What Is Water Cement Ratio | Water-Cement Ratio and Concrete Strength | Role of Water in Concrete
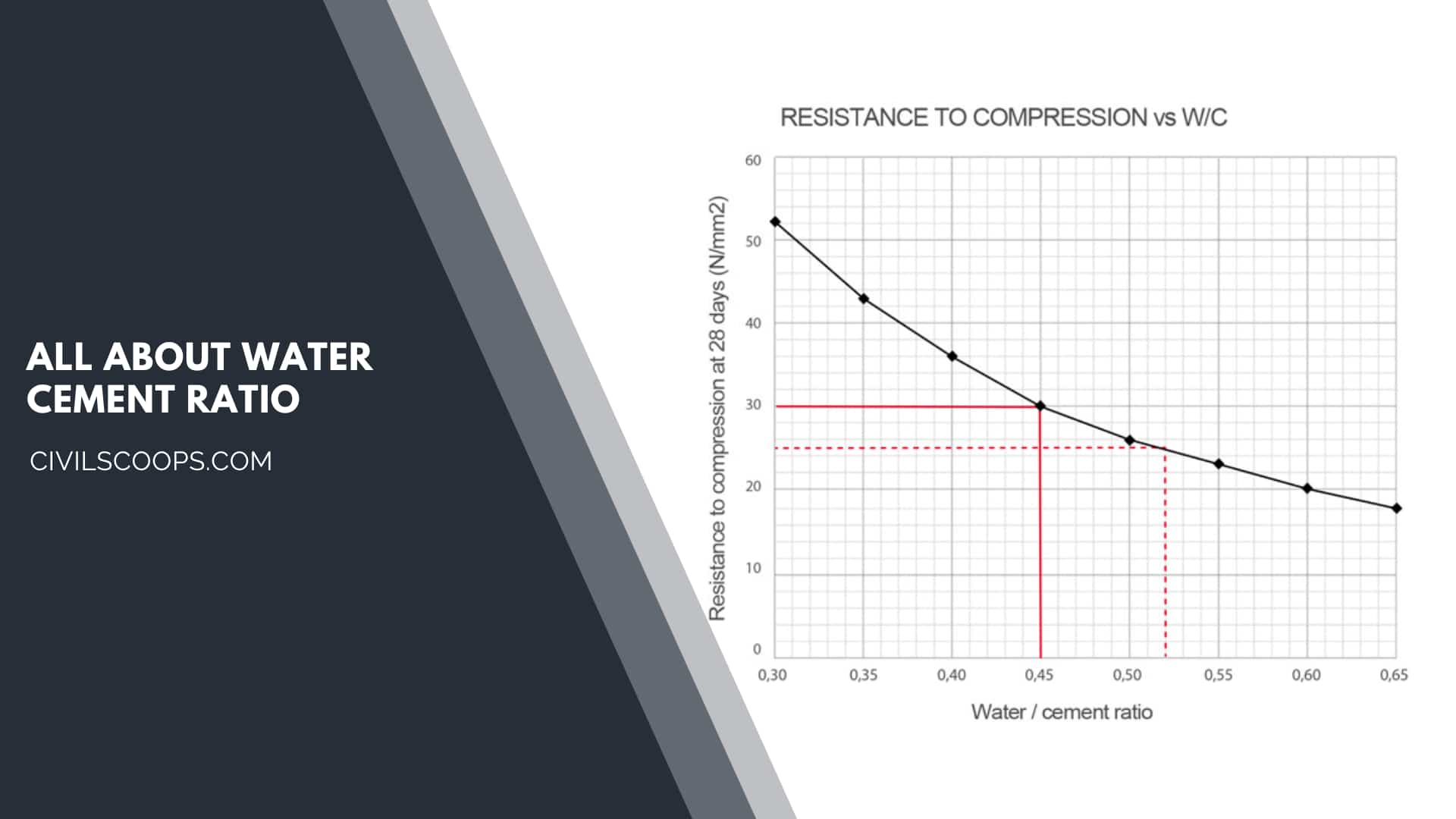
Table of Contents
What Is Water Cement Ratio?

