Table of Contents
What Is Mix Design?
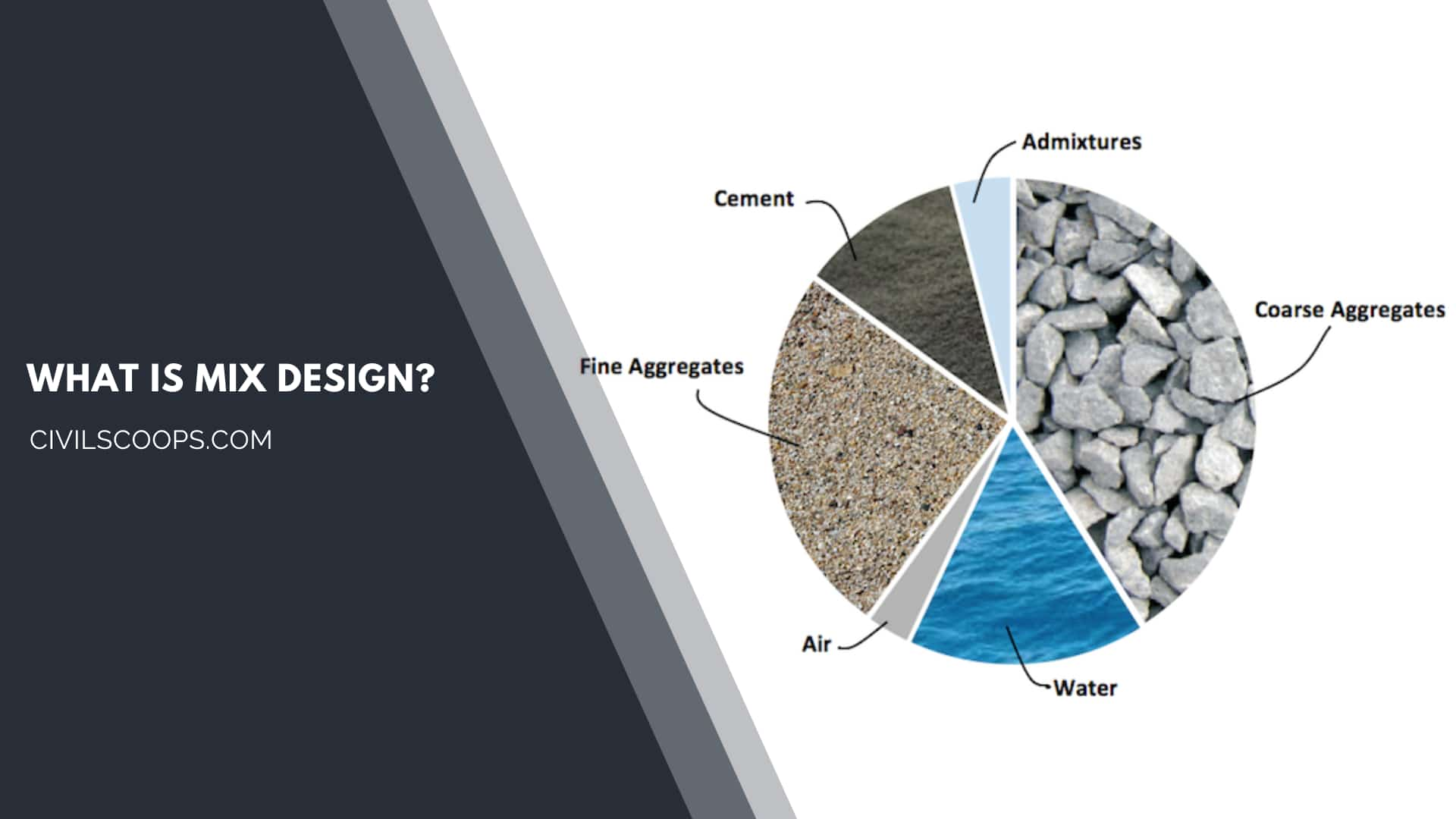
Concrete mix design is a procedure of manufacture of concrete with an ideal proportion of ingredients to fulfill the desired strength & sturdiness of the concrete structure.
This is essentially what is mix design of concrete.
Concrete is generally a blend of cement, sand & aggregates. Bridges, dams require an oversized amount of concrete, utilizing it incorrect quantity makes the structure economical.
Hence, to find the proper quantity of cement, sand & aggregate construction mix design of concrete is required.
Types of Concrete Mix Design
Three different types of mix design are as follows, which also covers types of concrete mix design.
1. Nominal Concrete Mix
Nominal concrete blend, also known as design mix, are low quality concrete blends utilized for bijou & unimportant jobs.
