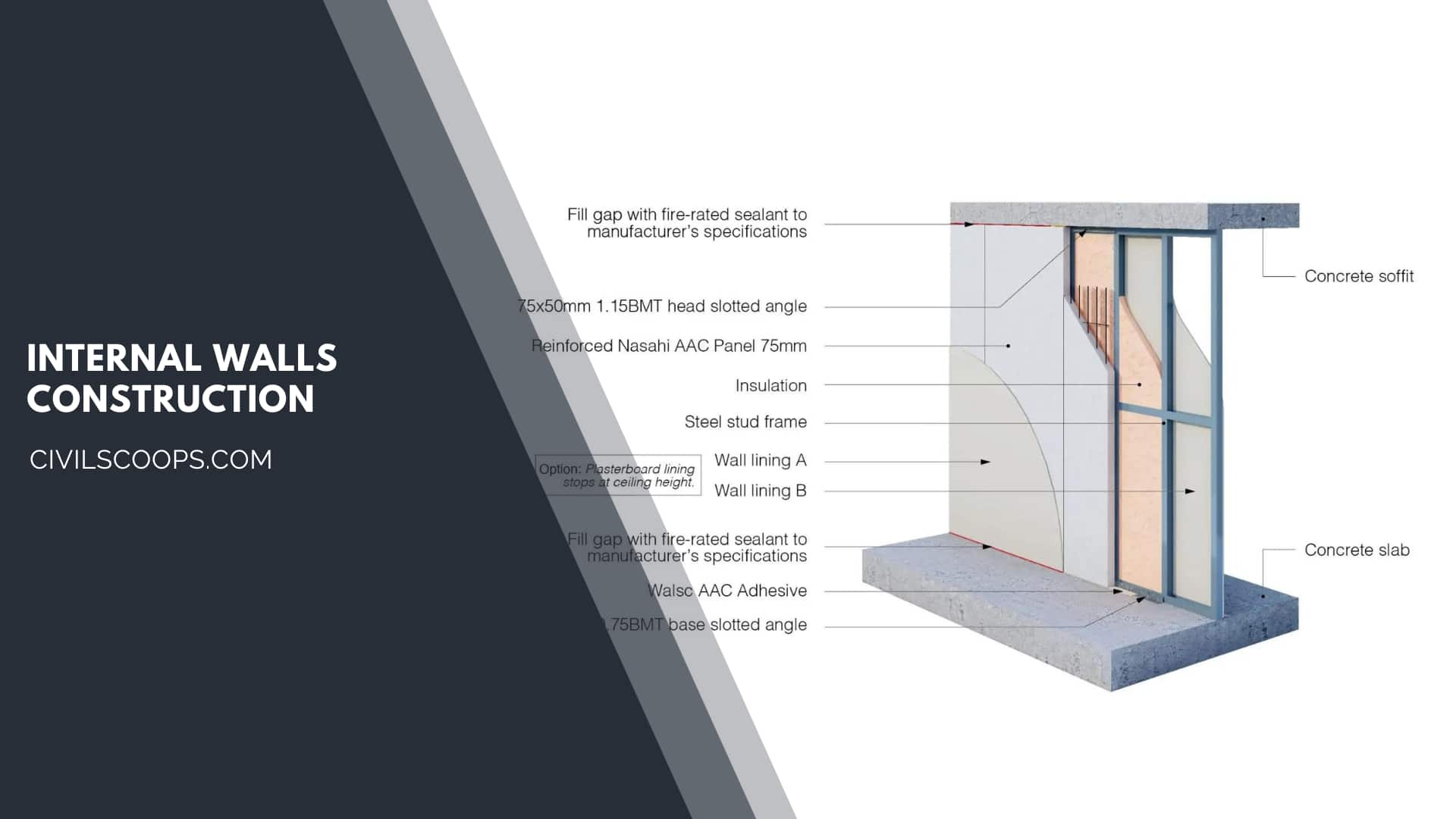
- The walls that divided the building into many compartments or created a private space is called internal walls or partitions walls.
- They can provide privacy, acoustic, fire resistance, and flexibility of layout.
- The partition wall may be hollow or solid, and it is constructed of bricks, cinder blocks, or RCC concrete blocks.
- It can be a form of frame structure like timber, steel, or aluminum frame clad with timber board, steel board, metal, or fiberboard. Sometimes the internal wall may be glazed.
- Sometimes it is used as a load-bearing wall and create a designer modular system.