It is the ratio of cement and water utilized in the preparation of concrete. The quantity of water used at mixing concrete is very important.
If the percentage of water used is less, then there will not be a sufficient quantity of water to hydrate cement. It will result in weak and porous concrete.
Therefore, the usual tendency is to use too much water which gives a more workable mix, but it doesn’t give sound concrete. Too much water results in the segregation of aggregates and give porous concrete of low strength and low density.
A certain minimum proportion of water is necessary to hydrate the cement completely. To create the concrete sufficiently workable to be placed in position, some more water is needed.
So long as the concrete is sufficiently workable, for the way of placing used, its strength depends on the proportion of water to the cement in the mix.
The water-cement ratio shouldn’t be allowed to exceed the specified limits for various types of concrete and should usually be kept as low as the methods of placing will allow.
Abrahms, as a result of a large number of experiments, states that“with given materials and conditions of the test, the ratio of the quantity of mixing water into the quantity of cement alone determines the potency of concrete as long as the mix is of workable plasticity.“
This is known as water-cement ratio law. According to this law, the strength of concrete won’t increase by simply increasing the quantity of cement unless the water-cement ratio is reduced.
Required Water-Cement Ratio (British Standard Specifications)
[su_table responsive=”yes” alternate=”no”]
| Proportion |
Water-Cement Ratio
|
| 1:02:04 | 0.58 |
| 1:1.5:3 | 0.51 |
| 1:01:02 | 0.43 |
[/su_table]
Water-Cement Ratio Table
[su_table responsive=”yes” alternate=”no”]
| Exposure | Plain Cement Ratio | Reinforced Cement Concrete | ||||
| IS 10262 | Minimum Cement Content | W/C Ratio | Grade | Minimum Cement Content | W/C Ratio | Grade |
| Mild | 220 | 0.6 | 300 | 0.55 | M20 | |
| Moderate | 240 | 0.6 | M15 | 300 | 0.5 | M25 |
| Severe | 250 | 0.5 | M20 | 320 | 0.45 | M30 |
| Very Severe | 260 | 0.45 | M20 | 340 | 0.45 | M35 |
| Extreme | 280 | 0.4 | M25 | 360 | 0.4 | M40 |
[/su_table]
Different Water Cement Ratios

Different Water-cement ratios are utilized for different concrete applications. For high-quality concrete construction, a lower water-cement ratio of 0.4 could be employed.
For concrete construction like sidewalks and drives, a w/c ratio ranging from 0.6 to 0.7 is normally used.
The practical range of water-cement ratio ranges from 0.3 to 0.8, which gives weak and stiff concrete, respectively. Weak concrete means a fairly wet concrete.