Superior aggregate quantity is fixed regardless of cement & coarse aggregate proportions.
Therefore, the standard of concrete blend are varied in range & required brawn might not be achieved.
However, the nominal concrete for given workability ranges in brawn on account of the discrete combination of design materials.
2. Designed Concrete Mix
Designed concrete blends, which is what is design mix concrete, doesn’t possess any specified ranges in proportions.
Planning is done in terms of the necessities of concrete brawn. So, it is possible to achieve the desirable features of concrete.
Fresh concrete properties like workability, setting time & hardened concrete properties like compressive strength, durability, etc.
are achieved by this procedure.
Utilization of additives like admixtures, retarders, etc.
is done to ameliorate the properties of blend.
The range of grades of concrete can be designed from as low as M10 grade to loftier grades like M80, M100.
Workability requirements of every blend can be attained utilizing this procedure from 0 to 150 mm slump.
The performance of the concrete is marked by the designer & combination ratio is set by the manufacturer.
This is the principal rational strategy for the selection of blending ratios with specific substances, considering discrete features.
The strategy ultimately ends up in manufacturing concrete at a low-cost price. There is no control test required according to the mass of the substance.
3. Standard Mix
Nominal blends of constant cement-aggregate proportion range in sturdiness & will lead to fewer or over-content blends.
That’s why, minimal compressive sturdiness obtained in many features & therefore these blends are referred to as standard mixtures, or what is a design mix.
Letter M denotes the amount which is specified by 28-day cubic energy of the mixture in N/mm2.
The mixture grades M10, M15, M20 & M25 approximately correspond to mixing ratios (1: 3: 6), (1: 2: 4), (1: 1.5: 3) and (1: 1: 2).
Also Read: What Is Concrete Forms | Types of Concrete Forms, Uses, Advantage, Disadvantages and Applications
Useful Article for You
- What Is a Highway Flyover
- What Is Grouting
- What Is a Pile Cap
- What Is a Bond Beam in Masonry
- What Is Sapwood
- What Is Crane
- What Is a Gable
- What Is Superelevation
- What Is Kerb
- What Is the Purpose of Washers
- What Is the Size of a Brick in Inches
- What Is Reinforced Masonry
- What Is Workability
- What Is Bond Breaker
- What Is Plasticizer in Concrete
- What Is Luminous Flux Vs Lumens
- What Is Caisson
- What Is an Undercoat
- What Is a Benchmark Surveying
- What Is Bracing in Construction
- What Is a Beam in Construction
- What Is the Standard Door Frame Size
- What Is a Spandrel Beam
- What Is a Fire Escape
- What Is a Weep Hole
- What Is Tie Beam
- What Is Fine Aggregate
- What Is Pony Wall
- What Is Flag Stone
- What Is Development Length
- What Is Cement Plaster
- What Is a Pitched Roof
- What Is Rafters
- What Is a Slab in Construction
- What Is a Monolithic Slab
- What Is Linear Distance
- What Is Shovel
- What Is Lintel in Construction
- What Is a Concept Sketch
- What Is Mezzanine Floor
- What Is Man Sand
- What Is Plaster Made Out of
- What Is a Floating Slab
- What Is Falsework
- What Is Bituminous
- What Is a Spillway
- What Is Curb and Gutter
Advantages of Mix Design
1. Desired Proportions of Every Ingredient
Main goal of the concrete blend design or concrete mix design, is to search the specified proportion of every module like cement, coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, water, etc.
2. Quality Concrete Mix:
Every module utilized in the concrete blend design is examined for its superior quality. The aggregates with good brawn, shape, relative density & free from organic content are utilized.
Superior concrete ameliorates its features like brawn, durability, etc. the design blend which is ready from ideal modules in definite proportions itself ameliorates the concrete features.
Concrete blend generated is examined utilizing compressive strength machines, tensile strength machines within concrete cubes & cylinders.
3. Economical Concrete Mix:
For generating concrete in nominal mix, or what is mix, is employed in place of other materials to inflict more brawn which affects the price of the project.
It additionally surges the warmth of hydration & causes cracks in concrete. But by utilizing a mix design, concrete of required sturdiness is designed with the precise quantity of cement.
It saves the value of the project & an economical concrete blend is derived & it also shields the formation cracks by lowering heat of hydration.
4. Best Use of Locally Available Material:
Mix design, or define concrete mix design, permits the employment of locally achievable materials like coarse aggregates, fine aggregates, etc.
as long as it’s of eximious quality.
This may diminish the value of the project.
5. Desired Properties of Mix:
The concrete thus achieved, through design mix definition, possesses features like workability, sturdiness, setting time, strength, impermeability, etc.