Useful Article for You
- What Is a Highway Flyover
- What Is Grouting
- What Is a Pile Cap
- What Is a Bond Beam in Masonry
- What Is Sapwood
- What Is Crane
- What Is a Gable
- What Is Superelevation
- What Is Kerb
- What Is the Purpose of Washers
- What Is the Size of a Brick in Inches
- What Is Reinforced Masonry
- What Is Workability
- What Is Bond Breaker
- What Is Plasticizer in Concrete
- What Is Luminous Flux Vs Lumens
- What Is Caisson
- What Is an Undercoat
- What Is a Benchmark Surveying
- What Is Bracing in Construction
Brick Cavity Wall:
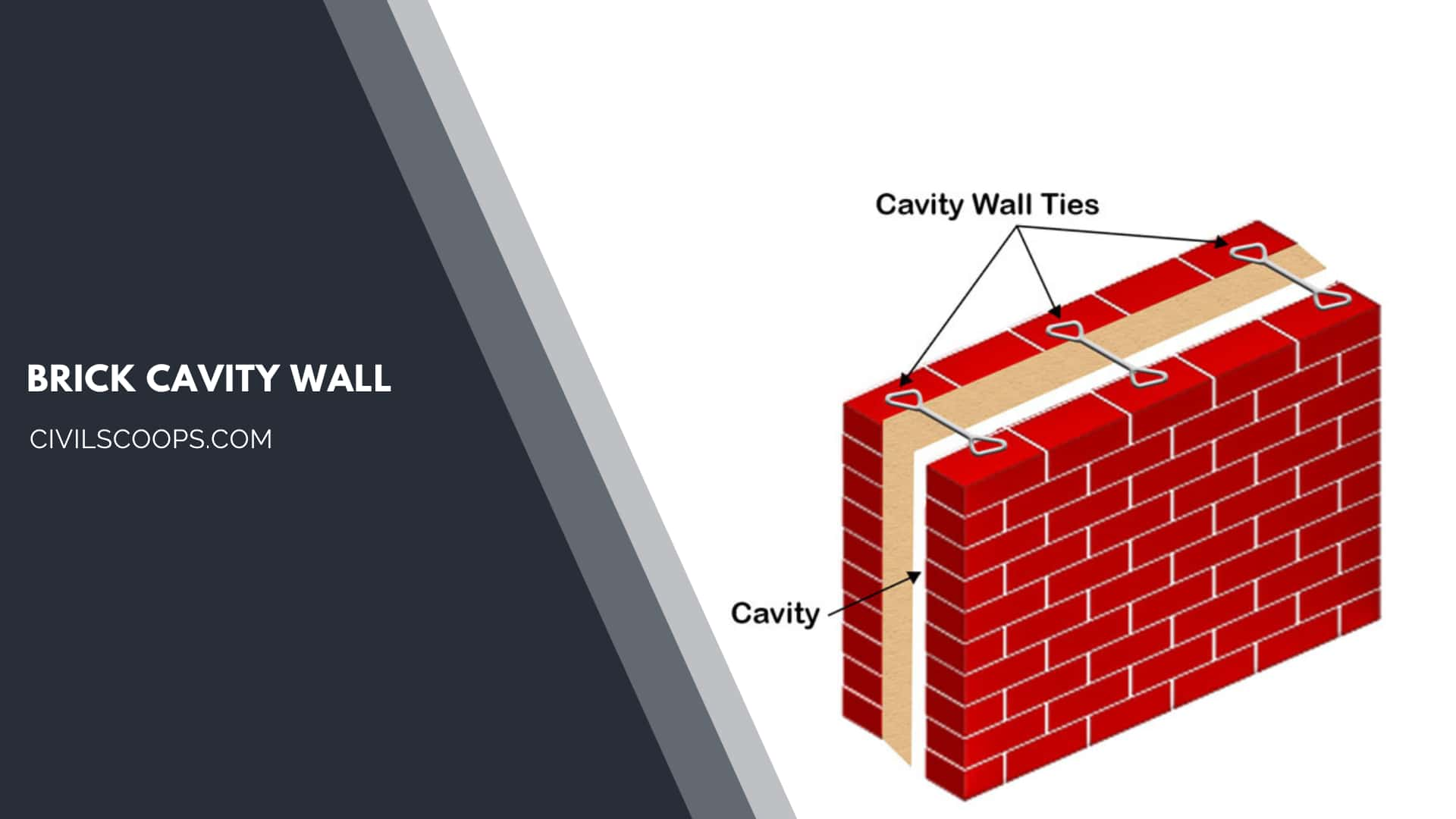
The cavity wall we can construct by many things that should be bricks, RCC concrete blocks, or cinder blocks.
Brick Cavity Walls:
- The cavity walls are made of two brick walls or leaves called brick cavity walls.
- In the two leaves or walls of the brick, a hollow space is a lie that is called a cavity.
- The weep hole is constructed above the window or base to draw out the rainwater from the brick cavity walls.
- It is joined together by metal ties and at suitable intervals.
Also Read: What Is Classification of Bricks | Classification of Bricks Different Base
Cavity Wall Insulation Pros and Cons:

- In building construction, there are have many pros and cons to cavity wall insulation.
- But there have more pros than cons-
Pros of Cavity Wall Insulation:
There are have many pros to cavity wall insulation –
- It controls the atmosphere in the house.
- It helps to keep the house warm in winter and cool in summer.
- it’s reduced the monthly electricity bill to reduce the uses of the room heater or air conditioner.
- The polystyrene bead is used as an insulation material that is so small so it can pump easily if even the cavity is lean.
- The loss of heat in the winter season should be reduced by using cavity wall insulation. Space between two walls is work as a lid that prevents the escaping of heat from the house.
- The material that is used in cavity wall insulation is cheaper and recycled materials.
Cons of Cavity Wall Insulation:
There are have some cons of the cavity walls insulation –
- Sometimes the cavity wall insulation cost is increased by using expert workers or special tools to inject the cavity with insulation materials.
- The risk of an inexperienced installer is another disadvantage of cavity wall insulation. The poor work of the inexperienced installer makes the wall damp.
- The cost amount of cavity wall insulation depends on the cavity or gap between the internal and external walls.
- If the width of the cavity is so small then the heat is not properly balanced in winter and summer.
- This cavity wall construction does not apply to all houses.it is not used in old buildings where the wall is solid.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
What Is a Cavity Wall?
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two “skins” separated by a hollow space. The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material that can slowly draw rainwater or even humidity into the wall.
What Is the Purpose of a Cavity Wall?
Cavity walls serve a number of purposes in the construction of a property. The primary purpose is to prevent moisture from outside from penetrating up the outer walls and into the inner rooms. When constructing a cavity wall, this leaves a gap in the middle which could make it easy to lose heat through your walls.
What Is Cavity Wall Insulation?
Cavity wall insulation is the insulation material that is installed into the cavity of a building, which is the space between the inner and outer wall. Cavity wall insulation traps the warm air in and prevents air from circulating around the cavity.
What Is Cavity Wall Insulation Made Of?
Materials used
The three most common types of cavity wall insulation used are: Blown mineral fibre. Polystyrene beads or granules. Urea formaldehyde foam.
What Is the Best Type of Cavity Wall Insulation?
Foam. Foam insulation, typically made of polyurethane, has been hailed as the best thermal cavity wall insulation.
How to Build a Cavity Wall?
Step-by-Step construction
- Load-bearing cavity walls must be laid on a level, stable concrete foundation.
- Fill the trench with concrete to 150 mm below the ground level.
- Mix the mortar (generally a Class 2 or 1:6 mix).
- Lay the first course/row of bricks for the inner leaf.
How to Insulate a Wall Without Cavity?
One such option to insulate walls without cavities is to insulate solid walls internally. This process involves adding an additional layer of insulation to your internal walls. This process is akin to building another wall or insulation board to the internal side of an external wall.
Cavity Wall Detail
A cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center. They can be described as consisting of two “skins” separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material that can slowly draw rainwater or even humidity into the wall.
Cavity Wall Construction Details
A cavity wall is composed of two masonry walls separated by an air space. The outer wall is made of brick and faces the outside of the building structure. The inner wall may be constructed of masonry units such as concrete block, structural clay, brick or reinforced concrete.
Cavity Wall Foundation Detail
In general, cavity wall doesn’t require any footings under it, just a strong concrete base is provided on which cavity wall is constructed centrally. Two leaves are constructed like normal masonry, but minimum cavity must be provided in between them.
Cavity Wall Thickness
Cavity Wall Thickness
Generally, these walls have a thickness of 260 or 275 mm according to the building codes. The inner and outer thickness of the wall is approximately 102.5 mm thick, consider 65 to 70 mm thick.
Brick Cavity Wall
A brick cavity wall is a type of construction with two layers of bricks separated by a gap (cavity) for insulation and moisture control.
Cavity Wall Insulation Pros and Cons
Advantages and disadvantages of cavity walls
- Moisture prevention. The main advantage of a cavity wall is moisture prevention.
- Heat insulation. The ability of a cavity wall to insulate better than a solid wall of the same overall thickness is a big advantage.
- Sound insulation.
- Material savings.
How Much Is Cavity Wall Insulation?
Generally, detached houses have the highest cavity wall insulation costs which go up to £800. Semi-detached houses can have insulation costs around £450-£500. Whereas, in mid-terraced houses, insulation costs are usually half the price, ranging from £340-£400.
Is Cavity Wall Insulation Worth It?
Benefits. About a third of all the heat lost in an uninsulated home escapes through the walls. By properly insulating cavity walls, you will save energy and cut costs off your heating bill.
What Material Is Used for Cavity Wall Insulation?
Common materials for cavity wall insulation include mineral wool (Rockwool or Glasswool), expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads, extruded polystyrene (XPS) boards, and polyurethane foam.
How to Insulate Cavity Walls?
Cavity wall insulation explained
Many cavity walls can be insulated by injecting insulation material into the cavity from the outside. A specialist company will drill holes in the outside walls, inject insulation through the holes and then seal them with cement.
How to Fill a Hole in a Cavity Wall?
Foam. Foam insulation, typically made of polyurethane, has been hailed as the best thermal cavity wall insulation. Installing it, however, can be tricky. So it’s important to get a professional in to make it work.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- What Is Timber
- All About of Tiles
- All About Chalk Paint
- How to Get Wet Blood Out of Carpet?
- What Is the Best Foundation for a House
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-09-18 10:34:04.