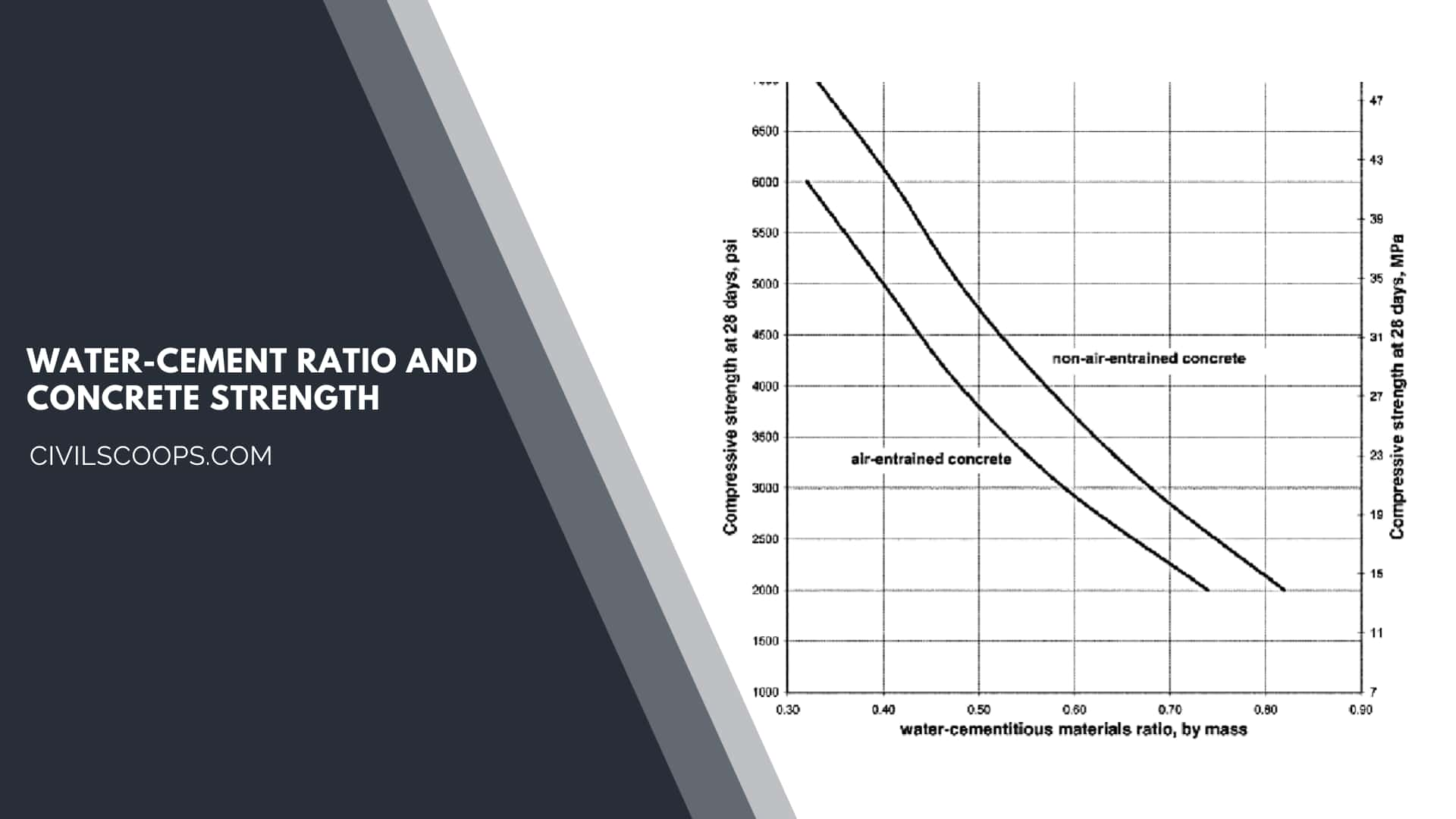
Compressive strength of about 5600 psi can be obtained in the concrete of the water-cement ratio 0.4. This value will go down to 2000 psi when a water-cement ratio of 0.8 is used.