Design is done by keeping in mind a few vital factors like water-cement ratio, gradation of aggregates, etc.
According to the development conditions, admixtures are utilized to ameliorate the features of concrete.
Designed concrete blend fulfills the brawn requirement of a structure against several tyrannical environmental effects.
Also Read: What Is Bulkage of Sand (Fine Aggregate )
Disadvantages of Mix Design
- It requires a high initial cost.
- Also, require skilled labor.
- Also, requires specific attention.
Useful Article for You
- How Wide Is a Cinder Block
- How Much Is a Coffered Ceiling
- How to Make Mortar
- How Long Does Hempcrete Last
- How to Use a Hand Sight Level
- How to Construction
- How to Build a Lean to Roof
- How Are Tunnels Built
- How to Layout a Building
- How Wide Is a Car Parking Space
- How Do Shear Walls Work
- How to Measure Concrete Slump
- How Are Bridge Foundations Built
- How to Use Washers with Screws
- How Dense Is Sand
- How High Is a Window from the Floor
- How to Fix Spalling Concrete Foundation
- How Does a Beam Bridge Work
- How Do They Pour Concrete Under Water
- How Does a Sewer System Work
- How High Are Countertops
- How to Seal Brick Wall Interior
- How to Resurface Cement
- How to Use Portland Cement
- How Is Plaster Made
- How to Find Fineness Modulus
- How to Get Rid of Spray Paint Smell on Metal
- How Many Types of Slope Are There
- How Big Is a Stair Landing
- How Does Rebar Help Concrete
- How to Identify a Load Bearing Wall
- How to Get Paint Off Concrete Without Chemicals
- How to Fix Water Damaged Drywall
- How Much to Get Septic Pumped
- How to Cut a Nail or Screw
- How Long Does Wet Concrete Take to Dry
- How Is Varnish Made
- How Does Ejector Pump Work
- How Does a Cantilever Bridge Work
- How Does Hydrometer Work
- How to Get Wet Blood Out of Carpet
- How to Build House on Slope
- How Thick Is Plaster Wall
- How Suspension Bridges Work
- How to Seal a Concrete Roof
- How Was Cement Invented
Application of Mix Design

- Find out the mean target brawn ft from compressive brawn at 28-day fck & quality control level, which is a key aspect in types of mix design. ft= fck + 1.65 S, where S = standard deviation.
- Derive water-cement ratio for the target utilizing the relationship between compressive strength & water-cement proportion.
- Evaluate air quantity which is entrapped for optimum nominal size of the blend.
- Select the water content, for the specified workability & optimum size of blends.
- Derive the share of fine mixture in total combination by absolute volume for the concrete utilizing coarse aggregate.
- Regulate values of water & percentage of sand supplied for difference in workability & water-cement proportion.
- Evaluate cement content from the water-cement proportion & additionally the final water content.
- From water & cement per unit volume of concrete & percentage of sand already calculated, derive the quantity of coarse & fine aggregates per unit volume of concrete:
V =[W + (C/Sc)+{(1/p) x (fa/Sfa)}] x [1/1000]
V =[W + (C/Sc)+{(1/1-p) x (ca/Sca)}] x [1/1000]
- V = Absolute volume of concrete = Gross vol (1m3) – entrapped air vol
- Sc= Relative density of cement
- W = Mass of water/m3 concrete determined in kg
- C = Mass of cement/m3 concrete evaluated in kg
- p = Fine aggregate: total aggregate by absolute volume
- fa, Ca= Total masses of fine & coarse aggregates/m3 of concrete, respectively evaluated in kg
- Sfa, Sca= Specific gravities of saturated surface dry fine & coarse aggregates, respectively
Also Read: What Is Fine Aggregate | Types of Fine Aggregates (Classification)
Uses of Mix Design
Various area uses of mix design are as follows
- Designed to achieve the desired functionality within the plastic phase.
- Determine the minimal energy within the rigid phase.
- Supply concrete at a low cost.
Purpose of Mix Design
- Superior concrete mix design generates the foundation of a sound infrastructure.
- It is actually is a combination of modules which generates desired strength & sturdiness for the concrete structure.
- Because every ingredient within the mixture possesses a range of features, it’s not effortless to prepare a good concrete blend.
- Every one ingredient needs to be tested to note their features & therefore additionally the bearing capacity of the project location is also required to be examined.
- Water, fine sand, coarse aggregate, cement, chemicals, reinforcement, & soil needs to be checked.
- Values derived after testing are utilized for all mix designs. This makes sure that the structure is able to resist failure.
