Types of Concrete Blocks
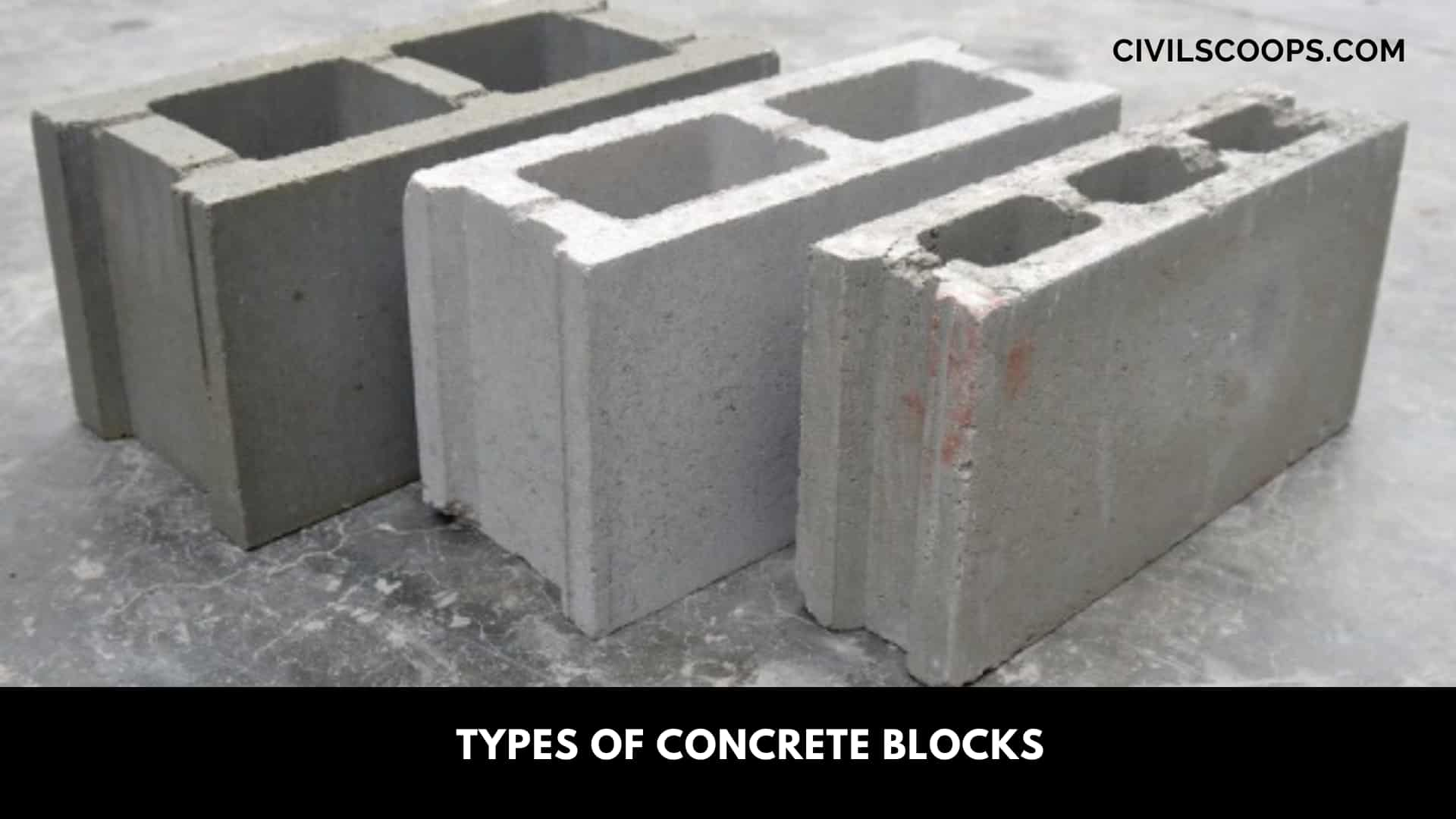
Table of Contents
Introduction of Concrete Blocks
Concrete blocks, widely known as Concrete Masonry Unit (CMU), encompass various types of blocks such as solid concrete blocks, hollow concrete blocks, and more These types of concrete blocks have some advantages with compare to brick and stone masonry blocks. This concrete blocks may be solid in shape or hollow
The normal size of concrete block is 39cm x 19cm x (30cm or 20 cm or 10cm) or 2/4/6/8/10/12 inches. Generally cement, aggregate (coarse and fine) and water is used to construct those concrete blocks. 1:6 is the cement-aggregate ratio where 60% is for fine aggregate and 40% is for fine aggregate.
The normal minimum strength of these blocks are 3N/mm2.
Types of Concrete Blocks
Generally various types of concrete are available in the market, those types are
- Solid concrete block
- Hollow concrete block
- Concrete corner block
- Concrete stretcher block
- Jamb concrete block
- Partition concrete block
- Concrete pillar block
- Lintel blocks
- Bull nose concrete blocks
- Frogged brick block
- Paving blocks
- Light aerated concrete blocks
- Cellular lightweight concrete blocks
- Fly ash blocks
- Concrete bricks
1. Solid Concrete Blocks

Solid concrete blocks, one of the different types of concrete blocks, are widely used in construction but they are very heavy in weight because it is manufactured from dense concrete.
This types of bricks are strong in nature and it provides good stability. Solid Concrete blocks are very suitable in load bearing structure and this is highly preferable. Solid concrete blocks are available in many size and this is generally larger than normal clay bricks.
Also Read: All About Green Concrete | What Is Environmentally Friendly Concrete
Useful Article for You
- What Is a Highway Flyover
- What Is Grouting
- What Is a Pile Cap
- What Is a Bond Beam in Masonry
- What Is Sapwood
- What Is Crane
- What Is a Gable
- What Is Superelevation
- What Is Kerb
- What Is the Purpose of Washers
- What Is the Size of a Brick in Inches
- What Is Reinforced Masonry
- What Is Workability
- What Is Bond Breaker
- What Is Plasticizer in Concrete
- What Is Luminous Flux Vs Lumens
- What Is Caisson
- What Is an Undercoat
- What Is a Benchmark Surveying
- What Is Bracing in Construction
- What Is a Beam in Construction
- What Is the Standard Door Frame Size
- What Is a Spandrel Beam
- What Is a Fire Escape
- What Is a Weep Hole
- What Is Tie Beam
- What Is Fine Aggregate
- What Is Pony Wall
- What Is Flag Stone
- What Is Development Length
- What Is Cement Plaster
- What Is a Pitched Roof
- What Is a Slab in Construction
- What Is a Monolithic Slab
- What Is Linear Distance
- What Is Shovel
- What Is Lintel in Construction
- What Is a Concept Sketch
- What Is Mezzanine Floor
- What Is Man Sand
- What Is Plaster Made Out of
- What Is a Floating Slab
- What Is Falsework
- What Is Bituminous
- What Is a Spillway
- What Is Curb and Gutter
- What Is Dampness
- What Is Lap Length
- What Is the Full Form of Fsi
- What Is Door Frame
- What Is Plinth Protection
- What Is Traffic Rotary
- What Is Grade Slab
- What Is Rolling Margin of Steel
- What Is Modulus of Rupture
- What Is Fresh Concrete
- What Is Dpc in Construction
- What Is Earthen Dam
- What Is Plum Concrete
- What Is Shell Structure.
- What Is Lumber
- What Is the Strongest Foundation for a House
- What Is the Meaning of Soundness of Cement
- What Is Flyover Bridge
- What Is Under Reamed Pile
- What Is Weir
- What Is Inverted Beam
- What Are the Advantages of Levelling?
- What Is Sunk Slab
- What Is Brick Bat Coba
- What Is Isolated Footing
- What Is Long Column
- What Is Plate Load Test
- What Is Formwork
2. Hollow Concrete Blocks

Hollow concrete blocks, representing one of the types of cinder blocks, have more than 25% of gross concrete. This type of blocks are light weight and easy to install in the construction site. Hollow concrete blocks are divided into several components and they are divided into some types, those are
3. Concrete Corner Block

This type of concrete blocks are used in the corner part of concrete masonry. These blocks are widely used in window and door openings. These blocks are laid in the same plane and locked with the other stretcher bond.
Also Read: Concrete Construction Tools for Construction Sites
4. Concrete Stretcher Block

Concrete stretcher blocks are also used the corner of the masonry. Concrete hollow blocks are widely used in the concrete stretcher block. Concrete stretcher blocks are laid with the parallel length to the face.
5. Jamb Concrete Block
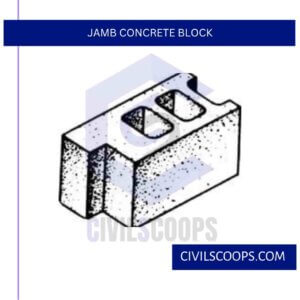
In a building where a elaborated window opening is found then we use jamb concrete block. Stretcher and corner blocks are connected with the Jamb concrete block. In double hung window; jamb concrete blocks are used to provide some space for window members.
6. Partition Concrete Block

Partition are only constructed and used for partition purpose and the height o this type of block is slightly higher than the breadth of the block. These blocks are mainly hollow in nature and this hollow section are divided into two or three parts.
7. Concrete Pillar Blocks

Double corner block is the another name of concrete pillar block. It is generally used where two joints are clearly visible, this only happens in pillar that’s why the name of the block is concrete pillar block.
8. Lintel Blocks

This type of concrete blocks are used for constructing beam or lintel beam, it generally bears the upper portion load of door and window portion. These concrete blocks have a groove portion along with the length of the block. After placing the lintel blocks, it is filled with concrete and reinforcement to increase it’s strength.
9. Bull Nose Concrete Block

Bull nose concrete blocks are also used in the corner portion, the purpose of this type of block is also same. We only use this type of blocks when we want rounded edges at the corner.
10. Frogged Brick Blocks

This type of blocks have a frog portion on top surface of the block along with header and stretcher. Frog helps to hold the mortar and create a strong bond with another brick.
11. Paving Blocks

Paving blocks are generally square or rectangular in size and these blocks are constructed with reinforced cement concrete. Paving blocks are normally laid in the shoulder part of the highway and these are painted with the paint of high visibility to attract the automobile drivers.
These type of blocks are rigid in nature so it increases the probability of road accidents. Paving blocks are also used in the parks, parking area or sometime in the footpath of any road. The general dimension of the paving block is 60 mm.
12. Light Aerated Concrete Blocks

Light aerated concrete blocks are lightweight in nature. These blocks are constructed with Portland cement, aggregates, sand, high quality, etc. So, they are produced using caerated concrete.
13. Cellular Lightweight Concrete Block

Cellular lightweight concrete blocks are also light weight in nature. These type of blocks have good mechanical strength and low thermal conductivity property.
Cellular light weight concrete block are made of low density Portland cement which have a large variety with small air bubbles.
Useful Article for You
- How Wide Is a Cinder Block
- How Much Is a Coffered Ceiling
- How to Make Mortar
- How Long Does Hempcrete Last
- How to Use a Hand Sight Level
- How to Build a Lean to Roof
- How Are Tunnels Built
- How to Layout a Building
- How Wide Is a Car Parking Space
- How Do Shear Walls Work
- How to Measure Concrete Slump
- How to Use Washers with Screws
- How Dense Is Sand
- How High Is a Window from the Floor
- How Does a Beam Bridge Work
- How Do They Pour Concrete Under Water
- How Does a Sewer System Work
- How High Are Countertops
- How to Seal Brick Wall Interior
- How to Resurface Cement
- How to Use Portland Cement
- How Is Plaster Made
- How to Get Rid of Spray Paint Smell on Metal
- How Many Types of Slope Are There
- How Big Is a Stair Landing
- How to Get Paint Off Concrete Without Chemicals
- How to Fix Water Damaged Drywall
- How Much to Get Septic Pumped
- How to Cut a Nail or Screw
- How Long Does Wet Concrete Take to Dry
- How Is Varnish Made
- How Does Ejector Pump Work
- How Does Hydrometer Work
- How to Get Wet Blood Out of Carpet
- How to Build House on Slope
- How Thick Is Plaster Wall
- How Suspension Bridges Work
- How to Seal a Concrete Roof
- How Was Cement Invented
- How to Calculate Area of Steel
- How to Check Silt Content in Sand
- How a Building Is Constructed
- How Are Roads Classified in India
- How Many Types of Cement in India
- How to Find Contour Interval
- How to Stop Leakage from Ceiling
- How Hardness of Brick Is Tested
- How Many Types of Paint Brushes Are There
- How to Calculate Skirting Area
- How Many Types of Beam
- How to Make Road
- How Many Types of Chain in Surveying
- How to Find One Way and Two Way Slab
- How Many Types of Houses
- How to Find Steel Bar Weight
- How to Calculate Septic Tank Capacity in Liters
- How to Calculate the Bearing Capacity of Soil
- How Many Types of Bricks Are There
- How Many Types of Cement Are There
- How to Make Block
- How to Build House Step by Step
14. Fly Ash Blocks

Fly ash blocks are light weight than the clay bricks and they are also economical than those clay bricks. They are generally made from waste materials which are come from combustion of coals in thermal power plant.
15. Concrete Blocks

Concrete blocks, encompassing various block types like types of concrete bricks, are small rectangular symmetric blocks which create a rigid wall.
These bricks have greater compressive strength than normal clay bricks and also have less water absorption property tan the clay bricks.
Concrete bricks are generally made of cement, sand, slight amount of fly ash, etc. These type of blocks are generally used in facades, fences due to it’s beautiful and modern aesthetic look.
Type of Concrete Blocks and Their Dimensions
[su_table responsive=”yes” alternate=”no”]
| Concrete Block | Dimensions |
| Hollow Concrete Block |
400 x 200 x 100 / 150 / 200 mm
|
| Concrete Brick |
230 x 110 x 70 mm
|
| Solid Concrete Block | 8 x 8 x 16 inch |
| Paving Block |
200 x 100 x 60 mm
|
| Light Aerated Concrete Block |
600 x 200 x 100 mm
|
| Cellular Lightweight Concrete Block | 24 x 8 x 4 inch |
| Fly Ash Block |
230 x 110 x 70 mm
|
[/su_table]
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Types of Concrete Blocks
- Bullnose Block
- Lintel block
- Pillar block
- Corner block
- Paving block
- Stretcher block
Concrete Blocks
A concrete block, also known as a cinder block in North American English, breeze block in British English, concrete masonry unit, or by various other terms, is a standard-size rectangular block used in building construction.
Types of Paving Blocks
- Concrete
- Concrete block
- Brick
- Flagstone
- Bluestone
- Marble
Cinder Block Column Footing
Column footing ,simply, is a reinforced concrete block ,setting up under the earth with a calculated depth based on the loads affecting the building, the Column is fixed at the footing. Civil engineers design it to prevent the column from settlement due to the vibration of the soil.
Block and Pier Foundation
A full block foundation consists of concrete block, mortar and reinforcement. The block is laid to form a wall around the perimeter of the home. A “pier and curtain” foundation consists of concrete block, mortar and brick. Concrete block piers are built every 6 to 8 feet providing support for your home.
Concrete Block Pavement
Concrete block paving provides a hard surface which is aesthetically pleasing, comfortable to walk on, trafficable, extremely durable and easy to maintain. Paving blocks are fully engineered products, manufactured in factory conditions, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
Concrete Block Pier Foundation
A concrete block pier foundation is a type of foundation used in construction to support a structure, such as a house or building. It involves the use of concrete blocks or concrete masonry units (CMUs) to create a series of piers or supports upon which the structure is built.
Solid Concrete Blocks
Fully solid concrete blocks look like gray bricks but are typically larger. They’re good for creating walls that provide protection against the elements, such as strong winds. They can also be used for projects such as garden walls and planters, retaining walls, foundations, steps, and firepits.
How Much Does a Solid Concrete Block Weigh?
The most commonly used is a hollow 8″x8″x16″ block which weighs 38 lbs. / 17 kg.
Hollow Concrete Blocks
Hollow blocks, which have holes that take up more than one-quarter (and usually more than half) of their cross-sectional area, are used when building boundary fences and other large structures. The holes make them lighter and can be useful when running wiring or piping through them.
Concrete Corner Block
Concrete Corner Blocks are durable and versatile. Build interior and exterior walls, partitions, terrace walls and other enclosures. Blocks are a standard gray color with a natural finish and uniform shape. Meets ASTM C-90 specifications. Recommended for use in corner returns.
Concrete Stretcher Block
Stretcher Block—Stretcher concrete blocks are smaller than standard hollow concrete blocks. They have a flat length and specially shaped ends that are used to connect the corner in masonry work. Corner Block—Corner concrete blocks have flat lengths, one flat end and one specially shaped end.
Jamb Concrete Block
Jamb blocks are made with a shallow groove across the two holes and a deeper groove at one end. They provide space for the casing members of a window and are often used specifically in double-hung windows.
Concrete Blocks Dimensions
Blocks are produced in a broad range of sizes, but for general building work the most commonly used is referred to as a standard block and measures 440mm x 100mm x 215mm.
Partition Concrete Block
Concrete Partition Block is most commonly used as a partition for interior non-load bearing walls. Concrete block is most sustainable and most long-lasting building product investments available. Gains strength with age, is exceptionally durable and offers unsurpassed protection against fire, termites and wind.
Concrete Pillar Blocks
Concrete blocks — or concrete masonry units (CMUs) — are used for building walls, pillars and other structures. Concrete blocks offer several advantages, including: Lower costs for materials and maintenance. Easier handling due to lightweight aggregates. Better insulating properties for dampness, heat and sound.
Lintel Blocks
Lintel or channel blocks are U-shaped concrete masonry units used above openings to create lintels. Since lintel block units are solid along the bottom, the underside can be exposed at openings. However, because of this feature, these block units do not allow vertical reinforcement to extend through them.
Bullnose Concrete Block
Bullnose units are often used in the construction of exposed walls. They provide safety, unique aesthetics, and the rounded corners are very resistant to chipping. One of the most common applications for bullnose units are horse stables. We can produce single and double bullnose units in 6-inch and 8-inch widths.
Frogged Brick Blocks
A frog is a depression in one bearing face of a molded or pressed brick. The frog reduces the weight of the brick and makes it easier to remove from the forms. ASTM specifications C 62 (building brick), C 216 (facing brick), and C 652 (hollow brick) all set limits on the size of frogs.
Paving Blocks
Paving Blocks means cement or plastic grids with void spaces. Paving blocks make the surface more rigid and gravel or grass planted inside the holes allows for infiltration. Depending on the use and soil types, a gravel layer can be added underneath to prevent settling and allow further infiltration.
Cellular Lightweight Concrete Block
Lightweight Cellular Concrete (LCC) contains type (I) II‐V Portland cement, water, and a preformed foam. The foam looks like shaving cream and is varied in quantity to control the unit weight of the cellular concrete.
Fly Ash Blocks
Fly ash brick is a building material, specifically masonry units, containing class C or class F fly ash and water. Compressed at 28 MPa and cured for 24 hours in a 66 °C steam bath, then toughened with an air entrainment agent, the bricks can last for more than 100 freeze-thaw cycles.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- H-Beam vs I-Beam
- Properties of Sand
- Basic Plumbing System
- Construction Risk Management
- What Is Recycled Concrete Aggregate
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-11-20 13:00:50.