Also Read: Concrete Material Calculation / Concrete Quantity
Useful Article for You
- What Is a Highway Flyover
- What Is Grouting
- What Is a Pile Cap
- What Is a Bond Beam in Masonry
- What Is Sapwood
- What Is Crane
- What Is a Gable
- What Is Superelevation
- What Is Kerb
- What Is the Purpose of Washers
- What Is the Size of a Brick in Inches
- What Is Reinforced Masonry
- What Is Workability
- What Is Bond Breaker
- What Is Plasticizer in Concrete
- What Is Luminous Flux Vs Lumens
- What Is Caisson
- What Is an Undercoat
- What Is a Benchmark Surveying
- What Is Bracing in Construction
- What Is a Beam in Construction
- What Is the Standard Door Frame Size
- What Is a Spandrel Beam
- What Is a Weep Hole
- What Is Tie Beam
- What Is Fine Aggregate
- What Is Pony Wall
- What Is Flag Stone
- What Is Development Length
- What Is Cement Plaster
- What Is a Pitched Roof
- What Is a Slab in Construction
- What Is a Monolithic Slab
- What Is Linear Distance
- What Is Shovel
- What Is Lintel in Construction
- What Is a Concept Sketch
- What Is Mezzanine Floor
- What Is Man Sand
- What Is Plaster Made Out of
- What Is a Floating Slab
- What Is Falsework
- What Is Bituminous
- What Is a Spillway
- What Is Curb and Gutter
- What Is Dampness
- What Is Lap Length
- What Is the Full Form of Fsi
- What Is Door Frame
- What Is Plinth Protection
- What Is Traffic Rotary
- What Is Grade Slab
- What Is Rolling Margin of Steel
- What Is Modulus of Rupture
- What Is Fresh Concrete
- What Is Dpc in Construction
- What Is Earthen Dam
- What Is Plum Concrete
- What Is Shell Structure.
- What Is Lumber
- What Is the Strongest Foundation for a House
- What Is the Meaning of Soundness of Cement
- What Is Flyover Bridge
- What Is Under Reamed Pile
- What Is Weir
- What Is Inverted Beam
- What Are the Advantages of Levelling?
- What Is Sunk Slab
- What Is Brick Bat Coba
- What Is Isolated Footing
- What Is Long Column
- What Is Plate Load Test
- What Is Formwork
- What Is Concealed Beam
- What Is Acp
- What Is Wbm Road
- What Is Slab
- What Is Quick Setting Cement
- What Is Rapid Hardening Cement
Water-Cement Ratio and Concrete Strength
The general concrete strength is reduced with the increase in the water-cement ratio. The addition of more water gives dilute paste, which has more pores at the micro-level.
These make the concrete weak and results in shrinkage and cracks and issues. The Cement and aggregates particles take the excess water that’s present in concrete.
This consumption is uncontrollable if a large excess of water is present in the concrete. Therefore, separate water channels are created, resulting in bleeding on the surface.
This creates weak zones in concrete that are susceptible to cracking under service loads.
A lower water-cement ratio may contribute to high strength and high-quality concrete. But the water-cement ratio alone cannot give good concrete.
A good mix proportion and quality aggregates and binding materials contribute to a good mix design. A low water-cement ratio is thus one of the factors influencing good mix design.
Also Read: 10 Different Types of Loads on Structures | What Are Structural Loads
Water-Cement Ratio and Permeability
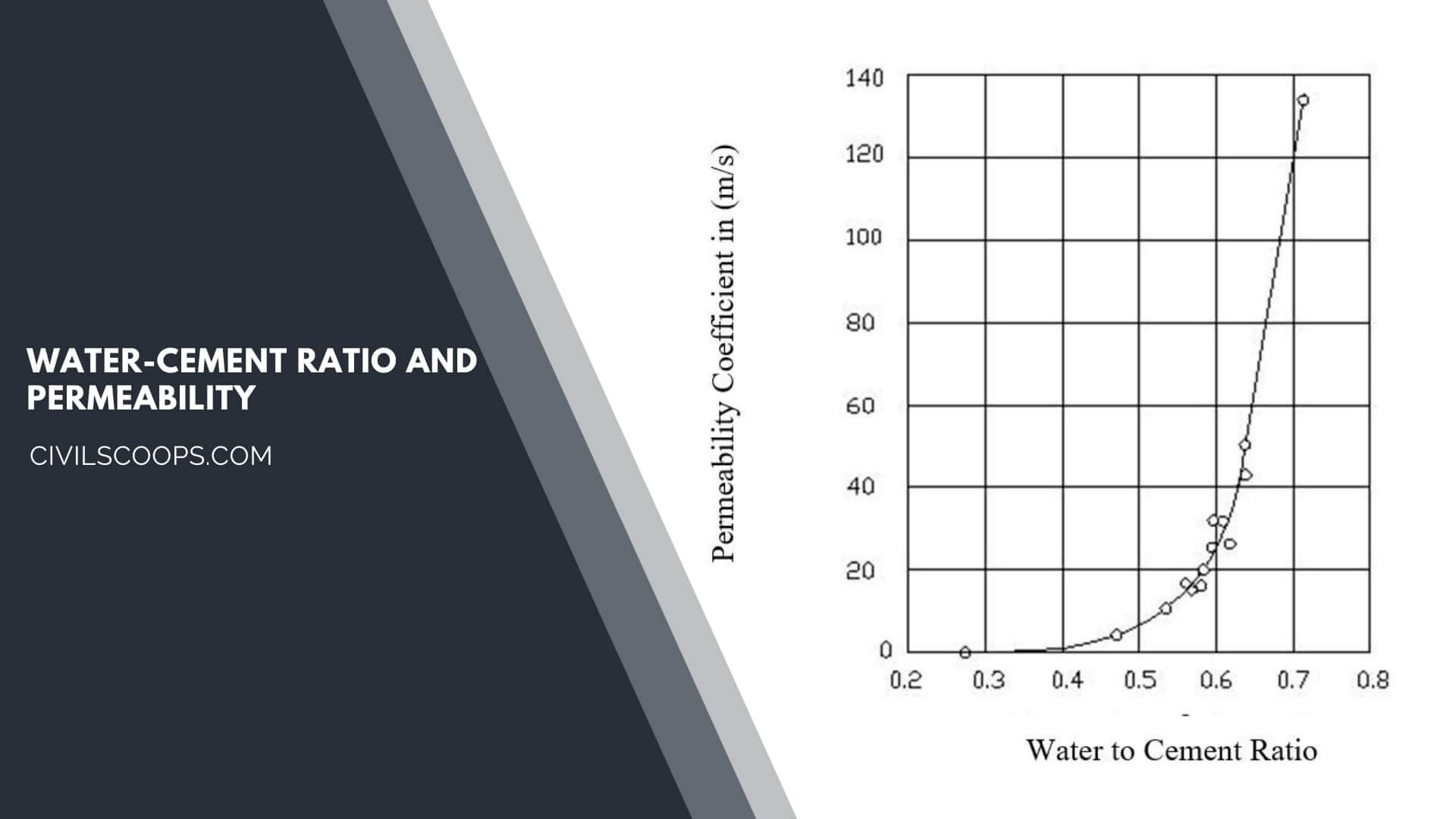
A mix design using a lower water-cement ratio or higher cement content will give low permeability concrete. A high strength concrete tends to give less pervious concrete.
This will increase the durability of the concrete structure. The above figure shows the relationship between the concrete water-cement ratio and the coefficient of permeability.
Role of Water in Concrete

It contains micro-ingredients like cement, sand, fine aggregate & Coarse aggregate. To acquire high-strength concrete, that withstands up to our desired compressive strength, We need a correct proportion of admixture to combine those materials.
Here comes the Water, which will initiate this chemical process by incorporating 23% to 25% of the cement volume.
This initiates the chemical process and makes 15% of water-cement paste, also known as a gel, to fill the voids in the concrete.
Useful Article for You
- How Wide Is a Cinder Block
- How Much Is a Coffered Ceiling
- How to Make Mortar
- How Long Does Hempcrete Last
- How to Use a Hand Sight Level
- How to Build a Lean to Roof
- How Are Tunnels Built
- How to Layout a Building
- How Wide Is a Car Parking Space
- How Do Shear Walls Work
- How to Measure Concrete Slump
- How to Use Washers with Screws
- How Dense Is Sand
- How High Is a Window from the Floor
- How Does a Beam Bridge Work
- How Do They Pour Concrete Under Water
- How Does a Sewer System Work
- How High Are Countertops
- How to Seal Brick Wall Interior
- How to Resurface Cement
- How to Use Portland Cement
- How Is Plaster Made
- How Many Types of Slope Are There
- How Big Is a Stair Landing
- How to Get Paint Off Concrete Without Chemicals
- How to Fix Water Damaged Drywall
- How Much to Get Septic Pumped
- How to Cut a Nail or Screw
- How Long Does Wet Concrete Take to Dry
- How Is Varnish Made
- How Does Ejector Pump Work
- How Does Hydrometer Work
- How to Get Wet Blood Out of Carpet
- How to Build House on Slope
- How Thick Is Plaster Wall
- How Suspension Bridges Work
- How to Seal a Concrete Roof
- How Was Cement Invented
- How to Calculate Area of Steel
- How to Check Silt Content in Sand
- How a Building Is Constructed
- How Are Roads Classified in India
- How Many Types of Cement in India
- How to Find Contour Interval
- How to Stop Leakage from Ceiling
- How Hardness of Brick Is Tested
- How Many Types of Paint Brushes Are There
- How to Calculate Skirting Area
- How Many Types of Beam
- How Many Types of Chain in Surveying
- How to Find One Way and Two Way Slab
- How Many Types of Houses
- How to Find Steel Bar Weight
- How to Calculate Septic Tank Capacity in Liters
- How to Calculate the Bearing Capacity of Soil
- How Many Types of Bricks Are There
- How Many Types of Cement Are There
- How to Make Block
- How to Build House Step by Step
- How Many Types of Bridge
- How Much Sand Required for 1 Sq.feet Area
- How to Texture Walls with Paint
- How Many Type of Beam
How to Calculate Water Cement Ratio? – W/C Ratio Calculation

We do not calculate the W/C Ratio. It is selected from various workability tests based on the structural members, transportation, concrete strength, selection of aggregation, etc.
At Site Level, we can make use of the below calculation for the nominal mix.
It is a guide to make your judgment.
Water Cement Ratio as per IS 10262-2009 Table-5
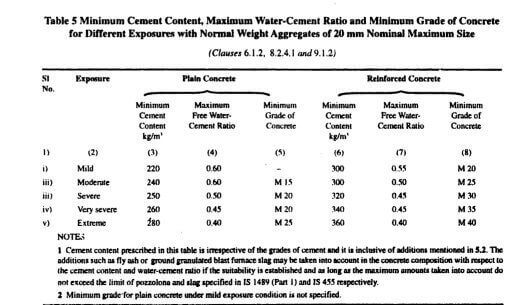
Calculation of Water Cement Quantity for Concrete
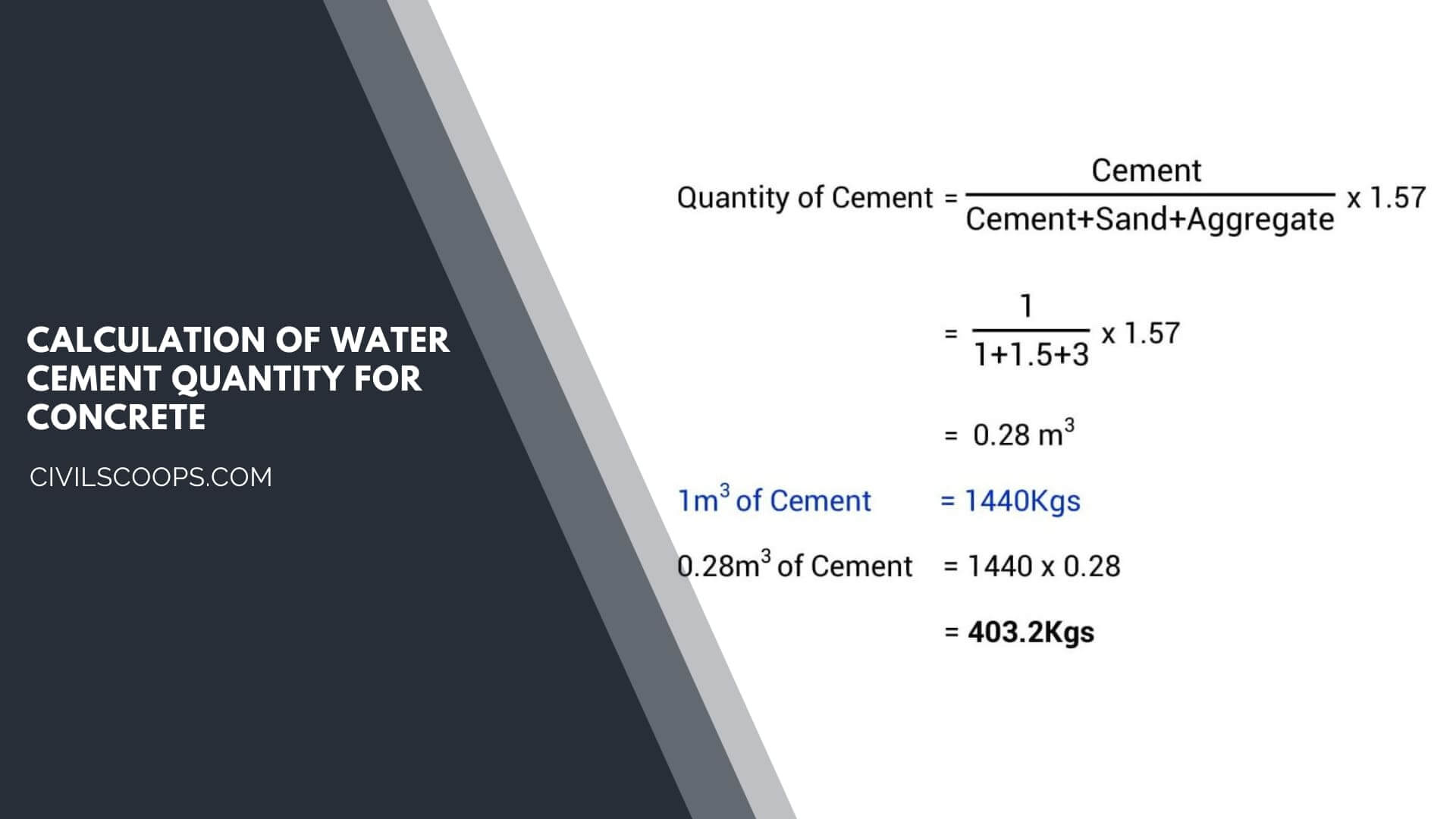
- As you can see from the Chart, the W/C ratio varies from 0.4 to 0.7 depending on exposure conditions.
- If we need to calculate Water quantity for concrete, first find the cement content for the volume.
- If we Assume the required cement volume as 50kg,
- The required amount of water = W/C Ratio x Cement Volume
- Therefore, Required amount of water = 0.45 x 50 kg = 22.50 litres / 50 kg cement bag.
- For the Design mix, the W/C ratio will depend upon the workability, strength requirements.
- In IS 10262-2009 Annex-A, they have explained the process for the design mix.
[su_box title=”FAQ” style=”default” box_color=”#333333″ title_color=”#FFFFFF” radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Water Cement Ratio
The water-cement ratio in concrete is the ratio of the weight of water to the weight of cement used in a mix. It greatly influences the strength and durability of concrete, with lower ratios generally leading to stronger and more durable concrete.
Water Cement Ratio and Concrete Strength
A w/c ratio of 0.4 means that for every 100 lbs of cement used in the concrete, 40 lbs of water is added. These two ingredients, cement and water, are responsible for binding everything together. The w/c ratio largely determines the strength and durability of the concrete when it is cured properly.
Role of Water in Concrete
As water is added to cement it creates a paste that glues all of the aggregates together. The cement paste then undergoes a chemical process known as hydration, this chemical reaction is what allows the concrete to harden and become strong and solid.
How to Calculate Water Cement Ratio?
The water to cement ratio is calculated by dividing the water in one cubic yard of the mix ( in pounds) by the cement in the mix (in pounds).
How Do You Calculate Water Cement Ratio?
The water to cement ratio is calculated by dividing the water in one cubic yard of the mix ( in pounds) by the cement in the mix (in pounds). So if one cubic yard of the mix has 235 pounds of water and 470 pounds of cement- the mix is a . 50 water to cement ratio.
Formula to Water Ratio
Powdered formulas are mixed 2 ounces (60 mL) of water per each level scoop of powder. Never add extra water because dilute formula can cause a seizure. Powdered formula costs the least. Ready-to-feed formula costs the most.
Concrete to Water Ratio
Typical Water-Cement Ratios in Concrete Mixes
The practical range of the w/c ratio is from about 0.3 to over 0.8. A ratio of 0.3 is very stiff (unless superplasticizers are used). A ratio of 0.8 makes a wet and weak concrete.
Water to Weight Ratio
Most people need to drink roughly half of their weight (in pounds) in ounces. For example, a 200-pound adult needs approximately 100 ounces of water each day.
Water Cement Ratio for High Strength Concrete
0.40 to 0.60
Water–cement ratios in the range of 0.40 to 0.60 are typically used. For higher-strength concrete, lower w/c ratios are necessary, along with a plasticizer to increase flowability.
Quikrete Water Ratio
QUIKRETE Concrete Mix may also be mixed by hand. Empty concrete bags into a suitable mixing container. For each 80 lb (36.2 kg) bag of mix, add approximately 6 pt (2.8 L) of clean water. Work the mix with a shovel, rake or hoe and add water as needed until a stiff, moldable consistency is achieved.
High Strength Concrete Mix Ratio
High-Strength Concrete Mix
Cement-to-aggregate ratios in high-strength concrete mixtures are generally 1:2:2 or 1:1.5:2.5. This mixture is utilised in situations where significant strength is necessary, such as in heavy-duty or tall constructions.
Water Cement Ratio Formula
The water–cement ratio (w/c ratio, or water-to-cement ratio, sometimes also called the Water-Cement Factor, f) is the ratio of the mass of water (w) to the mass of cement (c) used in a concrete mix: The typical values of this ratio f = w⁄c are generally comprised in the interval 0.40 and 0.60.
Water Cement Ratio in Concrete
It is the ratio of the mass of water to the mass of cement added to concrete. The water cement ratio formula directly affects the strength & durability of the concrete. The typical water-cement ratio varies between 0.40 – 0.60 for different grades of concrete mix.
How to Calculate Compressive Strength of Concrete?
The formula is: CS = F ÷ A, where CS is the compressive strength, F is the force or load at point of failure and A is the initial cross-sectional surface area.
How to Calculate Water to Cement Ratio?
For example if the water-cement ratio is 0.50 for concrete and cement added is 50 kg (weight of 1 bag of cement). Water = 0.50 x 50 = 25 liters. As you see, the water is reduced as we decrease the water-cement ratio.
Quikrete Fast Setting Water Ratio
Pour water into the dry mix until the powder is saturated with water. Depending on soil conditions, this will require about 1 gallon (3.8 L) of water per 50 lb (22.7 kg) bag. For holes deeper than 2′ 6″ (0.8 m), place the material in lifts of 2′ 6″ (0.8 m) or less to allow water to soak all the way through.
[/su_box]
[su_note note_color=”#F2F2F2 ” text_color=”#333333″ radius=”3″ class=”” id=””]
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Basic Plumbing System
- Rotten Egg Smell In Car
- Types of Concrete Blocks
- Construction Risk Management
- Difference Between Lap Length and Development Length
[/su_note]
Originally posted 2023-11-23 11:42:26.