Conclusion
The rules & blended proportions ought to be done attentively as a bijou blunder may result in an adverse effect on the structure. Select the suited ratios of water, cement, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate, admixture for concrete.
Mix Design
Concrete mix design is the science of choosing the types of ingredients, and the proportions to use them in, to create concrete that meets the technical specifications for a given construction project. The needed properties vary depending on the project.
What Is Concrete Mix Design?
Concrete mix design involves a process of preparation in which a mix of ingredients creates the required strength and durability for the concrete structure. Because every ingredient in the mix consists of different properties, it’s not an easy task to create a great concrete mix.
Shotcrete Mix Design
shotcrete mix design is divided into wet mix and gunite to dry mix. This article focuses on the target mix design of shotcrete. The bulk density of wet sprayed concrete can be 2200-2300 kg/m 3, The weight ratio of cement to sandstone is preferably 1. 0: 3. 5 to 1.
Types of Concrete Mix Design
You can use two different mixes to make concrete:
- Nominal mix: This mix is used for ordinary construction such as small residential structures.
- Design mix: The design mix, or mix design, relies on proportions finalized using lab tests to determine the compressive strength of the mixture.
Concrete Mix Design Example
The mix ratios and concrete constituent mix proportions are prefixed and specified. For example, in M20(1:1.5:3), the amount of cement, sand, and aggregate is batched in volume according to the predetermined ratio 1:1.5:3. Concrete proportions up to M25 grade are referred to as nominal mix concrete.
Nominal Concrete Mix
Nominal mix concrete is a type of concrete mix that is prepared using approximate proportions of ingredients rather than precise measurements by weight or volume. It is often used in small-scale construction projects or in situations where detailed testing and quality control may not be critical.
Designed Concrete Mix
In a broad sense “designing” a concrete mix means selecting the proportions of fine and coarse aggregate, cementitious materials, admixtures, and water, that when combined will produce concrete having certain desired qualities and properties.
Screed Concrete Mix Design
Screed mix ratio can range between 1:3 – 1:5 cement to sand depending on the desired consistency and other factors. However, the traditional standard screed mix ratio is 1:4 cement to sand, creating a soft, malleable texture that is easy to work with.
High Strength Concrete Mix Design
According to the American Concrete Institute, high strength is defined as that over 6000 psi (41 MPa) compressive strength.
Quality Concrete Mix
It is a fundamental requirement of good-quality concrete that it contains an adequate cement content, or more precisely, a sufficiently low water/cement ratio, to provide adequate durability for the intended exposure conditions.
Mix Design Ratio
A properly designed concrete mixture will possess the desired workability for the fresh concrete and the required durability and strength for the hardened concrete. Typically, the volume of a mix is about 10 to 15% cementitious material, 60 to 75% aggregate, and 15 to 20% water.
Standard Concrete Mix Ratio
Standard Concrete Mix
The standard mix, which has a ratio of 1:2:3 (cement: sand: aggregates) or 1:1.5:3.5, is the most popular kind of concrete mixture (cement: sand: gravel). This mix is malleable and hence can be used in multiple projects, such as foundations, walls, and slabs.
How to Calculate Concrete Mix Design?
MIX CALCULATION :
- Volume of concrete = 1m^3.
- Volume of cement = (373/3.15)x1/1000 = 0.118 m^3.
- Volume of water = ( 149/1)x1/1000= 0.149 m^3.
- Volume of admixture = ( 7.6/1.145)x1/1000 = 0.006.
- Volume of coarse aggregate and fine aggregate = a – ( b + c + d) = 1-( 0.118 + 0.149 + 0.006 )= 0.727 m^3.
How Much Is Concrete Mix?
The typical cost of concrete is between $110 and $165 per cubic yard on average (excluding labor cost). In addition to the price per cubic yard, you’ll have to pay someone about $8 to $18 per square foot of your project to pour and install the concrete.
How Much Is Ready Mix Concrete?
Having ready-mix concrete delivered to your home typically costs an average of $117 per cubic yard or between $104 to $144 per cubic yard. When you hire a concrete pro to install a concrete slab for you, labor and materials rates are typically charged per square foot rather than per cubic yard.
How Do You Mix Concrete?
Mixing
- Measure the water according to the instructions on the bag.
- Pour about 3/4 of the pre-measured water into the mixer – this is called “head water”.
- Wearing gloves and respiratory protection, place bagged concrete mix on the edge of the mixer, cut open the open the top and pour into the mixer.
- Switch on the mixer.
How Much Does Concrete Mix Cost?
Building Construction Ready Mixed Concrete
Prices range available in: Rs. 4000-4200.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –